Abstract
The renal extraction and excretion of bovine proinsulin, insulin, and C-peptide and the contribution of the kidney to their total metabolic clearance rate (MCR) were studied in the rat. Metabolic clearance rates were measured by the constant infusion technique and plasma and urine concentrations of each polypeptide were determined by radioimmunoassay.
The MCR of insulin (16.4±0.4 ml/min) was significantly greater than that of either proinsulin (6.7±0.3 ml/min) or C-peptide (4.6±0.2 ml/min). Metabolic clearance rates were independent of plasma levels over a range of steady-state plasma concentrations varying from 1 to 15 ng/ml.
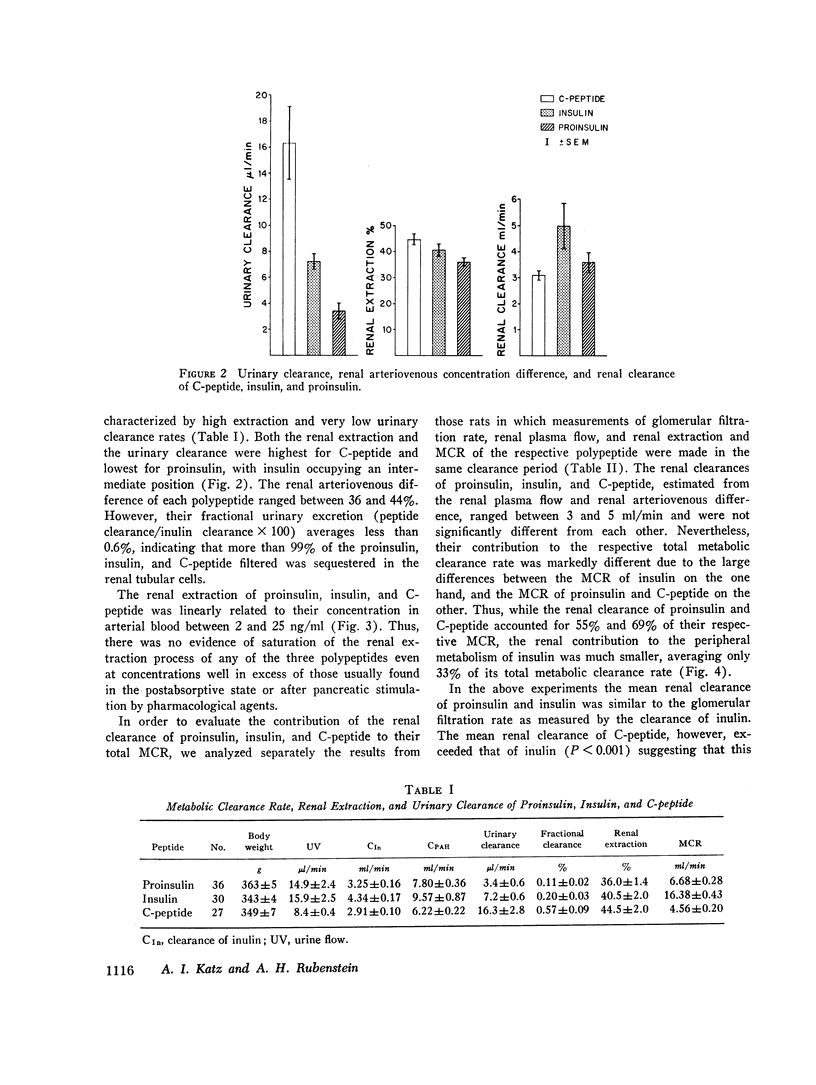
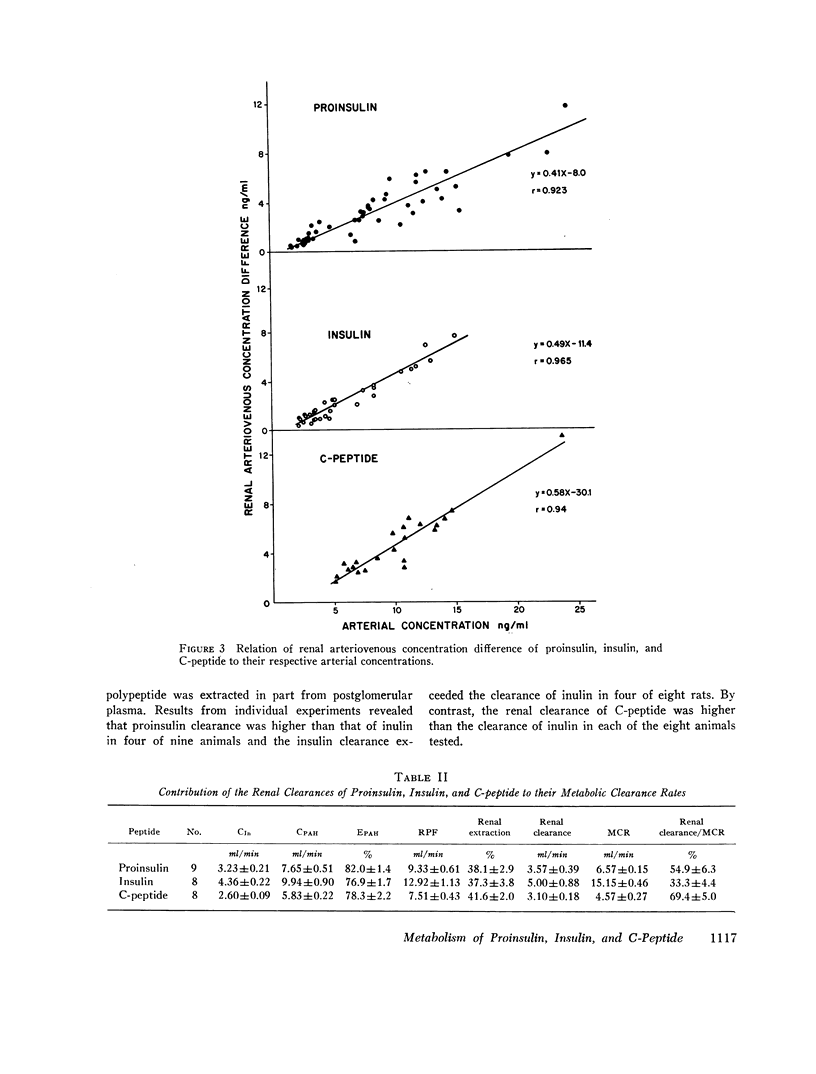
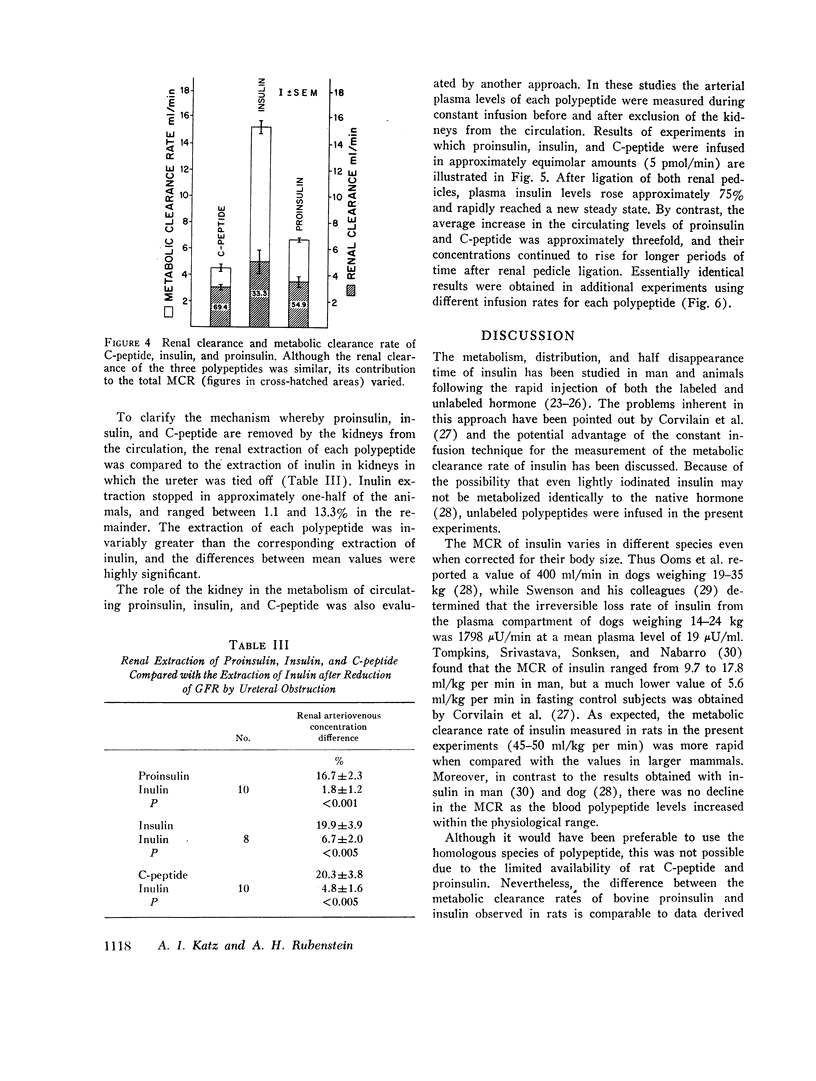
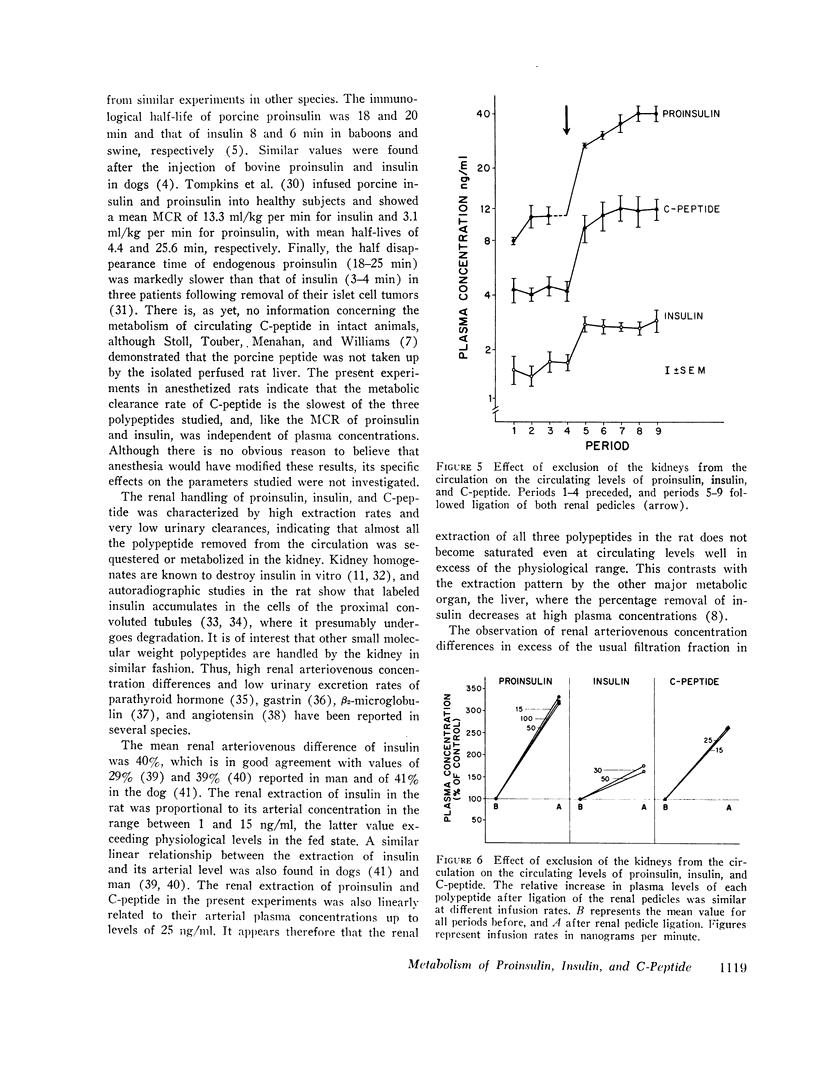
In contrast to the differences in their metabolic clearance rates, the renal disposition of the three polypeptides was similar, being characterized by high extraction and very low urinary clearance. The renal arteriovenous difference of proinsulin, insulin, and C-peptide averaged 36, 40, and 44%, respectively, and was linearly related to their arterial concentration between 2 and 25 ng/ml. When glomerular filtration was markedly reduced or stopped by ureteral obstruction, the renal extraction of proinsulin, insulin, and C-peptide was invariably greater than the simultaneously measured extraction of inulin, indicating that these polypeptides are removed from the renal circulation by both glomerular filtration and direct uptake from peritubular capillary blood. The fractional urinary clearance of each polypeptide never exceeded 0.6%, indicating that more than 99% of the amount filtered was sequestered in the kidney.
The renal removal of proinsulin and C-peptide from the circulation accounts for 55 and 69% of their metabolic clerance rates, while the renal contribution to the peripheral metabolism of insulin was smaller, averaging 33%. This difference is due to the fact that insulin, but not the other two polypeptides, is metabolized to a significant extent by the liver. These results define the renal handling of proinsulin, insulin, and C-peptide in the rat and indicate that in this species the kidney represents a major site for insulin metabolism and is the main organ responsible for the degradation of proinsulin and C-peptide.