Abstract
Five pediatric patients who were known to be previously healthy acutely developed lymphopenia during various viral or mycoplasma infections. In one case, fatal generalized varicella occurred and in another, severe toxic epidermal necrolysis ensued.
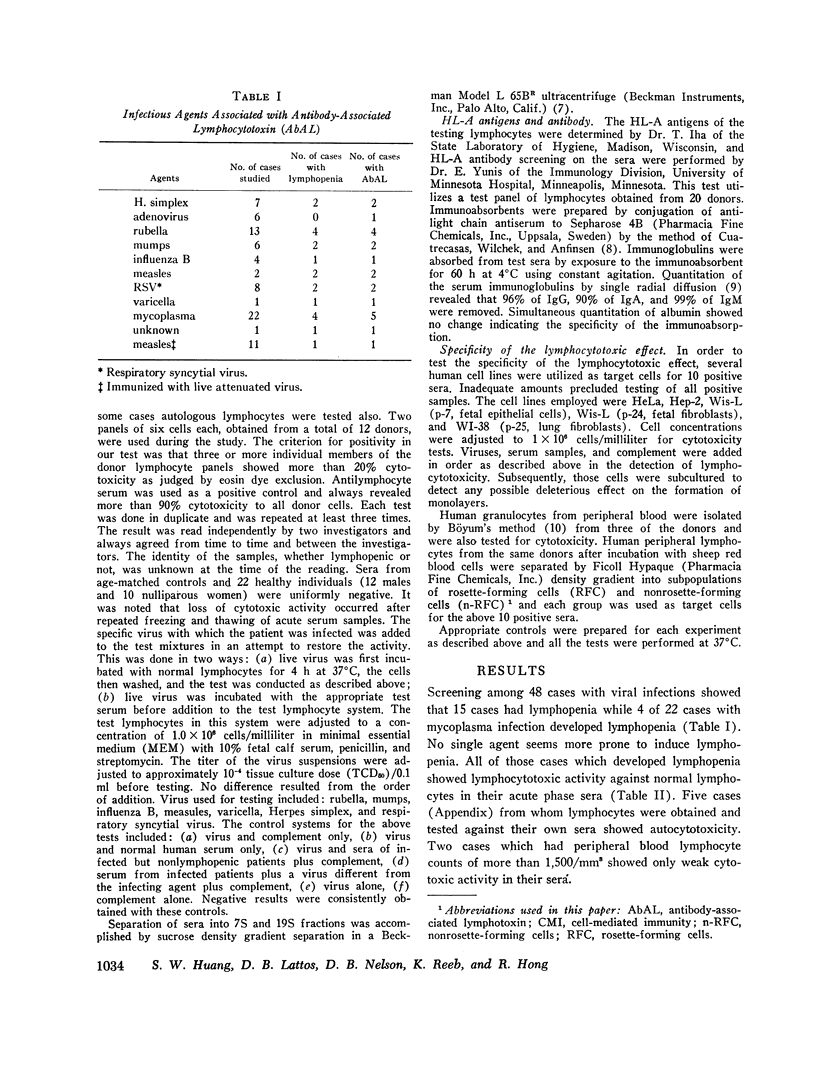
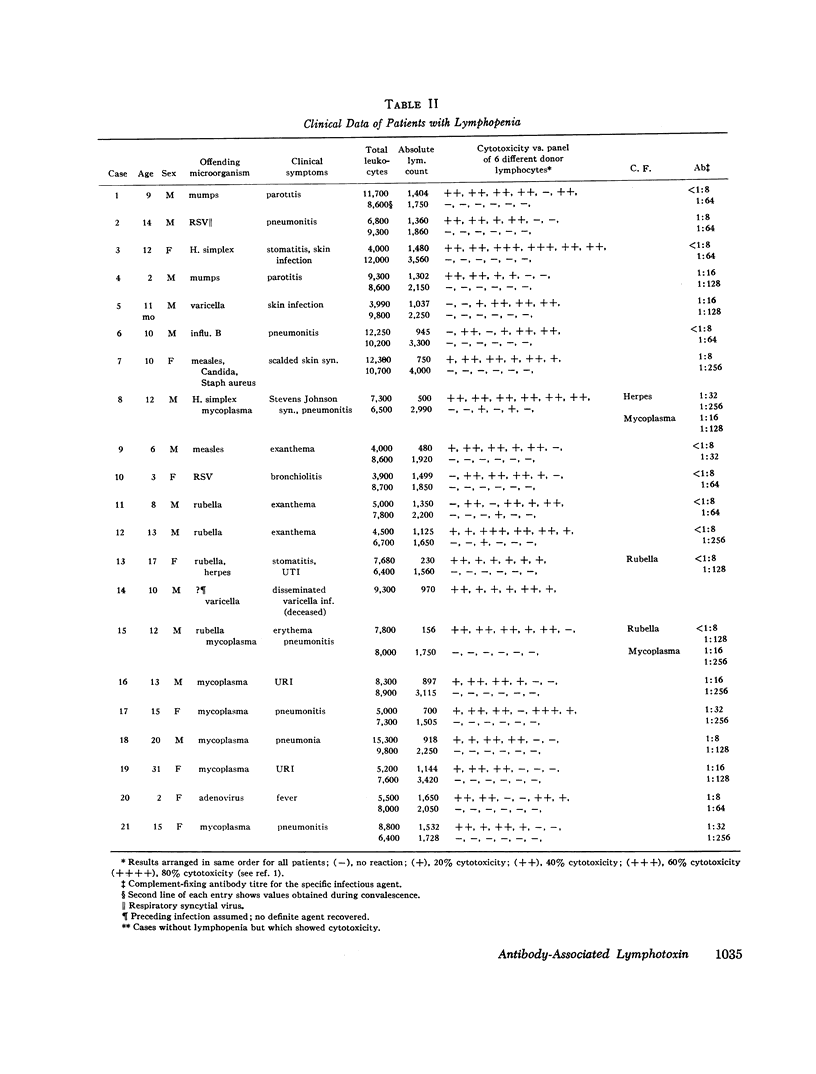
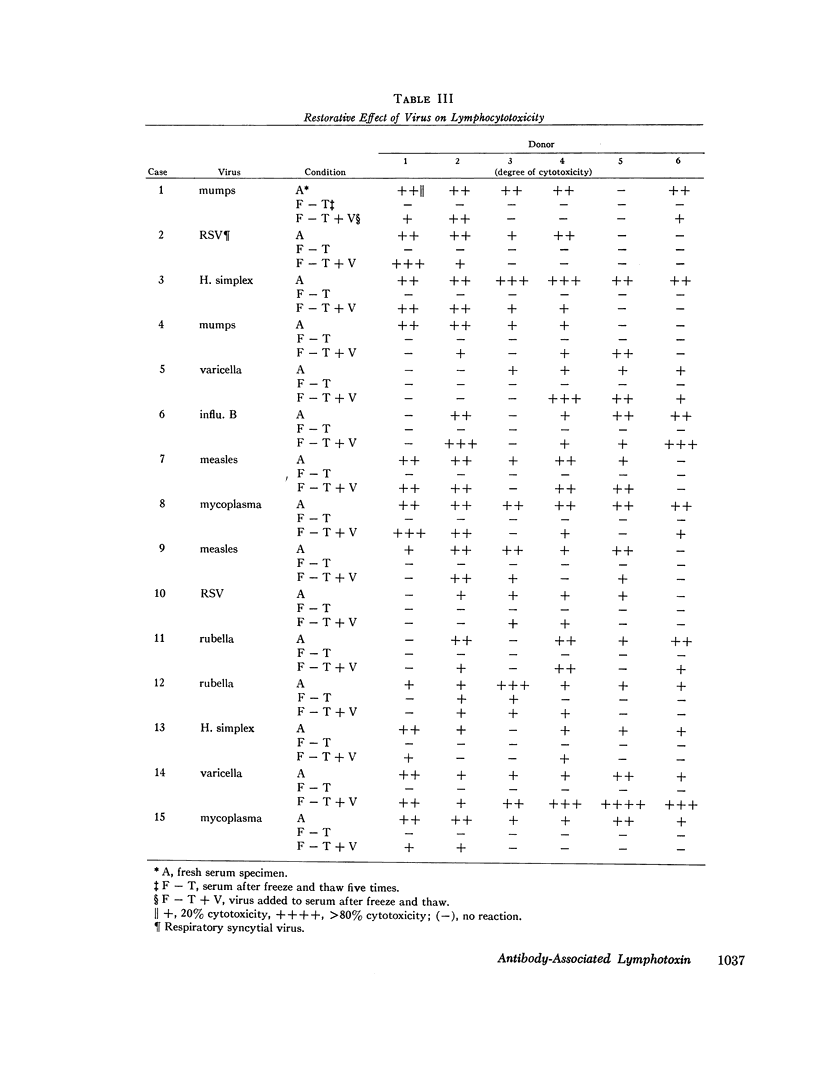
To further investigate this phenomenon, a study was done to determine the incidence of and elucidate the pathogenesis of lymphopenia occurring during the acute phase of viral or mycoplasma infections. Acute and convalescent sera from patients with viral or mycoplasma infection and children immunized with live measles virus were screened for lymphocytotoxic activity against normal lymphocytes by the microcytotoxicity method of Terasaki and McClelland (1). Sera with lymphocytotoxic activity were found in 15 of 48 cases of viral infections, 4 of 22 mycoplasma infections, and 1 of 11 measles virus immunized persons. All those who had sera which were cytotoxic to lymphocytes in vitro had lymphopenia. The lymphocytotoxic activity resided in 19S fractions in 8 of 11 positive sera while the remaining 3 had activity both in 19S and 7S fractions and could be completely removed by absorption with antilight chain antiserum. The cytotoxic activities were all complement-dependent and were greater at 37°C than at 4°C.
