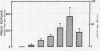Abstract
The effect of gastrin on basal- and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion was studied in 32 normal, young subjects. The concentration of gastrin and insulin in serum was measured radioimmunochemically.
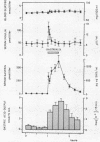
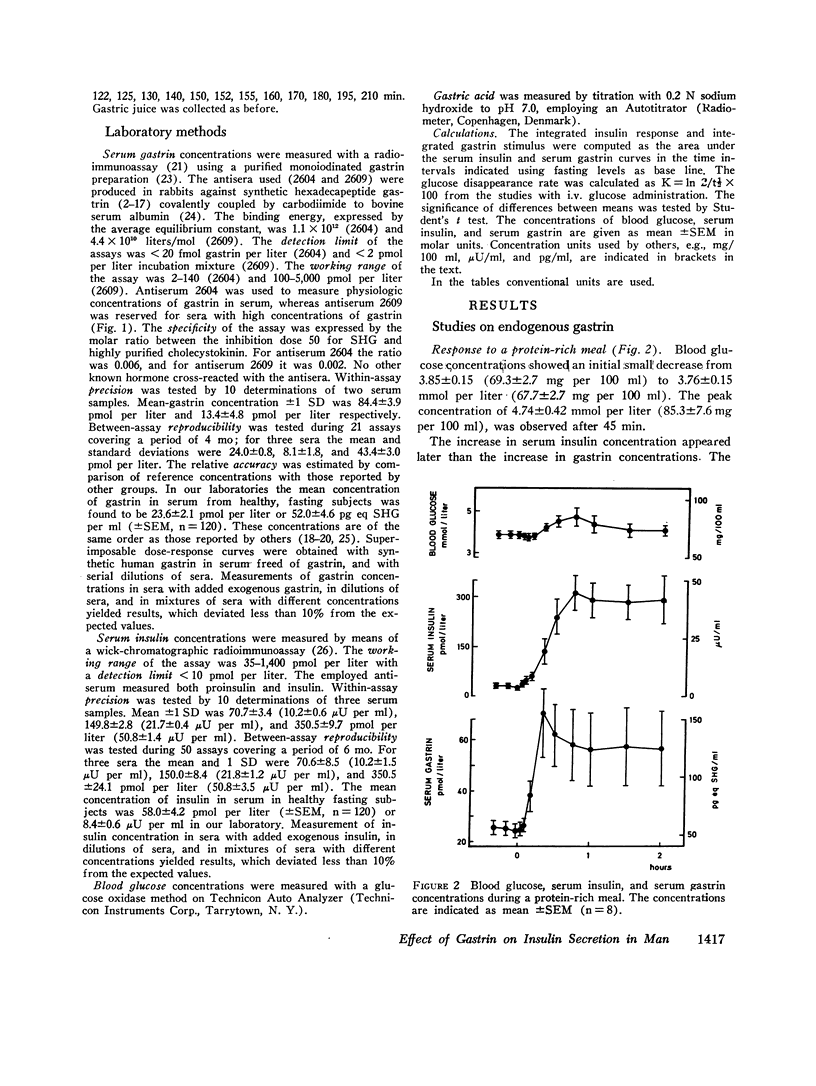
