Abstract
The hypothesis that diets high in carbohydrate produce hyperlipidemia in man was tested in new experiments which provided all calories either by the intravenous route or orally. After a base-line general diet, eight healthy men were fed fat-free diets consisting of 80% of the calories from glucose and 20% from an amino acid hydrolysate. The calories were adequate to maintain body weight. The solutions (1 cal/ml) were infused by constant drip over a 24 h period through either a superior vena cava catheter or a nasogastric tube. Each feeding was for 12 days in sequence but assigned in random order.
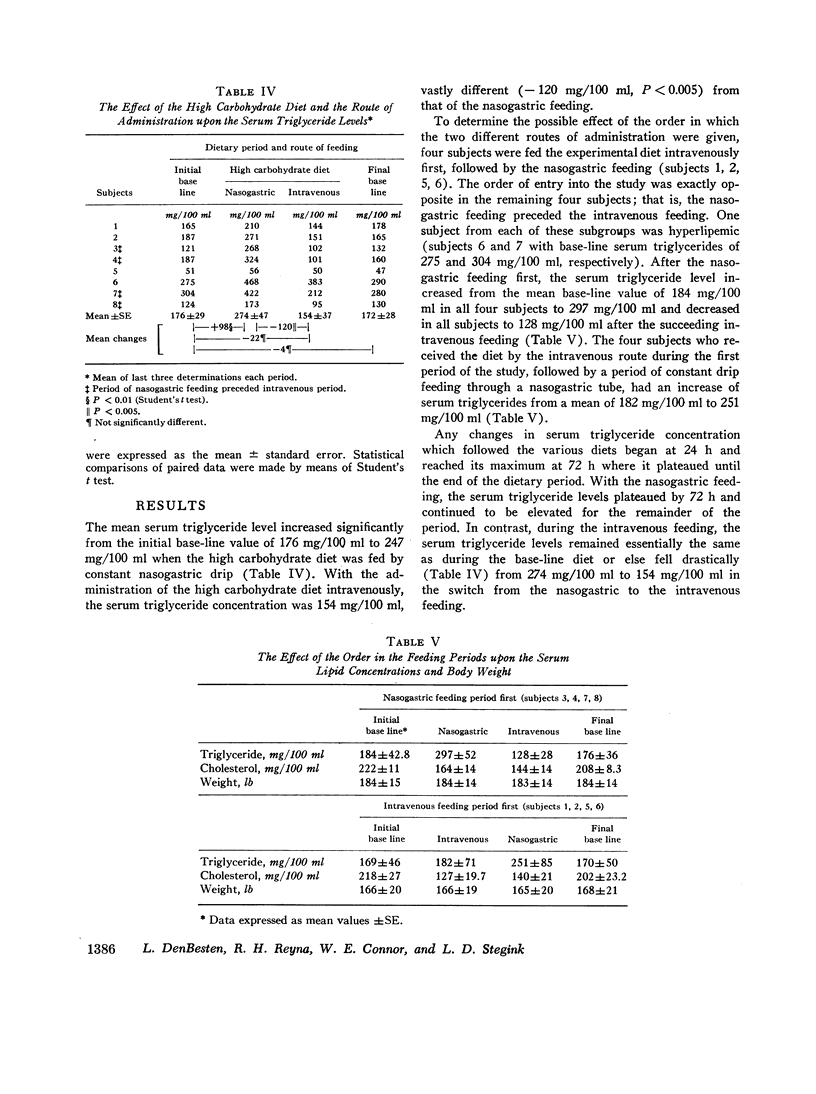
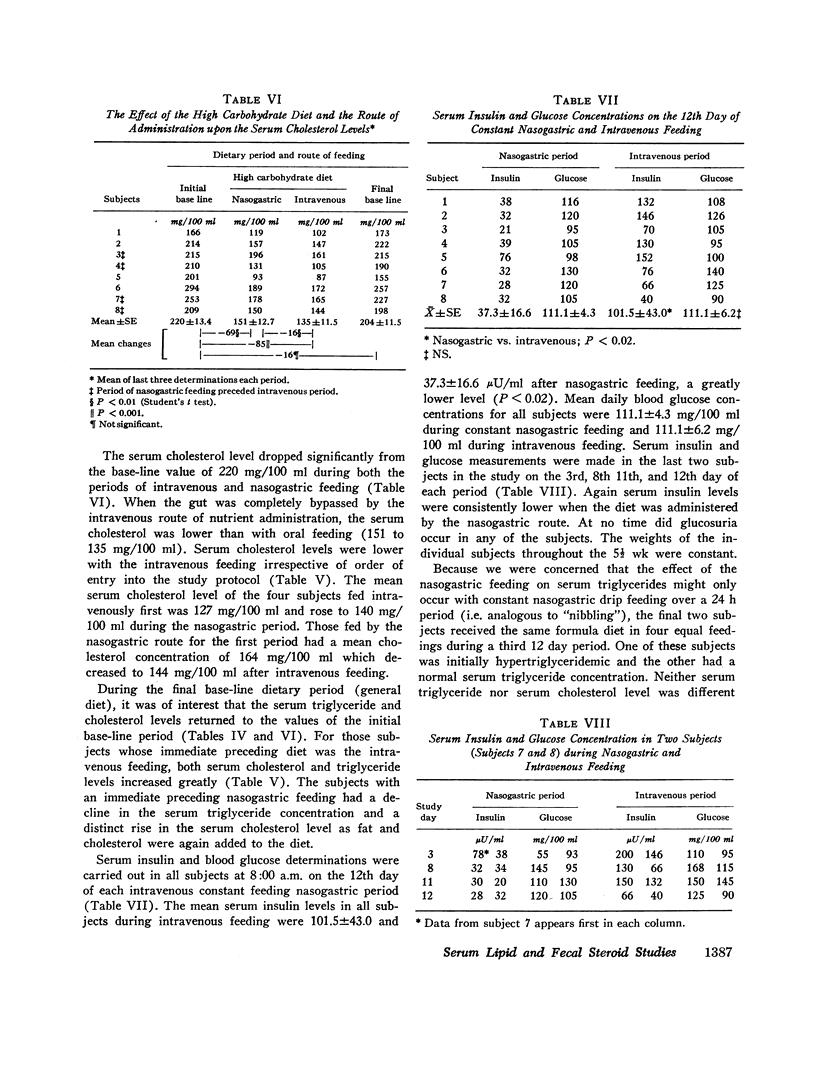
The high CHO diet given orally, as expected, increased the mean base-line serum triglyceride level from 176±29 (SE) to 274±47. The identical diet given intravenously (i.v.) failed to produce hypertriglyceridemia; triglyceride levels were not significantly changed, 154±37, nor were blood glucose levels. Serum insulin levels were higher during the intravenous feeding.
In contrast, both i.v. and oral feedings greatly lowered mean serum cholesterol concentration from the base-line value of 220±13 mg/100 ml to 135±11 and 