Abstract
Lysis of fibrin in tissue culture has been shown to be due to plasminogen activator identified immunologically as urokinase. The present study examines fibrinolytic events in culture, particularly mechanisms leading to increased urokinase levels and accelerated fibrinolysis.
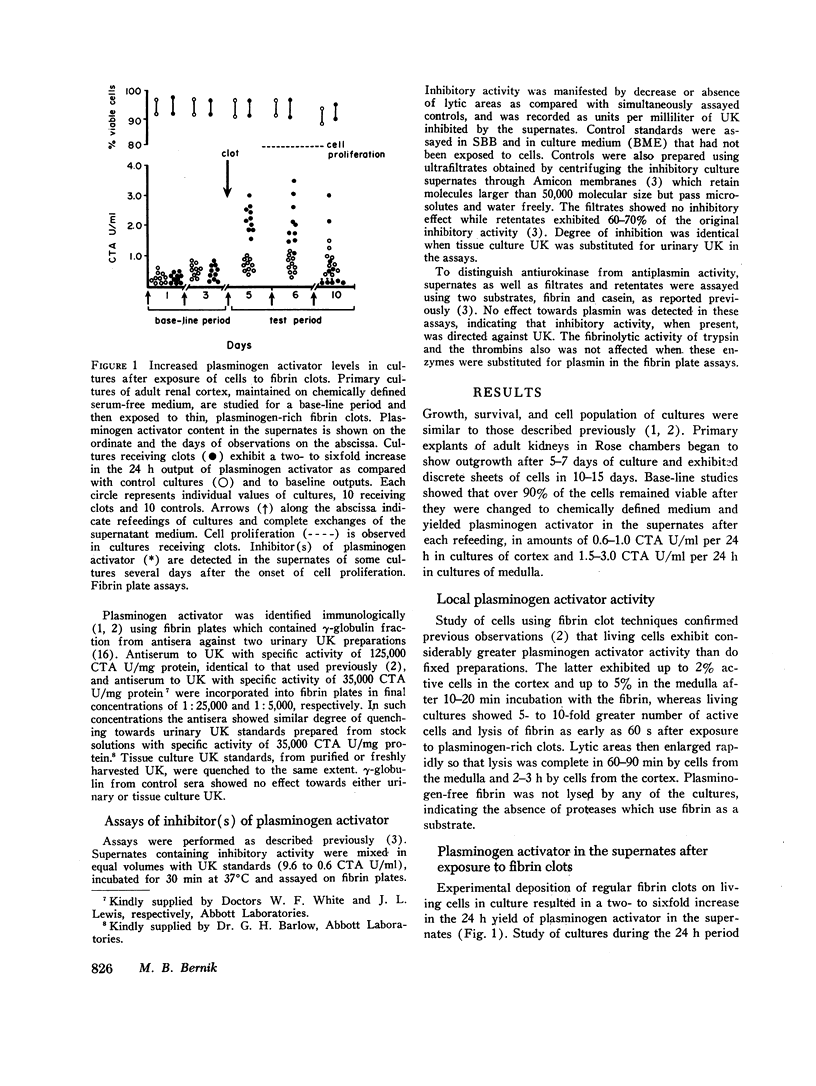