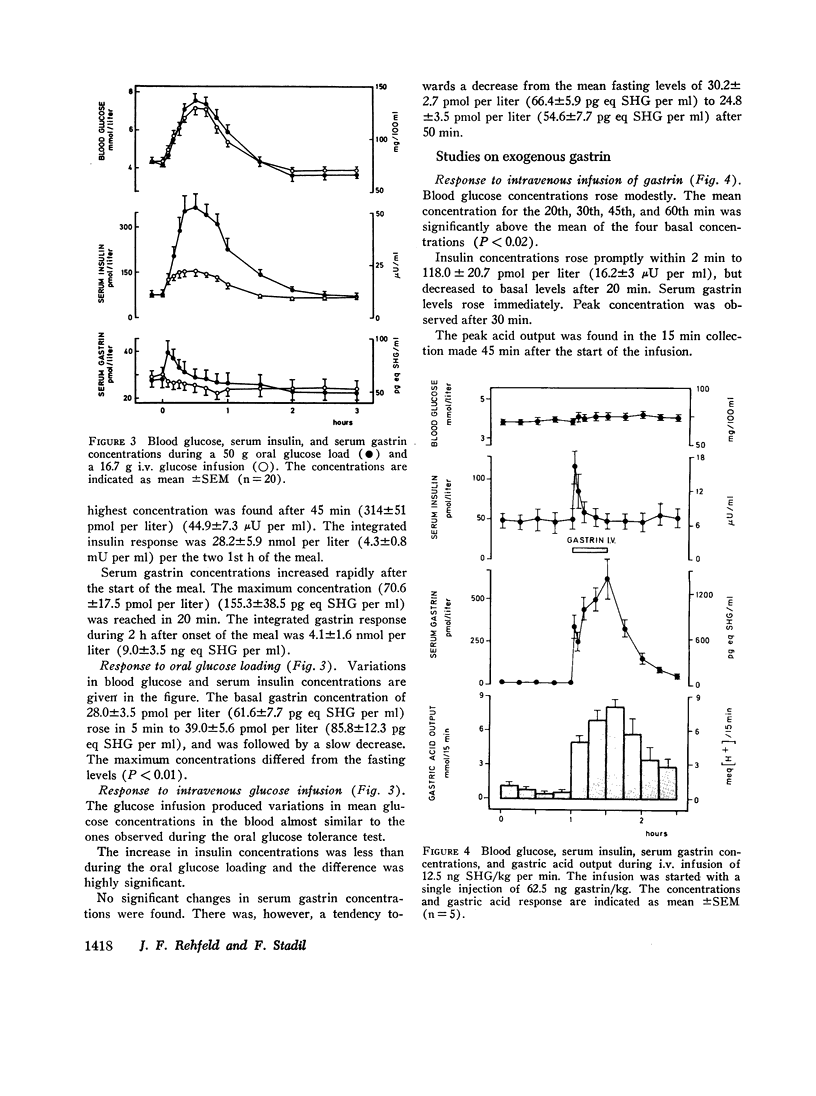
Maximal physiologic limit for the concentration of gastrin in serum was of the order of 160 pmol per liter as observed during a protein-rich meal. Oral ingestion of 50 g glucose produced a small gastrin response from 28±3 to 39±5 pmol per liter (mean ±SEM, P < 0.01).
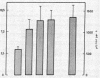
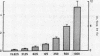