151±13, respectively. However, the serum cholesterol level was significantly lower (P < 0.01) with the intravenous feeding than with the oral feeding.
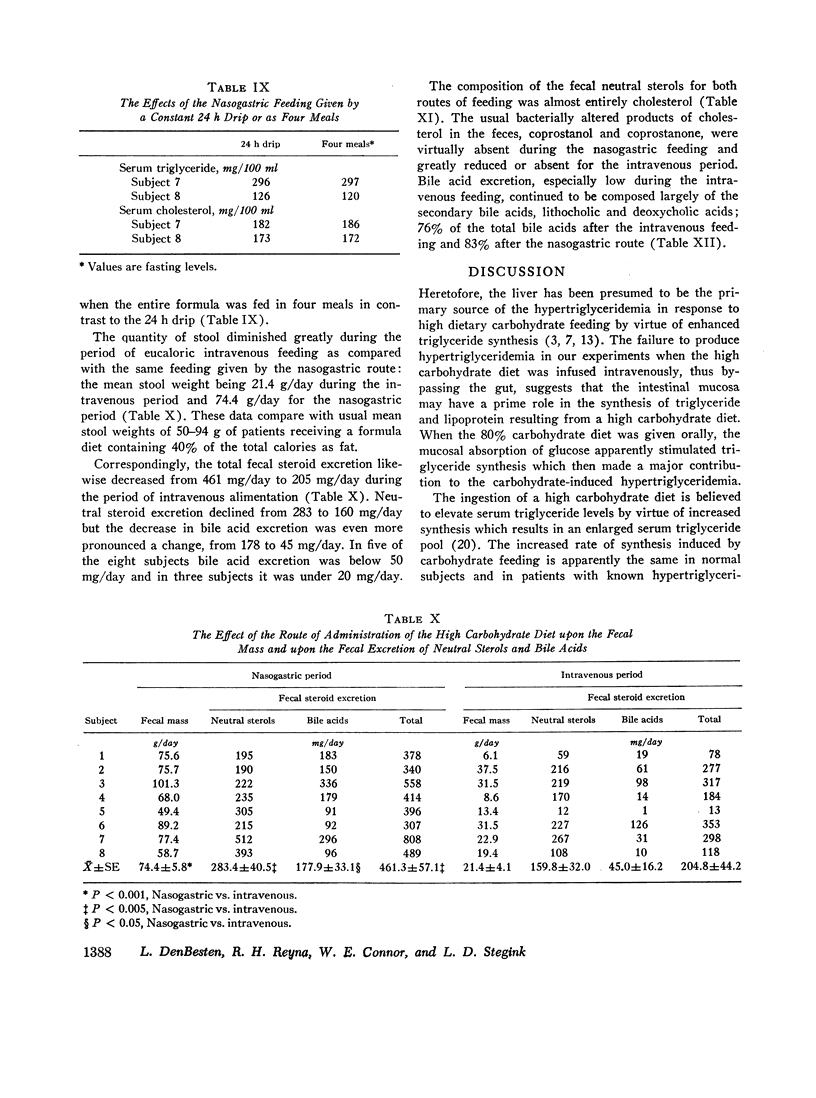
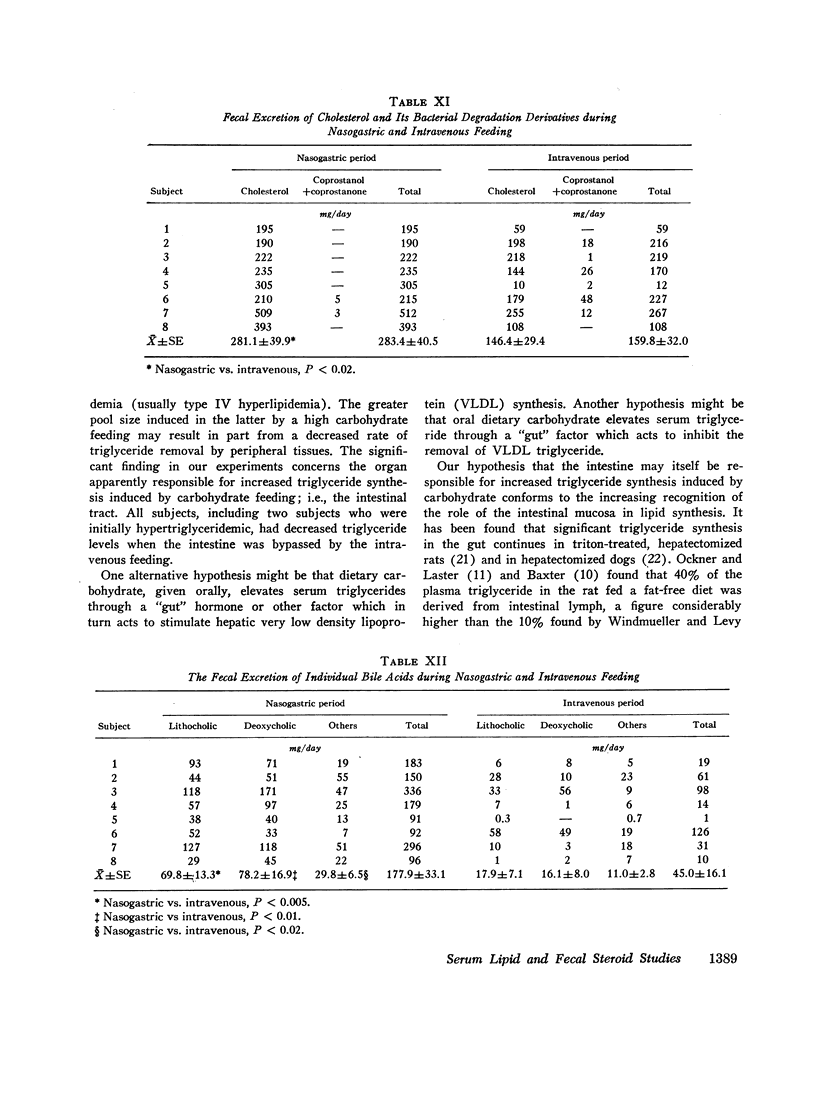
In addition, the fecal excretion of both neutral sterols and bile acids diminished greatly during the period of intravenous feeding. The fecal mass was likewise decreased. The bacterial conversion of cholesterol to conprostanol did not occur with either intravenous or oral feeding, but with both regimens secondary bile acids predominated, as usual, in the bile acid fraction of the stool.