The significance of acute acquired immunologic deficiency due to the development of antibody-associated lymphotoxin (AbAL) during acute infections is discussed and five cases having more severe clinical manifestations are presented (Appendix).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMOS D. B., GORER P. A., MIKULSKA B. M., BILLINGHAM R. E., SPARROW E. M. An antibody response to skin homografts in mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1954 Apr;35(2):203–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudding B. A., Wagner S. C., Zeller J. A., Gmelich J. T., French G. R., Top F. H., Jr Fatal pneumonia associated with adenovirus type 7 in three military trainees. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jun 15;286(24):1289–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197206152862403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C., HOLMAN H. R., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., KUNKEL H. G. An unusual protein component of high molecular weight in the serum of certain patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 1957 May 1;105(5):425–438. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.5.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisler M. J., Hirata A. A., Terasaki P. I. Cytotoxins in disease. 3. Antibodies against lymphocytes produced by vaccination. Transplantation. 1970 Nov;10(5):411–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisler M., Naito S., Terasaki P. I. Cytotoxins in disease. V. Various diseases. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):112–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer R., Janeway C. A., Rosen F. S. Immunologic amnesia. Study of an 11-year-old girl with recurrent severe infections associated with dysgammaglobulinemia, lymphopenia and lymphocytotoxic antibody, resulting in loss of immunologic memory. Pediatr Res. 1968 Jan;2(1):7–16. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196801000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzler A. D. Serum cytotoxin in human kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):787–792. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Mickey M. R., Singal D. P., Terasaki P. I. Serotyping for homotransplantation. 18. Refinement of microdroplet lymphocyte cytotoxicity test. Transplantation. 1968 Nov;6(8):913–927. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. K., Rossen R. D., Sharp J. T., Lidsky M. D., Butler W. T. Lymphocyte cytotoxic antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1255–1256. doi: 10.1038/2251255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris P. J., Williams G. M., Hume D. M., Mickey M. R., Terasaki P. I. Serotyping for homotransplantation. XII. Occurrence of cytotoxic antibodies following kidney transplantation in man. Transplantation. 1968 May;6(3):392–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Mergenhagen S. E., Howard R. J. Effect of virus infections on the function of the immune system. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:525–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Acute viral infection: tissue injury mediated by anti-viral antibody through a complement effector system. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1274–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail M., Holborow E. J., Keith H. I., Currey H. L. Subpopulations of human peripheral blood lymphocytes distinguished by combined rosette formation and membrane immunofluorescence. Lancet. 1972 Jul 8;2(7767):64–66. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91553-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ziff M. Antibodies against cell membrane constituents in systemic lupus erythematosus and related diseases. I. Cytotoxic effect of serum from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) for allogeneic and for autologous lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Apr;8(4):543–550. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ziff M. Direct lysis of lymphocytes by complement in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Nov-Dec;14(6):733–736. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P., Ziff M. Lymphocyte and platelet autoantibodies in S.L.E. Lancet. 1971 Jun 12;1(7711):1239–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91751-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Mickey M. R., Yamazaki J. N., Vredevoe D. Maternal-fetal incompatibility. I. Incidence of HL-A antibodies and possible association with congenital anomalies. Transplantation. 1970 Jun;9(6):538–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Mottironi V. D., Barnett E. V. Cytotoxins in disease. Autocytotoxins in lupus. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 1;283(14):724–728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010012831403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALFORD R. L., ANDERSON R. E., CARTER P. K., MIHAJLOVIC F. Leukocyte antibodies in inbred strains of guinea pigs following first- and second-set skin homografts. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:427–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALFORD R. L., GALLAGHER R., SJAARDA J. R. SEROLOGIC TYPING OF HUMAN LYMPHOCYTES WITH IMMUNE SERUM OBTAINED AFTER HOMOGRAFTING. Science. 1964 May 15;144(3620):868–870. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3620.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Emmons J. D., Yunis E. J. Studies of human sera with cytotoxic activity. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1514–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI106637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Carr M. C., Fudenberg H. H. The human rosette-forming cell as a marker of a population of thymus-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2537–2543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