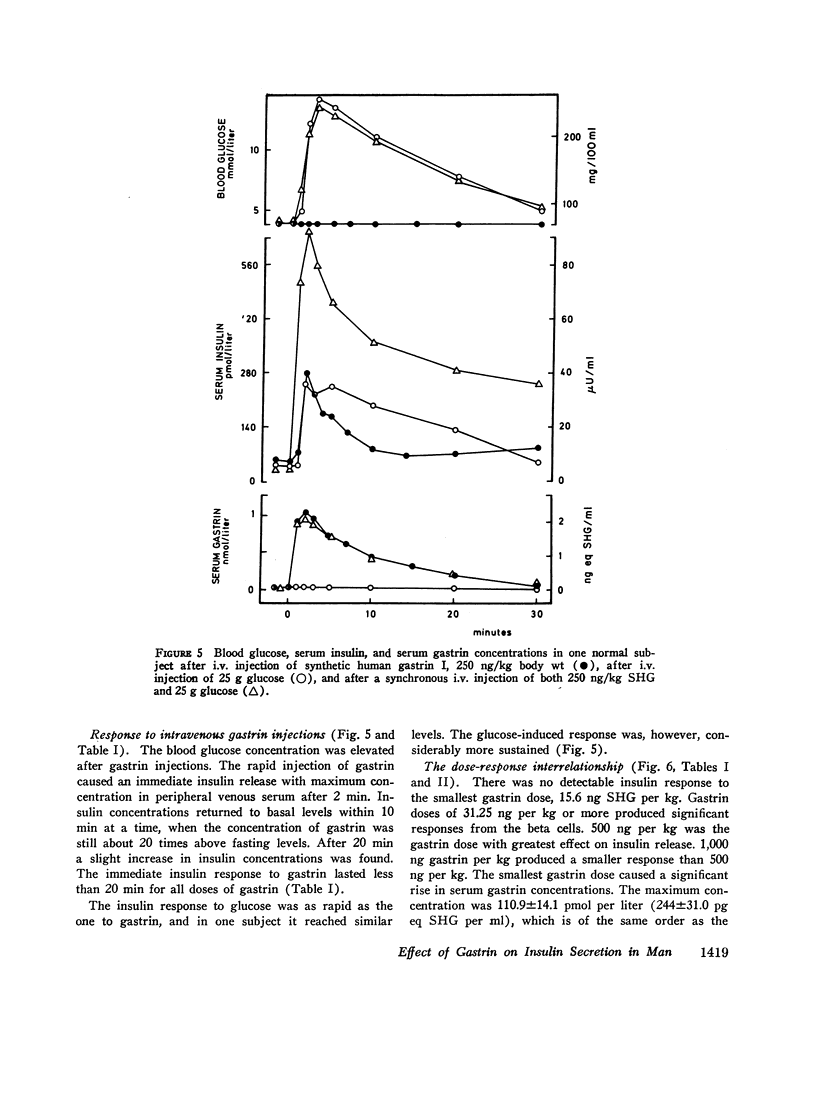
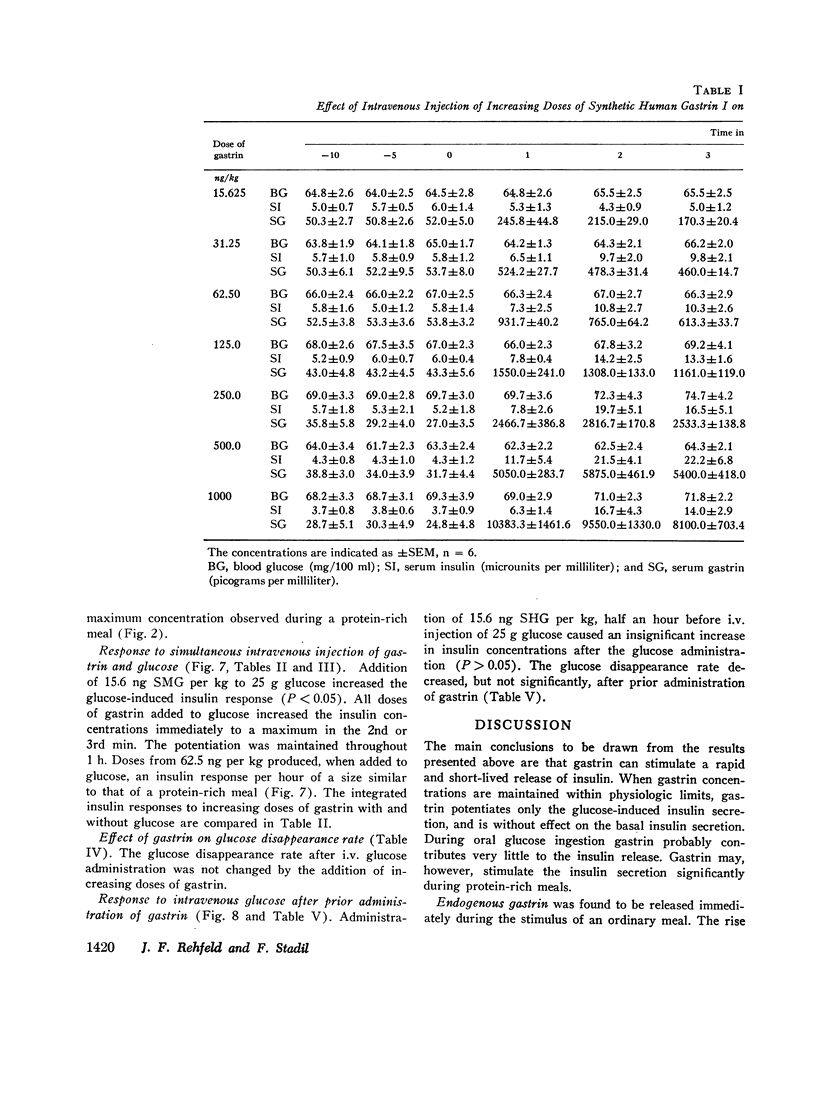
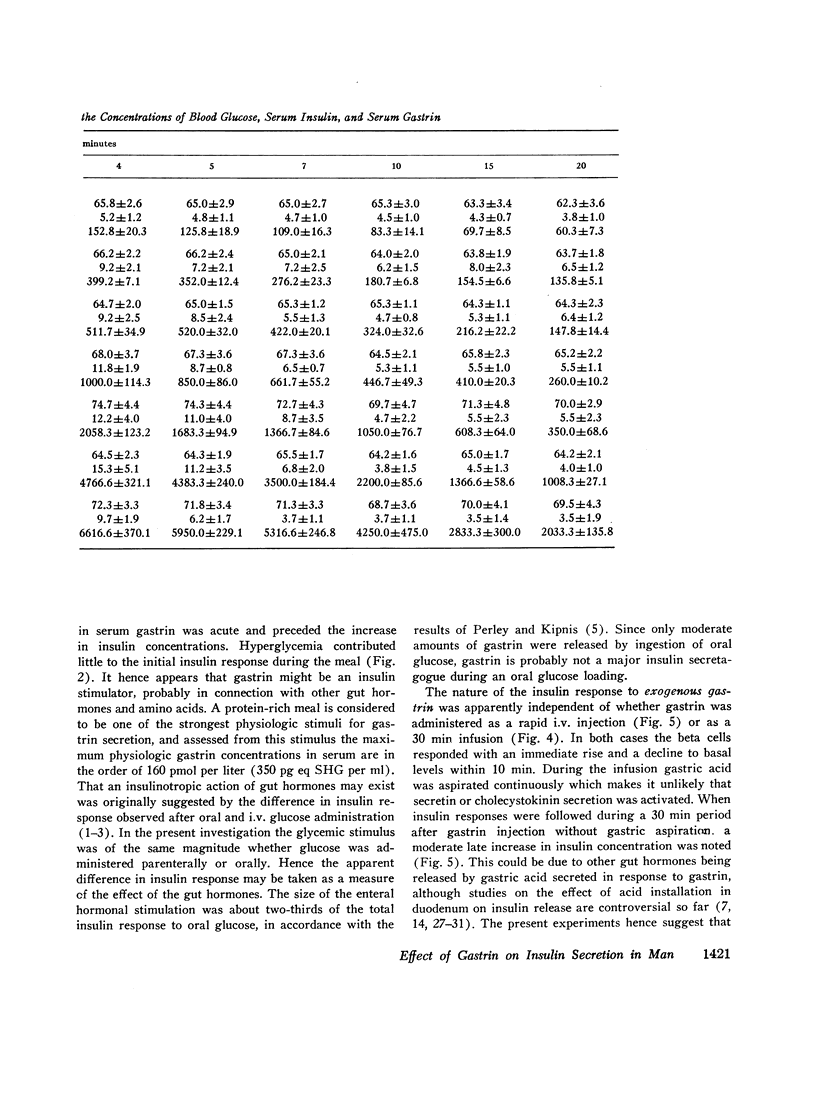
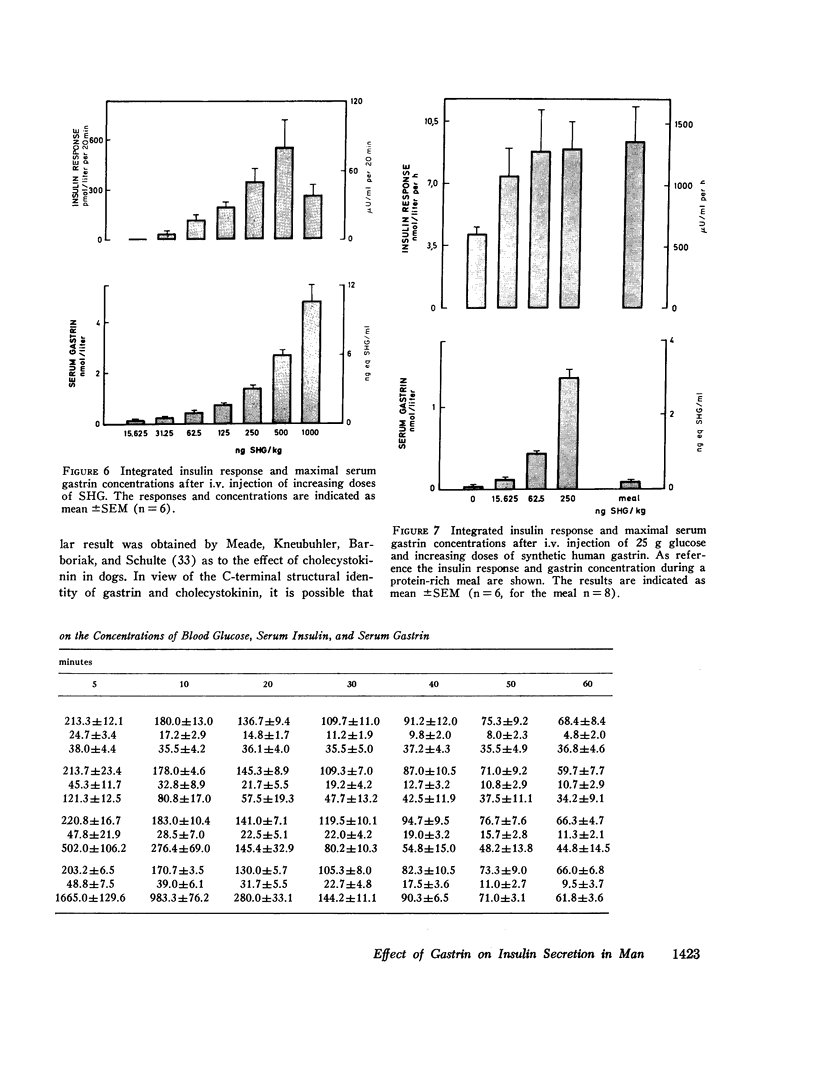
Intravenous injection or prolonged infusion of gastrin increased the concentration of insulin in peripheral venous blood to a maximum within 2 min followed by a decline to basal levels after a further 10 