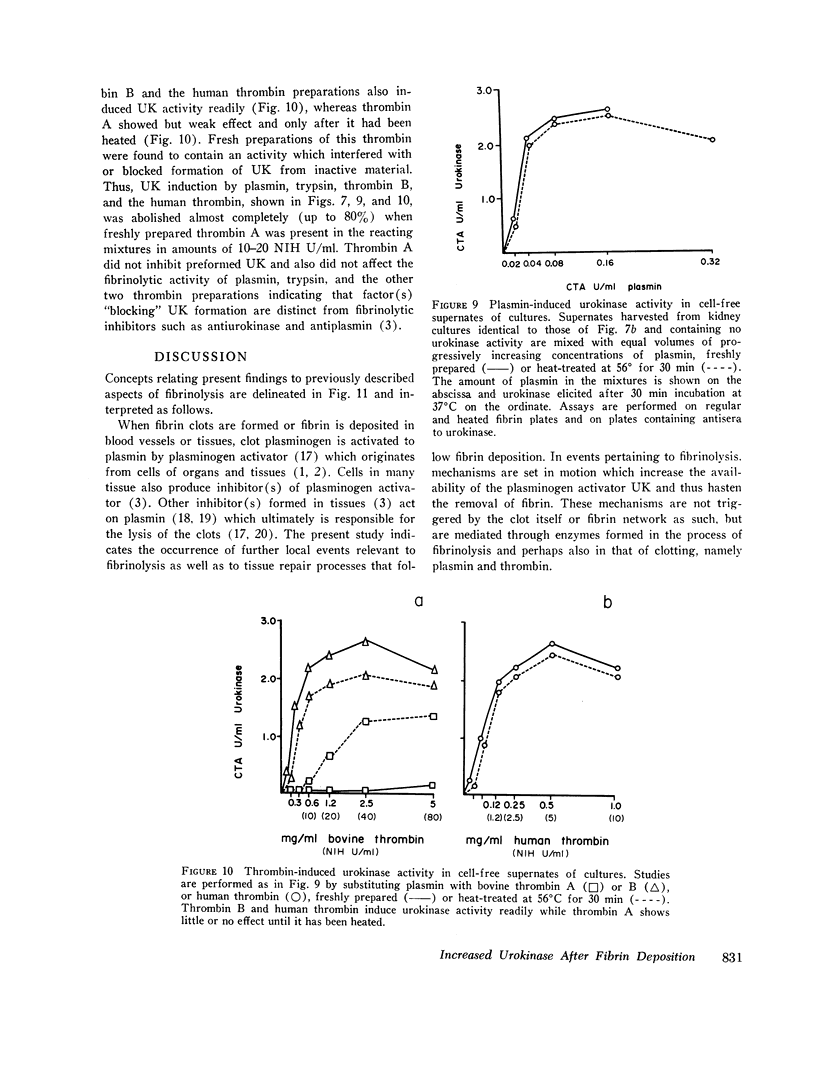
Deposition of fibrin on cells in culture was followed by a two- to six-fold increase in urokinase in the supernates and rapid disappearance of the fibrin. Investigation of factors that might be responsible for these events (including fibrin, fibrinogen, vasoactive stimuli, and the enzymes thrombin and