Abstract
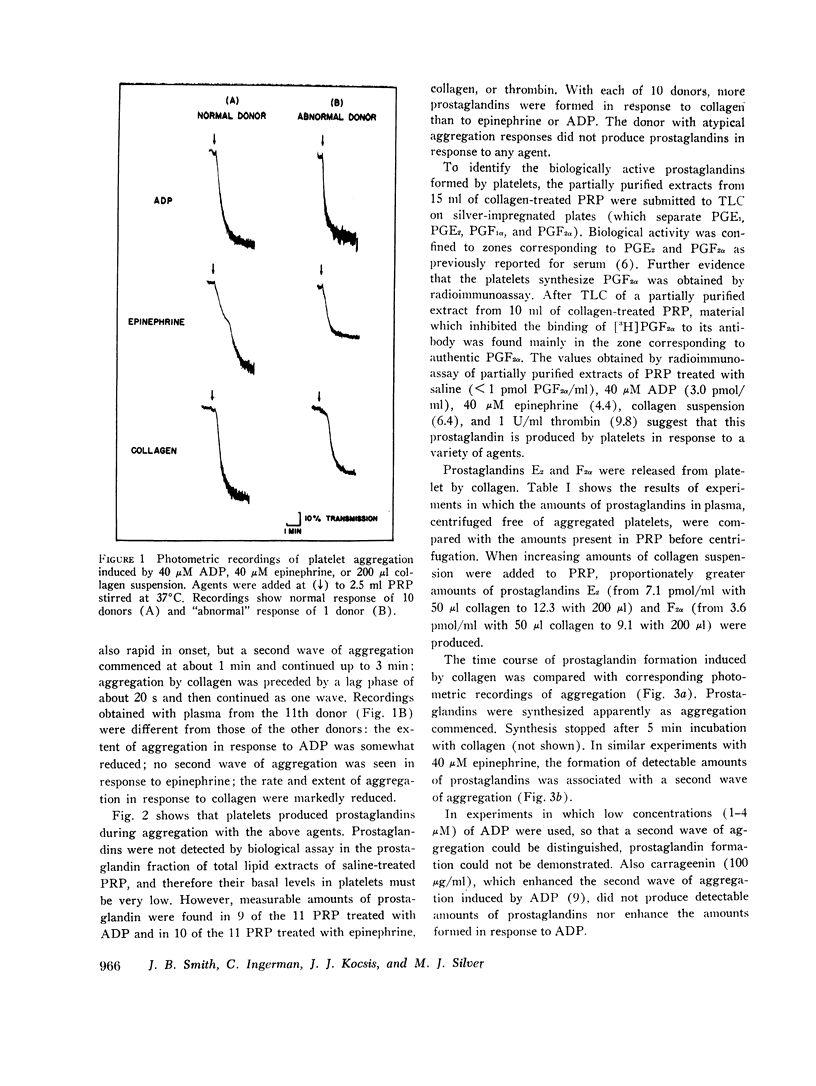
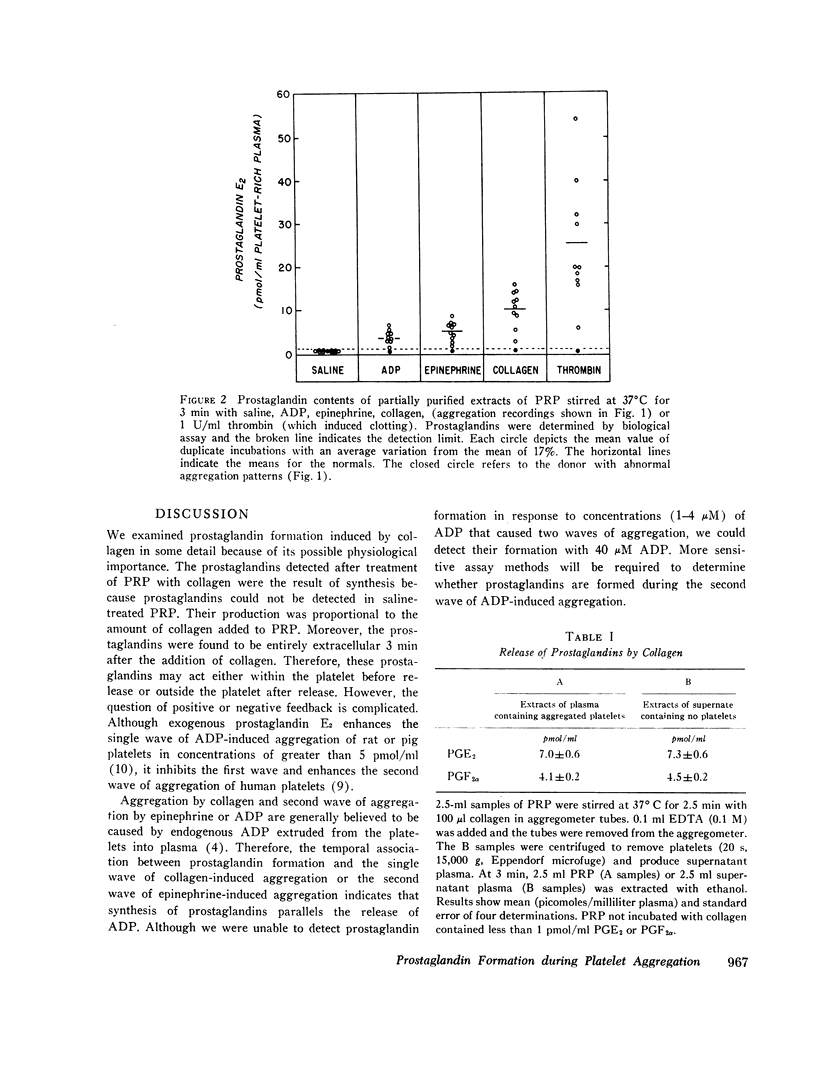
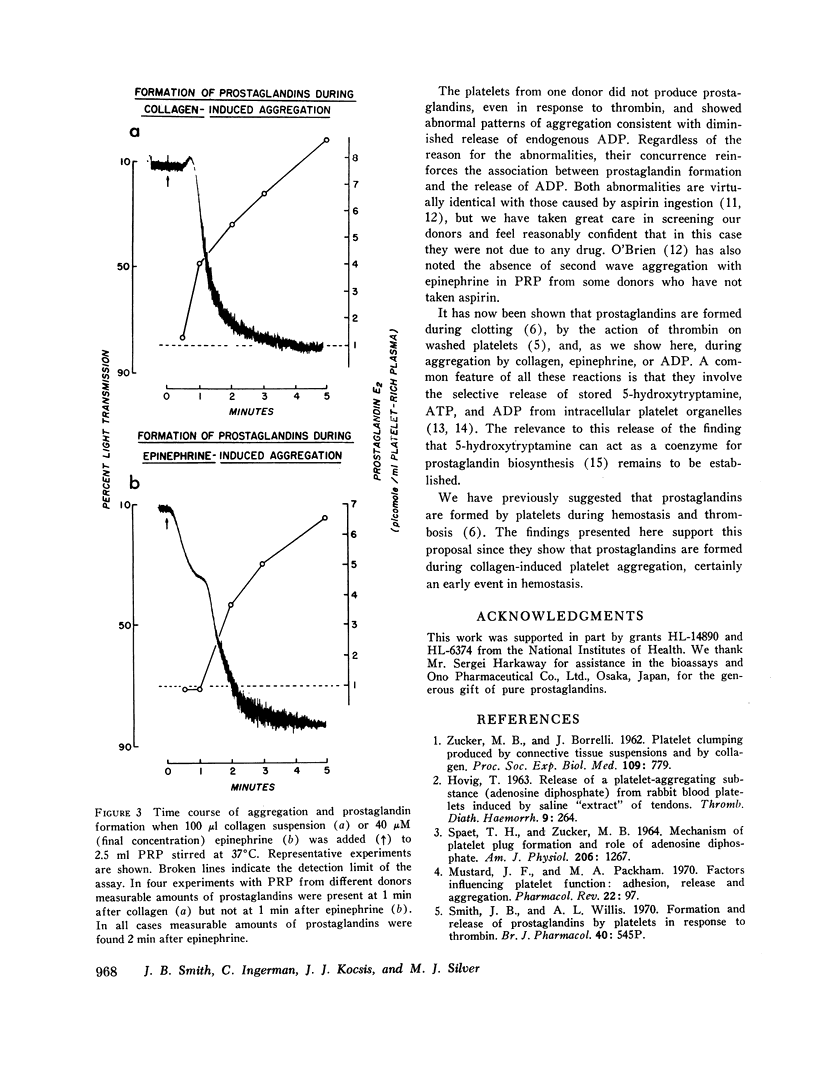
Prostaglandins E2 and F2α were formed in response to ADP, L-epinephrine, or collagen by human platelets suspended in plasma containing citrate anticoagulant and stirred at 37°C. The prostaglandins formed by platelets in response to collagen were rapidly released and the amounts formed were proportional to the amount of collagen added. The formation of the prostaglandins was associated with the single wave of aggregation induced by collagen or the second wave of aggregation induced by epinephrine. The above findings are discussed with reference to published studies on the biochemical changes occurring during platelet aggregation. It is suggested that the formation and release of prostaglandins is associated with the secretion of endogenous ADP and 5-hydroxytryptamine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Day H. J., Ang G. A., Holmsen H. Platelet release reaction during clotting of native human platelet-rich plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Mar;139(3):717–721. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOVIG T. RELEASE OF A PLATELET-AGGREGATING SUBSTANCE (ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE) FROM RABBIT BLOOD PLATELETS INDUCED BY SALINE "EXTRACT" OF TENDONS. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Jul 15;143:264–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R. G., Frank J. D. Effect of adenosine derivatives and antihistaminics on platelet aggregation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):654–660. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Packham M. A. Factors influencing platelet function: adhesion, release, and aggregation. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Jun;22(2):97–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. R. Effects of salicylates on human platelets. Lancet. 1968 Apr 13;1(7546):779–783. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAET T. H., ZUCKER M. B. MECHANISM OF PLATELET PLUG FORMATION AND ROLE OF ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jun;206:1267–1274. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.6.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sih C. J., Takeguchi C., Foss P. Mechanism of prostaglandin biosynthesis. 3. Catecholamines and serotonin as coenzymes. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Nov 4;92(22):6670–6670. doi: 10.1021/ja00725a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. J., Smith J. B., Ingerman C., Kocsis J. J. Human blood prostaglandins: formation during clotting. Prostaglandins. 1972 Jun;1(6):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):235–237. doi: 10.1038/newbio231235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Formation and release of prostaglandins by platelets in response to thrombin. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):545P–546P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger W. G., Stamford I. F., Bennett A. Extraction of prostaglandins from human blood. Nature. 1971 Oct 1;233(5318):336–337. doi: 10.1038/233336b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