min. The minimum dose required to induce a significant insulin response (31.2 ng gastrin per kg) increased the gastrin level in serum above the physiologic range. Maximum effect was obtained with 500 ng gastrin per kg.
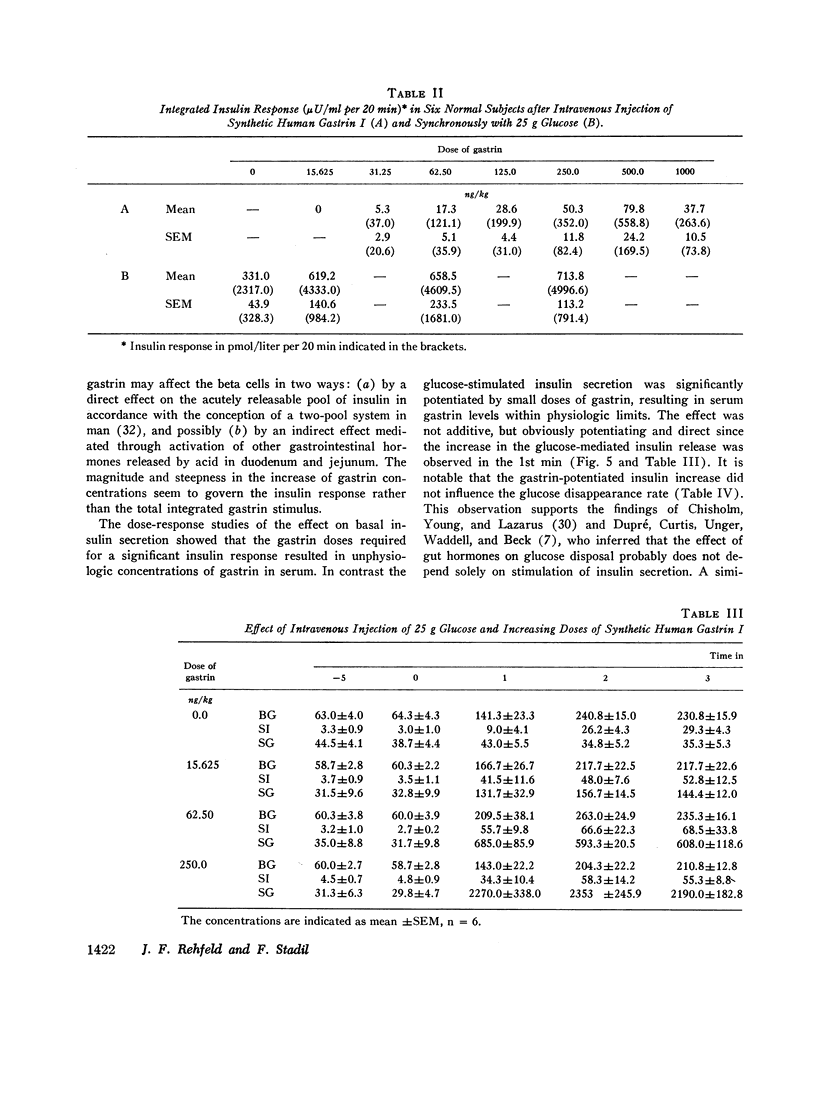
When 15.6 ng (7.1 pmol) gastrin per kg body weight and 25 g glucose were injected simultaneously, the glucose-induced insulin response was potentiated (from 2.32±0.33 to 4.33±0.98 nmol per liter per 20 min, P < 0.02), even though gastrin concentrations only increased to 71.2±6.6 pmol per liter. No effect, however, was noted on glucose disposal. 15.6 ng gastrin per kg given i.v. 30 min before an i.v. glucose tolerance test was without significant effect on the insulin response.