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailie M. D., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Angiotensin II in arterial and renal venous plasma and renal lymph in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):119–126. doi: 10.1172/JCI106465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier G. M., Conrad M. E. Catabolsm of human beta-2-microglobulin by the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1969 Nov;217(5):1359–1362. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.5.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brush J. S. Purification and characterization of a protease with specificity for insulin from rat muscle. Diabetes. 1971 Mar;20(3):140–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghen G. A., Kitabchi A. E., Brush J. S. Characterization of a rat liver protease with specificity for insulin. Endocrinology. 1972 Sep;91(3):633–642. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-3-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challoner D. R. Degradation of porcine insulin and proinsulin by rat adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1971 May;20(5):276–281. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.5.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain M. J., Stimmler L. The renal handling of insulin. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI105597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clendinnen B. G., Davidson W. D., Jackson B. M., Thompson J. C., Riddell A. G. Renal inactivation of gastrin. Br J Surg. 1970 Nov;57(11):864–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvilain J., Brauman H., Delcroix C., Toussaint C., Vereerstraeten P., Franckson J. R. Labeled insulin catabolism in chronic renal failure and in the anephric state. Diabetes. 1971 Jul;20(7):467–475. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.7.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARMADY E. M. CORRELATION OF RENAL FUNCTION AND STRUCTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Jul;18:493–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON W. D., SACKNER M. A. SIMPLIFICATION OF THE ANTHRONE METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF INULIN IN CLEARANCE STUDIES. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Aug;62:351–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Roth J. Plasma insulin: fluctuations in the "big" insulin component in man after glucose and other stimuli. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2225–2234. doi: 10.1172/JCI106188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. Glomerular permeability. Ultrastructural cytochemical studies using peroxidases as protein tracers. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGETT A. S., NIXON D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet. 1957 Aug 24;273(6991):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabchi A. E., Stentz F. B. Degradation of insulin and proinsulin by various organ homogenates of rat. Diabetes. 1972 Nov;21(11):1091–1101. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.11.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melani F., Rubenstein A. H., Oyer P. E., Steiner D. F. Identification of proinsulin and C-peptide in human serum by a specific immunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):148–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melani F., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. Human serum proinsulin. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):497–507. doi: 10.1172/JCI106259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melick R. A., Martin T. J. Parathyroid hormone metabolism in man: effect of nephrectomy. Clin Sci. 1969 Dec;37(3):667–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHARA H. T., EVERETT N. B., SIMMONS B. S., WILLIAMS R. H. Metabolism of insulin-I 131 and glucagon-I 131 in the kidney of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1958 Feb;192(2):227–231. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooms H. A., Arnould Y., Rosa U., Pennisi G. F., Franckson J. R. Clearances métaboliques globales de l'insuline cristalline et d'insulines substituées au radioiode. Pathol Biol. 1968 Mar;16(5):241–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov H., Christensen N. J. Plasma disappearance rate of injected human insulin in juvenile diabetic, maturity-onset diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1969 Oct;18(10):653–659. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.10.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin R., Colwell J. A. The renal uptake and excretion of insulin in the dog. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jun;73(6):893–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin R., Simon N. M., Steiner S., Colwell J. A. Effect of renal disease on renal uptake and excretion of insulin in man. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jan 22;282(4):182–187. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197001222820402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Lowy C., Welborn T. A., Fraser T. R. Urine insulin in normal subjects. Metabolism. 1967 Mar;16(3):234–244. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Pottenger L. A., Mako M., Getz G. S., Steiner D. F. The metabolism of proinsulin and insulin by the liver. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):912–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI106886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvers A., Swenson R. S., Farquhar J. W., Reaven G. M. Derivation of a three compartment model describing disappearance of plasma insulin-131-I in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1461–1469. doi: 10.1172/JCI106112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Finkelstein N., Aliminosa L., Crawford B., Graber M. THE RENAL CLEARANCES OF SUBSTITUTED HIPPURIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND OTHER AROMATIC ACIDS IN DOG AND MAN. J Clin Invest. 