plasmin) indicated that the enhanced urokinase yields were mediated through plasmin and thrombin.
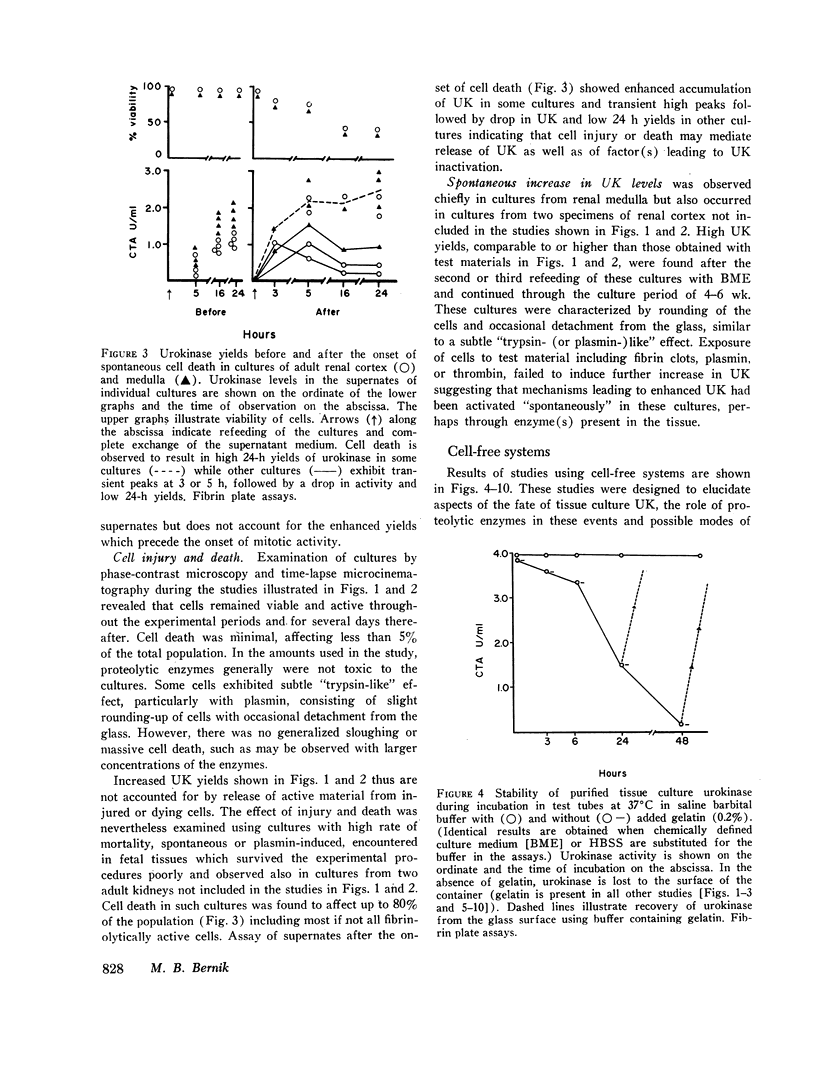
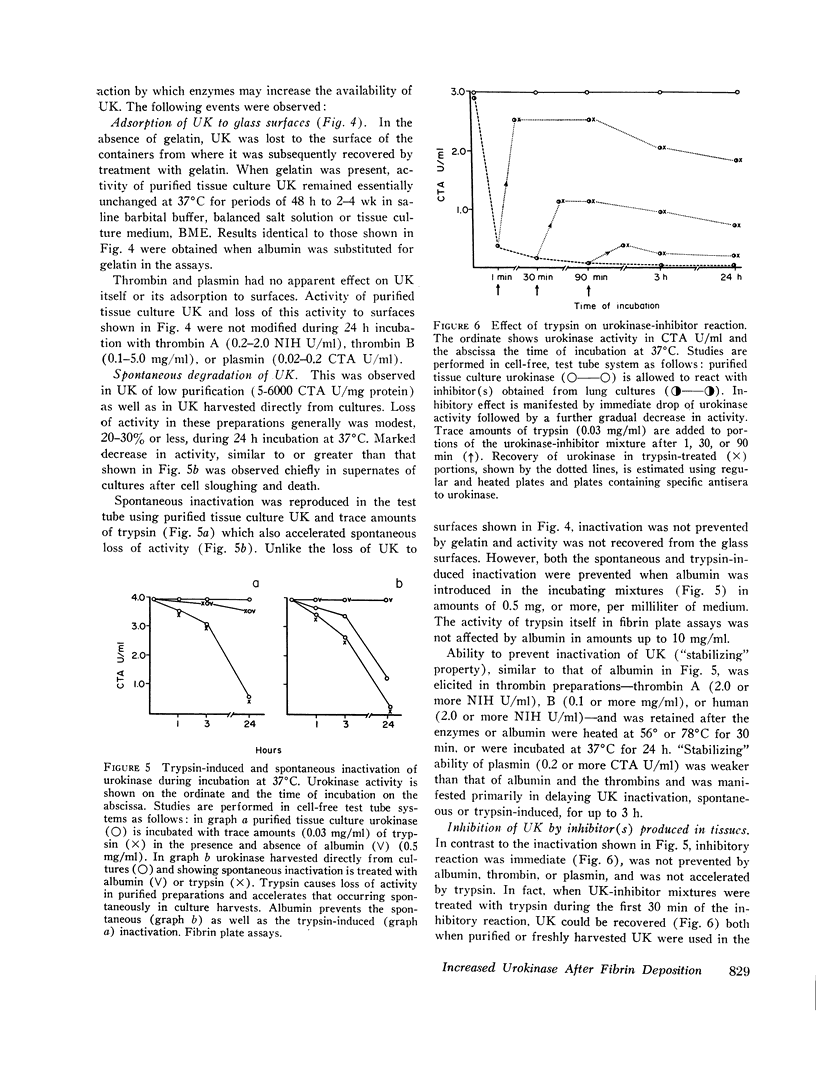
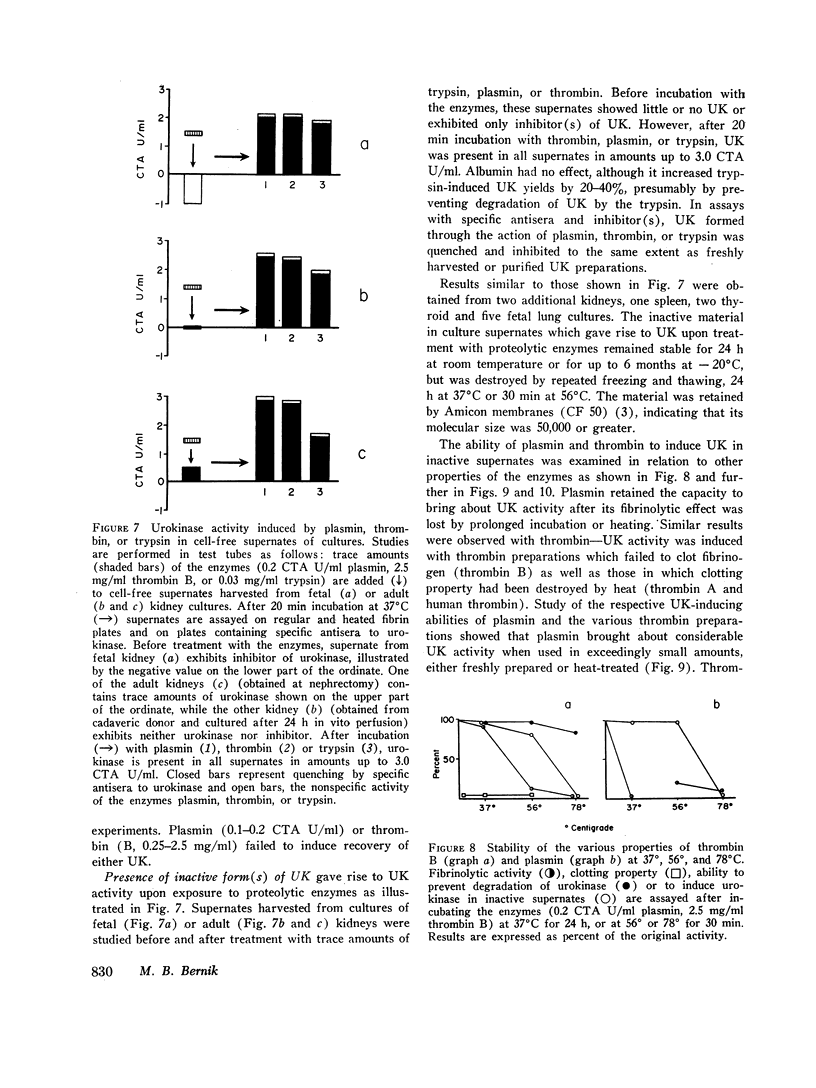
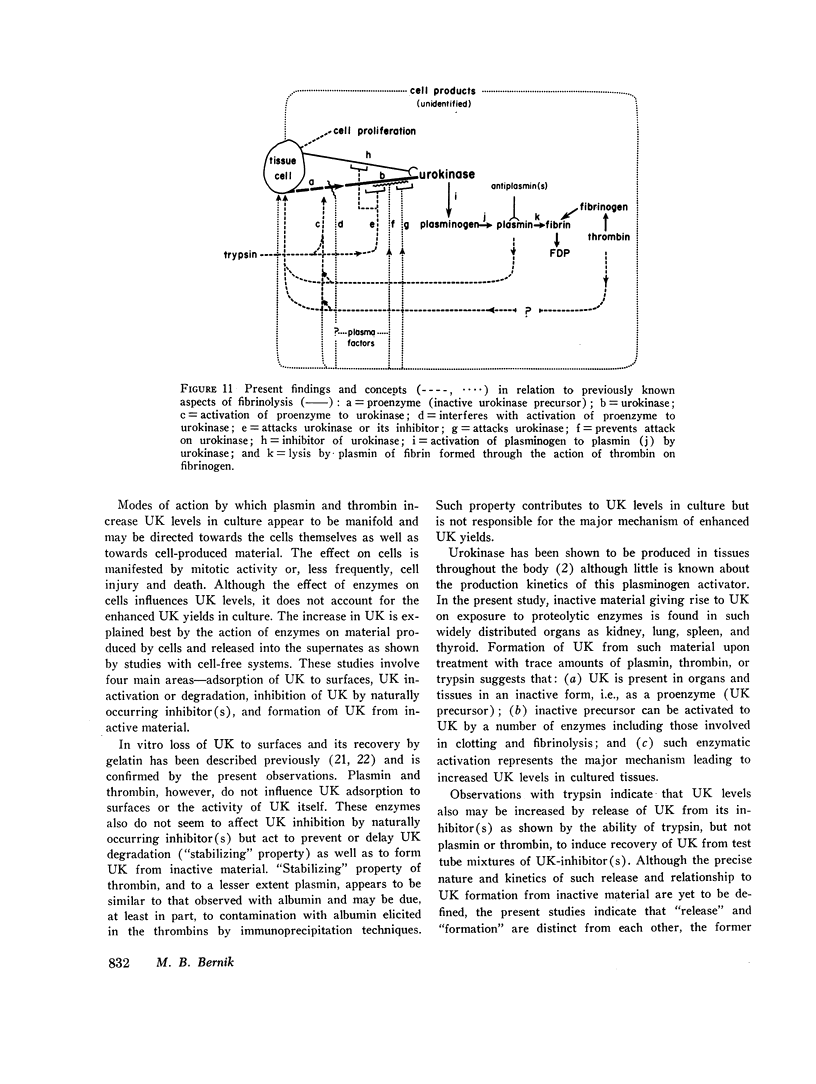
Study of the possible modes of action of thrombin and plasmin indicated that these enzymes are capable of acting on the cells themselves as well as on cell-produced material. The effect on cells was manifested by mitotic activity or, occasionally, cell injury and death. Although these effects influenced urokinase levels, enhanced yields were explained best by the action of enzymes on cellproduced material. Studies with plasmin and thrombin, and also trypsin, indicated that proteolytic enzymes may act in various ways—affect the stability of urokinase, interfere with inhibition of urokinase by naturally occurring inhibitor(s), and induce urokinase activity from inactive material. Plasma and thrombin appeared to act primarily through the latter mechanism.