The results indicate that gastrin can stimulate a rapid and short-lived release of insulin. In physiologic concentrations gastrin potentiates the glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and is without effect on basal insulin secretion. A small release of gastrin during oral glucose ingestion may to a limited extent contribute to the nonglycemic insulin secretion. During protein ingestion, gastrin probably stimulates insulin secretion significantly.
Full text
PDF
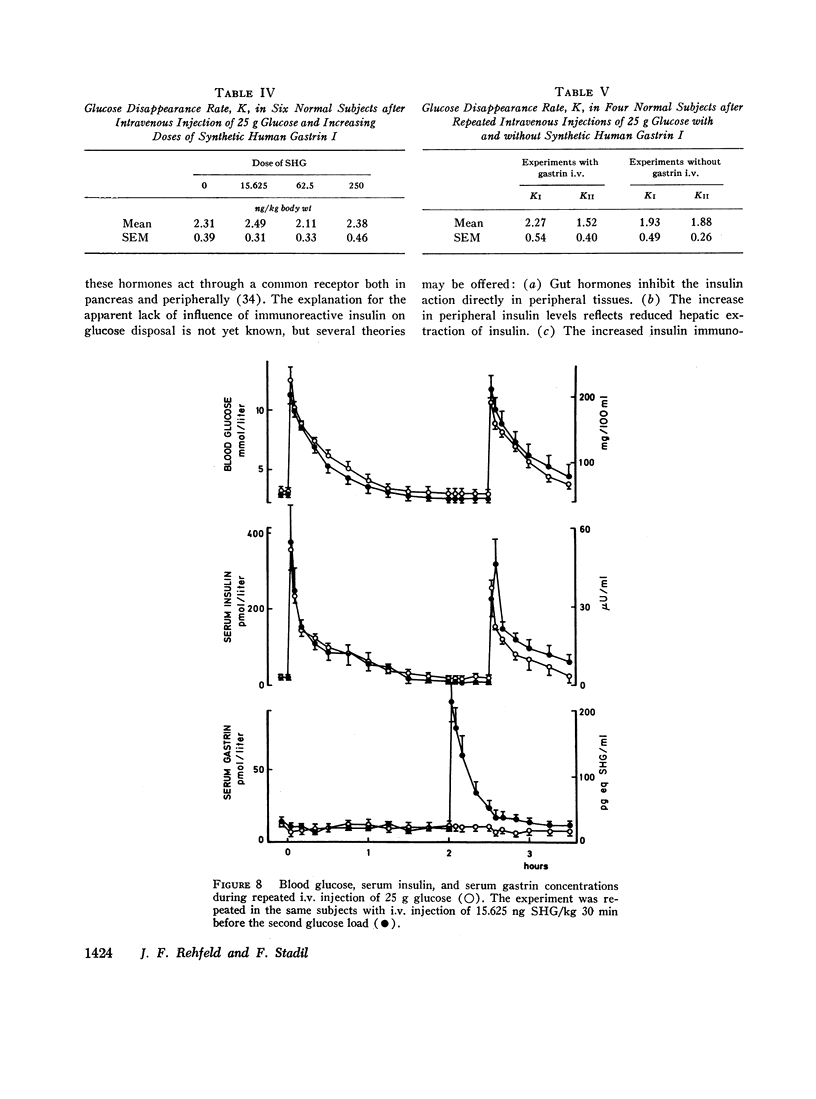


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyns D. R., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Intestinal hormones and plasma insulin: an insulinotropic action of secretin. Br Med J. 1967 Jun 10;2(5553):676–678. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5553.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan K. D., Vance J. E., Williams R. H. Insulin and glucagon release from isolated islets of Langerhans. Effect of enteric factors. Diabetes. 1969 Jun;18(6):381–386. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.6.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm D. J., Young J. D., Lazarus L. The gastrointestinal stimulus to insulin release. I. Secretin. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1453–1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI106111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupre J., Curtis J. D., Unger R. H., Waddell R. W., Beck J. C. Effects of secretin, pancreozymin, or gastrin on the response of the endocrine pancreas to administration of glucose or arginine in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):745–757. doi: 10.1172/JCI106032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELRICK H., STIMMLER L., HLAD C. J., Jr, ARAI Y. PLASMA INSULIN RESPONSE TO ORAL AND INTRAVENOUS GLUCOSE ADMINISTRATION. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Oct;24:1076–1082. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-10-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguli P. C., Hunter W. M. Radio-immunoassay of gastrin in human plasma. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(2):499–510. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman M. I. Gastrin, cholecystokinin, and secretin act on one receptor. Lancet. 1970 May 23;1(7656):1088–1089. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92758-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansky J., Cain M. D. Radioimmunoassay of gastrin in human serum. Lancet. 1969 Dec 27;2(7635):1388–1390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90933-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen J. Secretion of glucagon from the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2123–2136. doi: 10.1172/JCI106706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Cohen N. M. Intestinal hormones and plasma-insulin. Some observations on glucagon, secretin, and gastrin. Lancet. 