1945 May;24(3):388–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI101618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Cho S., Oyer P. E., Terris S., Peterson J. D., Rubenstein A. H. Isolation and characterization of proinsulin C-peptide from bovine pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1365–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Hallund O., Rubenstein A., Cho S., Bayliss C. Isolation and properties of proinsulin, intermediate forms, and other minor components from crystalline bovine insulin. Diabetes. 1968 Dec;17(12):725–736. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.12.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. P., Farquhar J. W., Silvers A., Reaven G. M. Insulin delivery rate into plasma in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):1947–1957. doi: 10.1172/JCI105884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll R. W., Touber J. L., Menahan L. A., Williams R. H. Clearance of porcine insulin, proinsulin, and connecting peptide by the isolated rat liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):894–896. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll R. W., Touber J. L., Winterscheid L. C., Ensinck J. W., Williams R. H. Hypoglycemic activity and immunological half-life of porcine insulin and proinsulin in baboons and swine. Endocrinology. 1971 Mar;88(3):714–717. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-3-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. S., Silvers A., Peterson D. T., Kohatsu S., Reaven G. M. Effect of nephrectomy and acute uremia on plasma insulin- 125 I removal rate. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 May;77(5):829–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAIT J. F. REVIEW: THE USE OF ISOTOPIC STEROIDS FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF PRODUCTION RATES IN VIVO. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Dec;23:1285–1297. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-12-1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaharko D. S., Beck L. V., Blankenbaker R. Role of the kidney in the disposal of radioiodinated and nonradioiodinated insulin in dogs. Diabetes. 1966 Sep;15(9):680–685. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.9.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


