Abstract
In genetic prediabetic subjects (the glucose tolerant offspring of two diabetic parents or the identical twin of a known diabetic) serum insulin concentrations after glucose administration are subnormal. Maintenance of glucose tolerance in this setting is apparently paradoxical, suggesting increased tissue insulin sensitivity. Accordingly, forearm tissue insulin sensitivity in nine genetic prediabetic males was compared with that of seven males without familial diabetes. Diabetes was excluded in all subjects by preliminary oral glucose tolerance testing.
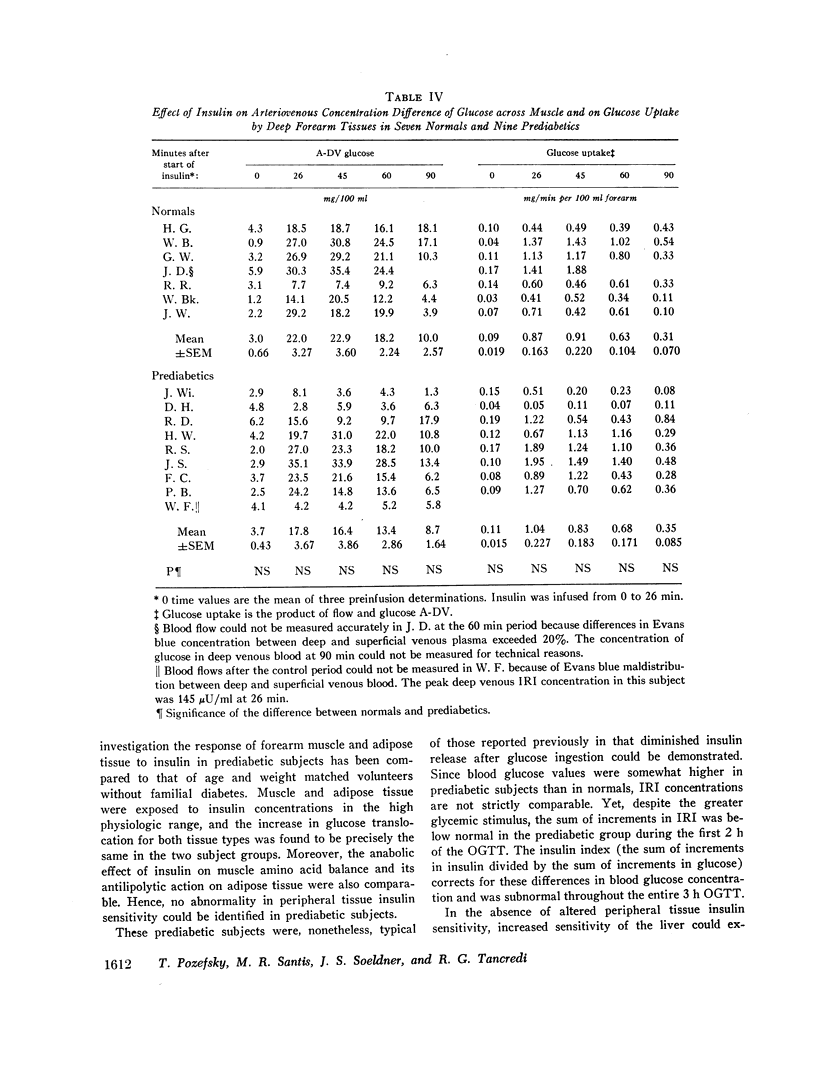
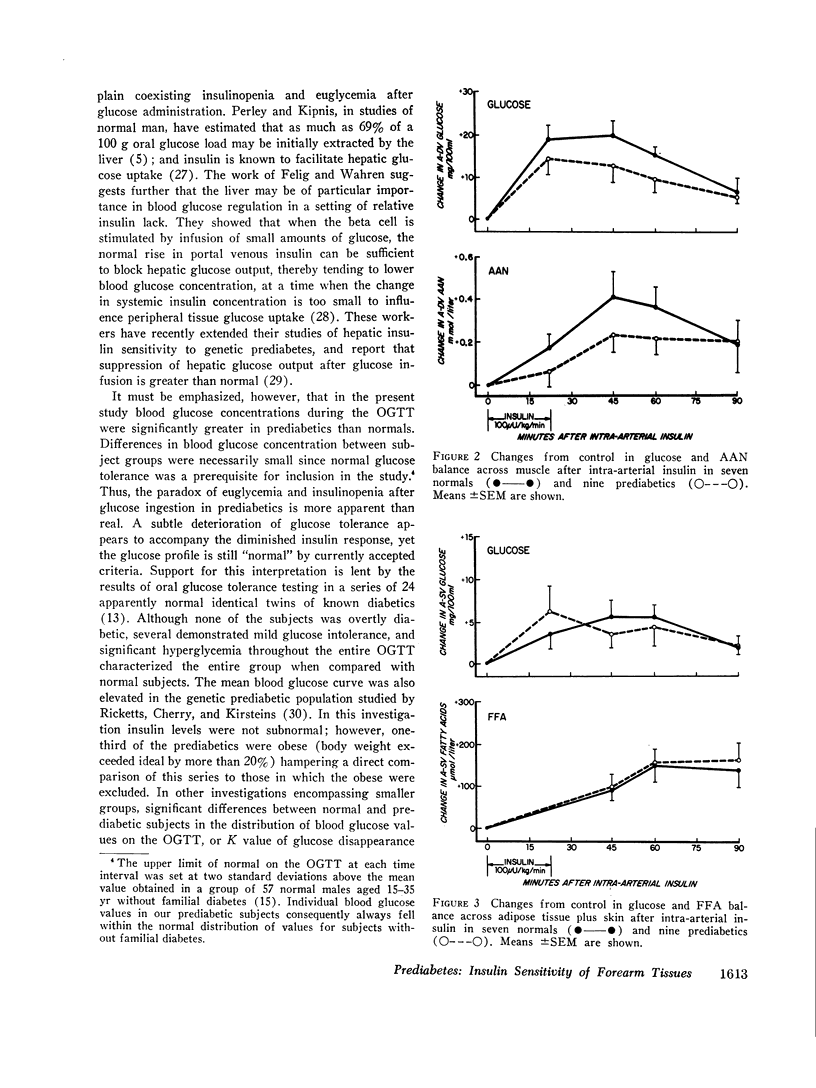
On the preliminary 3 h oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) the sum of increments in blood glucose above fasting was greater in prediabetic than in control subjects. Conversely, the sum of increments in serum insulin was subnormal for the first 2 h. The insulin index (the sum of increments in insulin divided by the sum of increments in glucose) was significantly lower in prediabetics throughout the test. High physiologic levels of insulin were produced in the forearm by intrabrachial arterial insulin infusion (100 μU/kg per min for 26 min). Balances of glucose and amino acids across forearm muscle became more positive, as did balances of glucose and free fatty acids across adipose tissue plus skin. There were no differences in response between prediabetic and normal subjects.