1967 Oct 21;2(7521):861–863. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92594-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaess H., Schlierf G. Untersuchungen über die exokrine und endokrine Pankreasfunktion nach exogener und endogener Stimulation mit Secretin sowie Pentagastrin. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1968;74:225–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaess H., Schlierf G. Veränderungen des Blutzuckers und der Plasmainsulinkonzentration nach Stimulierung der endogenen Sekretinfreisetzung. Diabetologia. 1969 Aug;5(4):228–232. doi: 10.1007/BF01212089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Tasaka Y., Kosaka K., Nakao K. Stimulation of insulin secretion by the C-terminal tetrapeptide amide of gastrin. Endocrinology. 1969 May;84(5):1098–1106. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-5-1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi M., Kuzuya T., Ide T. Plasma insulin response to intravenous administration of tetragastrin (C-terminal tetrapeptide amide of gastrin) in man. Metabolism. 1971 May;20(5):433–445. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., Chisholm D. J., Young J. D., Lazarus L. The gastrointestinal stimulus to insulin release. II. A dual action of secretin. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):524–529. doi: 10.1172/JCI106262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus N. R., Voyles N. R., Devrim S., Tanese T., Recant L. Extra-gastrointestinal effects of secretin, gastrin, and pancreozymin. Lancet. 1968 Aug 3;2(7562):248–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92353-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Hellman B., Coore H. G. Effects of gastrin on the release of insulin in vitro. J Endocrinol. 1969 Mar;43(3):371–375. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0430371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE N., HOLDSWORTH C. D., TURNER D. S. NEW INTERPRETATION OF ORAL GLUCOSE TOLERANCE. Lancet. 1964 Jul 4;2(7349):20–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan J. E., Trudeau W. L. Studies with antibodies to gastrin. Radioimmunoassay in human serum and physiological studies. Gastroenterology. 1970 Feb;58(2):139–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre N., Holdsworth C. D., Turner D. S. Intestinal factors in the control of insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1317–1324. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade R. C., Kneubuhler H. A., Barboriak J. J., Schulte W. J. Absence of glucose response to physiologic levels of serum insulin. Diabetes. 1969 Jun;18(6):397–401. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.6.