Inactive material, which gave rise to urokinase upon exposure to proteolytic enzymes and which may represent urokinase precursor, was found in cultures of kidney, lung, spleen, and thyroid. Urokinase in such inactive state appears to be readily accessible to activation by enzymes, particularly plasmin and thrombin, thus facilitating removal of fibrin and possibly also providing pathways to excessive fibrinolysis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI103885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Von Kaulla K. N. Human serum plasminogen antiactivator: its distinction from antiplasmin. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1137–1145. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrup T. Blood coagulation and fibrinolysis in tissue culture and tissue repair. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;(Suppl):241–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90310-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAKMAN P. BOVINE FIBRINOGEN WITHOUT DETECTABLE PLASMINOGEN. Anal Biochem. 1965 Apr;11:149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernik M. B., Kwaan H. C. Inhibitors of fibrinolysis in human tissues in culture. Am J Physiol. 1971 Sep;221(3):916–921. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.3.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernik M. B., Kwaan H. C. Origin of fibrinolytic activity in cultures of the human kidney. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):650–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernik M. B., Kwaan H. C. Plasminogen activator activity in cultures from human tissues. An immunological and histochemical study. J Clin Invest. 1969 Sep;48(9):1740–1753. doi: 10.1172/JCI106140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE E. R., KOPPEL J. L., OLWIN J. H. AUTOPROTHROMBIN C FROM A COMMERCIAL THROMBIN PRODUCT. Nature. 1964 Apr 18;202:301–302. doi: 10.1038/202301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. Fibrinolytic mechanisms and the development of thrombolytic therapy. Am J Med. 1962 Nov;33:738–752. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano T., Morimoto K., Uemura Y. Partial purification and properties of urokinase inhibitor from human placenta. J Biochem. 1970 Mar;67(3):333–342. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwaan H. C., Brakman P., Astrup T. Enhancement of fibrinolysis and thrombolysis by polysorbate 80 (tween 80). Experientia. 1967 Apr 15;23(4):261–262. doi: 10.1007/BF02135671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDABURU R. H., SEEGERS W. H. The acetylation of thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Nov;37:1361–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN M. Heat denaturation of plasminogen in the fibrin plate method. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Feb 28;27(4):371–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00951.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSEN M. The estimation of fibrinolytic components by means of the lysis time method. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1958;10(4):384–389. doi: 10.3109/00365515809051241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORAND L. Interaction of thrombin and fibrinogen. Physiol Rev. 1954 Oct;34(4):742–752. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1954.34.4.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landaburu R. H., Giavedoni E., Santillán R. Thrombin and acetylated thrombin in the activation of fibrinolysis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;46(6):809–813. doi: 10.1139/y68-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. G. Progress in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Calif Med. 1969 Sep;111(3):186–contd. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muirhead C. R., Triantaphyllopoulos D. C. Anticoagulants produced by thrombin from fibrin, the effect on blood coagulation, some physical characteristics. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Oct 31;26(2):211–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niléhn J. E. Split products of fibrinogen after prolonged interaction with plasmin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Aug 15;18(1-2):89–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman P. S. Antiplasmins. Fed Proc. 1966 Jan-Feb;25(1):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POMERAT C. M. Cinematography, indispensable tool for cytology. Int Rev Cytol. 1961;11:307–334. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62720-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS K. C., SUMMARIA L., ELWYN D., BARLOW G. H. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HUMAN PLASMINOGEN AND PLASMIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:541–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Erdmann F. Bleeding due to increased intravascular blood coagulation. Hemorrhagic syndromes caused by consumption of blood-clotting factors (consumption-coagulopathies). N Engl J Med. 1965 Dec 16;273(25):1370–1378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196512162732506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEEGERS W. H., LANDABURU R. H., JOHNSON J. F. Thrombin-E as a fibrinolytic enzyme. Science. 1960 Mar 11;131(3402):726–726. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3402.726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SGOURIS J. T., INMAN J. K., McCALL K. B., HYNDMAN L. A., ANDERSON H. D. The preparation of human fibrinolysin (plasmin). Vox Sang. 1960 Jul;5:357–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1960.tb03750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN N. R. Studies on the inhibition of proteolytic enzymes by serum. II. Demonstration that separate proteolytic inhibitors exist in serum; their distinctive properties and the specificity of their action. J Exp Med. 1952 Jun;95(6):593–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.6.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberman S., Bernik M. B., Potter E. V., Kwaan H. C. Effects of Ancrod (Arvin) in mice: studies of plasma fibrinogen and fibrinolytic activity. Br J Haematol. 1973 Jan;24(1):101–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb05731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triantaphyllopoulos D. C., Muirhead C. R. Formation of anticoagulants by digesting fibrin with thrombin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Jul 31;19(3):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., MCCLUSKEY R. T. THE PATHOGENIC ROLE OF FIBRIN DEPOSITION IN IMMUNOLOGICALLY INDUCED GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 27;116:1052–1062. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb52567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. F., Barlow G. H., Mozen M. M. The isolation and characterization of plasminogen activators (urokinase) from human urine. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2160–2169. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Wessler S. Bovine thrombin and activated factor X. Separation and purification. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):112–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



