Abstract
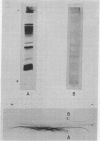
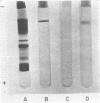
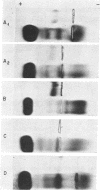
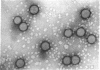
Hepatitis B antigen (HB Ag) has been purified from serum by pepsin digestion and equilibrium sedimentation. The sedimentation coefficient, density, particle size, and electrophoretic mobility have been determined before and after purification and found to be unaltered. In addition, the diffusion constant and molecular weight of purified HB Ag have been documented.
Because the biophysical characteristics found are not consistant with those of any known virus, it is believed that native HB Ag is made up almost entirely of incomplete virus.
Full text
PDF



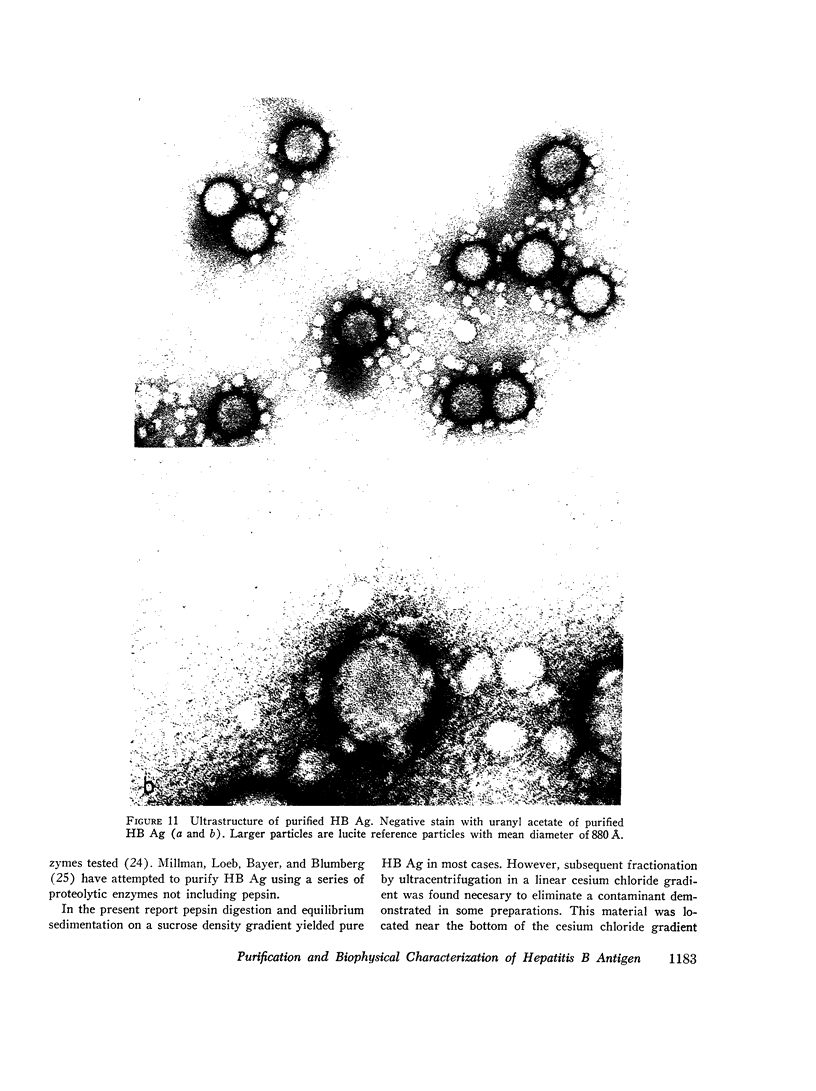



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. Immune complexes in hepatitis. Lancet. 1969 Nov 8;2(7628):983–986. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Blumberg B. S. Further studies on a "new" human isoprecipitin system (Australia antigen). Blood. 1966 Mar;27(3):297–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHRACH H. L., SCHWERDT C. E. Purification studies on Lansing poliomyelitis virus. II. Analytical electron microscopic identification of the infectious particle in preparations of high specific infectivity. J Immunol. 1954 Jan;72(1):30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. F., Smith K. O., Gehle W. D., Shulman N. R. Some antigenic and physical properties of virus-like particles in sera of hepatitis patients. J Immunol. 1969 Jun;102(6):1529–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Blumberg B. S., Werner B. Particles associated with Australia antigen in the sera of patients with leukaemia, Down's Syndrome and hepatitis. Nature. 1968 Jun 15;218(5146):1057–1059. doi: 10.1038/2181057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. S., Gerstley B. J., Hungerford D. A., London W. T., Sutnick A. I. A serum antigen (Australia antigen) in Down's syndrome, leukemia, and hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1967 May;66(5):924–931. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-5-924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Holland P. V., Purcell R. H. Australia antigen: large-scale purification from human serum and biochemical studies of its proteins. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):569–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.569-576.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Hoggan M. D., Holland P. V., Chanock R. M. Biophysical properties of Australia antigen. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.763-768.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman R. J., Shulman N. R., Barker L. F., Smith K. O. Virus-like particles in sera of patients with infectious and serum hepatitis. JAMA. 1969 Jun 2;208(9):1667–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kater R. M., Kim C. Y., Davidson C. S. Australia antigen and viral hepatitis. J Infect Dis. 1969 Sep;120(3):391–392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. Y. An immunochemical method for serum alpha-globulin. Quantitative determination by micro-ouchterlony double diffusion. Lab Invest. 1970 Jul;23(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. Y., Bissell D. M. Stability of the lipid and protein of hepatitis-associated (Australia) antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 May;123(5):470–476. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. Y., Spano J., Clark G. E. Use of pepsin-treated hepatitis-associated antigen in the production of precipitating antibody. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):411–414. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. Y., Tilles J. G. Immunologic and electrophoretic heterogeneity of hepatitis-associated antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):618–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. Y., Tilles J. G. Quantitation of hepatitis-associated antigen with a modified Ouchterlony precipitin test. J Infect Dis. 1971 Nov;124(5):512–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.5.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L. The heterogeneity of Australia antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):671–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGUCKIN W. F., McKENZIE B. F. An improved periodic acid fuchsin sulfite staining method for evaluation of glycoproteins. Clin Chem. 1958 Dec;4(6):476–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millman I., Loeb L. A., Bayer M. E., Blumberg B. S. Australia antigen (a hepatitis-associated antigen): purification and physical properties. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1190–1199. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M. An antigen detected in the blood during the incubation period of serum hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):814–821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP D. G. Purification and properties of animal viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1953;1:277–313. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. H., RUSSELL W. C., WILDY P. Electron microscopic particle counts on herpes virus using the phosphotungstate negative staining technique. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:250–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]