These results emphasize the key role of the intestinal mucosa in the etiology of carbohydrate-induced hypertriglyceridemia and as a direct or indirect contributor to plasma triglyceride and cholesterol levels in the absence of dietary lipids. When the gut mucosa was bypassed, carbohydrate-induced hypertriglyceridemia did not occur and both serum triglyceride and serum cholesterol levels decreased greatly at a time when the excretion of steroids in the stool was also reduced.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABEL L. L., LEVY B. B., BRODIE B. B., KENDALL F. E. A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AHRENS E. H., Jr, INSULL W., Jr, BLOMSTRAND R., HIRSCH J., TSALTAS T. T., PETERSON M. L. The influence of dietary fats on serum-lipid levels in man. Lancet. 1957 May 11;272(6976):943–953. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALFIN-SLATER R. B., SCHOTZ M. C., SHIMODA F., DEUEL H. J., Jr Effect of low fat and high fat diets on the synthesis of cholesterol in rats. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):311–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS S. O., FRIEDMAN M. Site of origin of plasma triglyceride. Am J Physiol. 1960 Mar;198:629–631. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.3.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barter P. J., Carroll K. F., Nestel P. J. Diurnal fluctuations in triglyceride, free fatty acids, and insulin during sucrose consumption and insulin infusion in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):583–591. doi: 10.1172/JCI106528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. Origin and characteristics of endogenous lipid in thoracic duct lymph in rat. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk J. L., Hagen J. F., Beyer W. H., Gerber M. J. Hypoglycemia of shock. Ann Surg. 1970 Mar;171(3):400–408. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197003000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHENG S. H., STANLEY M. M. Secretion of cholesterol by intestinal mucosa in patients with complete common bile duct obstruction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jun;101(2):223–225. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE W. A., PAYNE W. W., SIMPKISS M. J., WOOLF L. I. Familial hypoglycemia precipitated by amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1956 Apr;35(4):411–422. doi: 10.1172/JCI103292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNOR W. E., HODGES R. E., BLEILER R. E. The serum lipids in men receiving high cholesterol and cholesterol-free diets. J Clin Invest. 1961 May;40:894–901. doi: 10.1172/JCI104324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor W. E., Witiak D. T., Stone D. B., Armstrong M. L. Cholesterol balance and fecal neutral steroid and bile acid excretion in normal men fed dietary fats of different fatty acid composition. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1363–1375. doi: 10.1172/JCI106102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer G. M., Bilstad J. M., Faiman C., Moxness K. E. Circulating levels of anterior pituitary hormones and insulin after arginine infusion. Mayo Clin Proc. 1968 Nov;43(11):776–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Wilson J. D. Regulation of cholesterol metabolism. I. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1128–1138. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar P., Rabinowitz D., Merimee T. J. Effects of amino acids on insulin release from excised rabbit pancreas. Endocrinology. 1969 Apr;84(4):835–843. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-4-835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajans S. S., Floyd J. C., Jr, Knopf R. F., Conn F. W. Effect of amino acids and proteins on insulin secretion in man. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1967;23:617–662. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9826-2.50017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S., Conn J. W., Knopf R. F., Rull J. Insulin secretion in response to protein ingestion. J Clin Invest. 1966 Sep;45(9):1479–1486. doi: 10.1172/JCI105455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S., Conn J. W., Knopf R. F., Rull J. Stimulation of insulin secretion by amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1966 Sep;45(9):1487–1502. doi: 10.1172/JCI105456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasso S., Messina A., Saporito N., Reitano G. Serum-insulin response to glucose and aminoacids in the premature infant. Lancet. 1968 Oct 5;2(7571):755–756. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90954-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATCH F. T., ABELL L. L., KENDALL F. E. Effects of restriction of dietary fat and cholesterol upon serum lipids and lipoproteins in patients with hypertension. Am J Med. 1955 Jul;19(1):48–60. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(55)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Balasse E. O., Segel N., Basso L. V. Splanchnic metabolism of free fatty acids and production of triglycerides of very low density lipoproteins in normotriglyceridemic and hypertriglyceridemic humans. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):2017–2035. doi: 10.1172/JCI106422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J., Drasar B. S. Degradation of bile salts by human intestinal bacteria. Gut. 1968 Feb;9(1):22–27. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Ockner R. K. An electron microscopic study of endogenous very low density lipoprotein production in the intestine of rat and man. J Lipid Res. 1971 Sep;12(5):580–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARVINEN E., LIN T. M., IVY A. C. Capacity of human intestine to absorb exogenous cholesterol. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Sep;11(2):143–147. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. I., Stein J., Dannacker D., Narcessian P. Biosynthesis of low density lipoprotein by cell-free preparations of rat intestinal mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5281–5288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIETTINEN T. A., AHRENS E. H., Jr, GRUNDY S. M. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL DIETARY AND FECAL NEUTRAL STEROIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:411–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D. Stimulation of insulin secretion in vitro by essential aminoacids. Lancet. 1969 May 31;1(7605):1075–1076. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91709-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN A., SJOVALL J. On the transformation and enterohepatic circulation of cholic acid in the rat: bile acids and steroids 68. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):872–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Hughes F. B., Isselbacher K. J. Very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph: origin, composition, and role in lipid transport in the fasting state. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2079–2088. doi: 10.1172/JCI106174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Jones A. L. An electron microscopic and functional study of very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jul;11(4):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Laster L. Biosynthesis of delta-7-cholesten-3-beta-ol, delta-5,7-cholestadien-3-beta-ol, and delta-5-cholesten-3-beta-ol by guinea pig intestinal mucosa in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1966 Nov;7(6):750–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S. On the secretion of bile. J Physiol. 1915 Aug 31;49(6):457–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1915.sp001722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESSOA V. C., KIM K. S., IVY A. C. Fat absorption in absence of bile and pancreatic juice. Am J Physiol. 1953 Aug;174(2):209–218. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.174.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIHL A. The effect of dietary fat on the intestinal cholesterol absorption and on the cholesterol metabolism in the liver of rats. Cholesterol studies. III. Acta Physiol Scand. 1955 Oct 27;34(2-3):183–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1955.tb01239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Frank A., Shames D. M., Berman M., Steinberg D. Very low density lipoprotein triglyceride transport in type IV hyperlipoproteinemia and the effects of carbohydrate-rich diets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2281–2297. doi: 10.1172/JCI106448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENFELD R. S., FUKUSHIMA D. K., HELLMAN L., GALLAGHER T. F. The transformation of cholesterol to coprostanol. J Biol Chem. 1954 Nov;211(1):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Hill D. B., Gross R. C., Farquhar J. W. Kinetics of triglyceride turnover of very low density lipoproteins of human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1826–1833. doi: 10.1172/JCI105290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roheim P. S., Gidez L. I., Eder H. A. Extrahepatic synthesis of lipoproteins of plasma and chyle: role of the intestine. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):297–300. doi: 10.1172/JCI105343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. S., Zumoff B., Hellman L. Conversion of cholesterol injected into man to cholestanol via a 3-ketonic intermediate. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jan;8(1):16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWELL L., FLICK D. F., FIELD H., Jr, TREADWELL C. R. Role of fat and fatty acid in absorption of dietary cholesterol. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jan;180(1):124–128. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.180.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava B. K., Redgrave T. G., Simmonds W. J. The source of endogenous lipid in the thoracic duct lymph of fasting rats. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1967 Jul;52(3):305–312. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1967.sp001916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegink L. D., Den Besten L. Synthesis of cysteine from methionine in normal adult subjects: effect of route of alimentation. Science. 1972 Nov 3;178(4060):514–516. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4060.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. B., Ho K. J. A review of human cholesterol metabolism. Arch Pathol. 1967 Jul;84(1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATERHOUSE C., KEMPERMAN J. H., STORMONT J. M. ALTERATIONS IN TRIGLYCERIDE METABOLISM AS PRODUCED BY DIETARY CHANGE. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Apr;63:605–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D. Biosynthetic origin of serum cholesterol in the squirrel monkey: evidence for a contribution by the intestinal wall. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):175–187. doi: 10.1172/JCI105707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Levy R. I. Production of beta-lipoprotein by intestine in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4878–4884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