Hence, the insulin sensitivity of peripheral tissues is normal in genetic prediabetes. Increased tissue insulin sensitivity is not essential to explain coexisting euglycemia and insulinopenia in prediabetes because blood glucose values on the OGTT are, in fact, elevated although still within the range considered normal.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRES R., ZIERLER K. L., ANDERSON H. M., STAINSBY W. N., CADER G., GHRAYYIB A. S., LILIENTHAL J. L., Jr Measurement of blood flow and volume in the forearm of man; with notes on the theory of indicator-dilution and on production of turbulence, hemolysis, and vasodilatation by intra-vascular injection. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):482–504. doi: 10.1172/JCI102919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr The significance of basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1549–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI105646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. Further studies on healthy subjects with low and high insulin response to glucose infusion. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Jun;55(2):305–329. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. Insulin response to glucose infusion in diabetic and non-diabetic monozygotic twin pairs. Genetic control of insulin response? Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Jun;55(2):330–345. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0550330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell J. A., Lein A. Diminished insulin response to hyperglycemia in prediabetes and diabetes. Diabetes. 1967 Aug;16(8):560–565. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.8.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockford P. M., Hazzard W. R., Williams R. H. Insulin response to glucagon. The opposing effects of diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. 1969 Apr;18(4):216–224. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.4.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P., MEINERTZ H. Microdetermination of long-chain fatty acids in plasma and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2595–2599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J. Influence of endogenous insulin secretion on splanchnic glucose and amino acid metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1702–1711. doi: 10.1172/JCI106659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S., Conn J. W., Thiffault C., Knopf R. F., Guntsche E. Secretion of insulin induced by amino acids and glucose in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Feb;28(2):266–276. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRODSKY G. M., KARAM J. H., PAVLATOS F. C., FORSHAM P. H. SERUM-INSULIN RESPONSE TO GLUCOSE IN PREDIABETIC SUBJECTS. Lancet. 1965 Feb 6;1(7380):290–291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. B., Soeldner J. S., Gleason R. E., Rojas L., Camerini-Davalos R. A., Marble A. Clinical and chemical diabetes in offspring of diabetic couples. N Engl J Med. 1969 Aug 14;281(7):343–347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196908142810703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. A modified ninhydrin reagent for the photometric determination of amino acids and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. L. Role of insulin in the hepatic handling of glucose. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to glucose and tolbutamide of normal weight and obese diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):867–874. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effects of insulin at two dose levels. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2273–2282. doi: 10.1172/JCI106193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke D. A., Cassar J., Todd J., Taylor K. W. Glucose tolerance and serum insulin in identical twins of diabetics. Br Med J. 1970 Dec 12;4(5736):649–651. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5736.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricketts H. T., Cherry R. A., Kirsteins L. Biochemical studies of "prediabetes". Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):880–888. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas L., Soeldner J. S., Gleason R. E., Kahn C. B., Marble A. Offspring of two diabetic parents: differential serum insulin responses to intravenous glucose and tolbutamide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Dec;29(12):1569–1579. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-12-1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rull J. A., Conn J. W., Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S. Levels of plasma insulin during cortisone glucose tolerance tests in "nondiabetic" relatives of diabetic patients. Implications of diminished insulin secretory reserve in subclinical diabetes. Diabetes. 1970 Jan;19(1):1–10. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer H. S., Allen E. W., Herron A. L., Jr, Brennan M. T. Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):323–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI105534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Gleason R. E., Williams R. F., Garcia M. J., Beardwood D. M., Marble A. Diminished serum insulin response to glucose in genetic prediabetic males with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 1968 Jan;17(1):17–26. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. W., Sheldon J., Pyke D. A., Oakley W. G. Glucose tolerance and serum insulin in the unaffected first-degree relatives of diabetics. Br Med J. 1967 Oct 7;4(5570):22–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whichelow M. J., Butterfield W. J. Peripheral glucose uptake during the oral glucose-tolerance test in normal and obese subjects and borderline and frank diabetics. Q J Med. 1971 Apr;40(158):261–273. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.qjmed.a067269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Plasma insulin concentrations in nondiabetic and early diabetic subjects. Determinations by a new sensitive immuno-assay technic. Diabetes. 1960 Jul-Aug;9:254–260. doi: 10.2337/diab.9.4.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L., RABINOWITZ D. ROLES OF INSULIN AND GROWTH HORMONE, BASED ON STUDIES OF FOREARM METABOLISM IN MAN. Medicine (Baltimore) 1963 Nov;42:385–402. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196311000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