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohgawara H., Mizuno Y., Tasaka Y., Kosaka K. Effect of the C-terminal tetrapeptide amide of gastrin on insulin secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1261–1262. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Pupo A. A. Insulin responses to glucose: evidence for a two pool system in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2309–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI106197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehefeld J. F. Three components of gastrin in human serum. Gel filtration studies on the molecular size of immunoreactive serum gastrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 28;285(2):364–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F. Effect of gastrin and its C-terminal tetrapeptide on insulin secretion in man. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1971 Jan;66(1):169–176. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0660169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
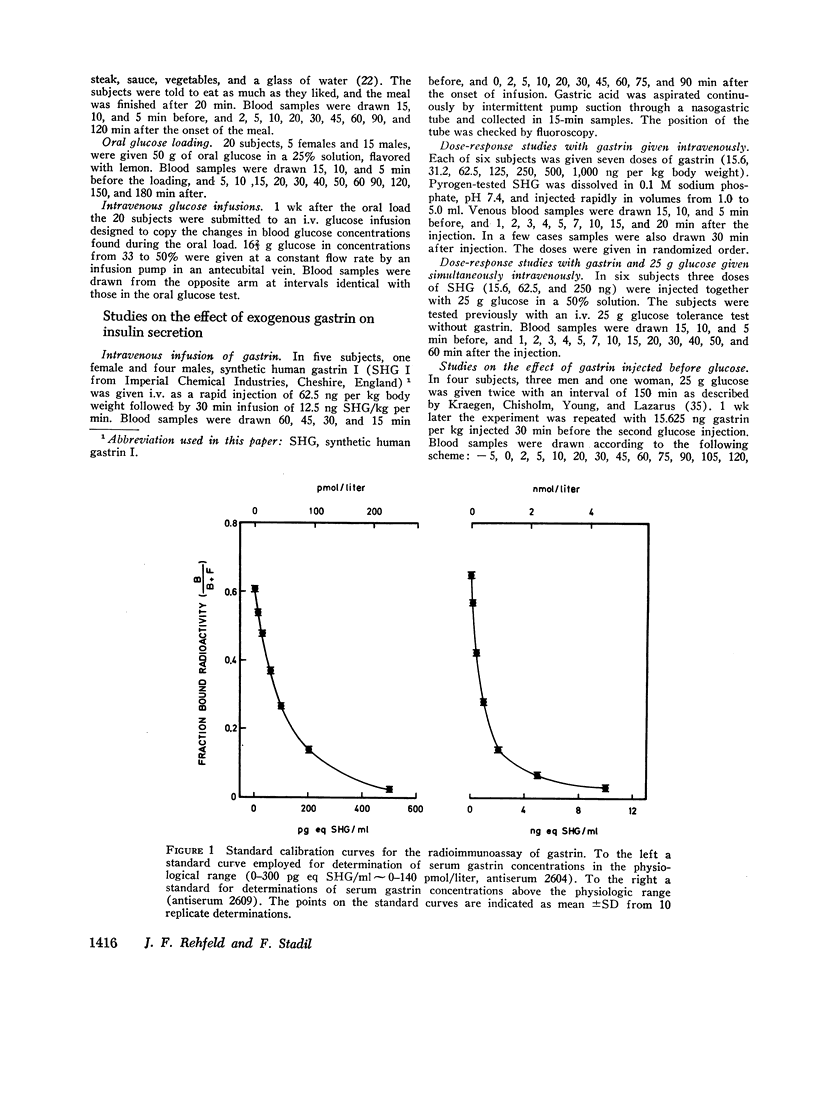
- Rehfeld J. F., Stadil F., Rubin B. Production and evaluation of antibodies for the radioimmunoassay of gastrin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Oct;30(2):221–232. doi: 10.3109/00365517209081114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rune S. J. Comparison of the rates of gastric acid secretion in man after ingestion of food and after maximal stimulation with histamine. Gut. 1966 Aug;7(4):344–350. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.4.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadil F., Rehfeld J. F. Preparation of 125 I-labelled synthetic human gastrin I for radioimmunoanalysis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Dec;30(4):361–368. doi: 10.3109/00365517209080271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadil F., Rehfeld J. F. Radioimmunoassay of gastrin in human serum. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1971;9:61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Eisentraut A. M. Entero-insular axis. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):261–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ketterer H., Dupré J., Eisentraut A. M. The effects of secretin, pancreozymin, and gastrin on insulin and glucagon secretion in anesthetized dogs. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):630–645. doi: 10.1172/JCI105565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Further studies on the nature of immunoreactive gastrin in human plasma. Gastroenterology. 1971 Feb;60(2):203–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Radioimmunoassay of gastrin. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jan;58(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]