Abstract
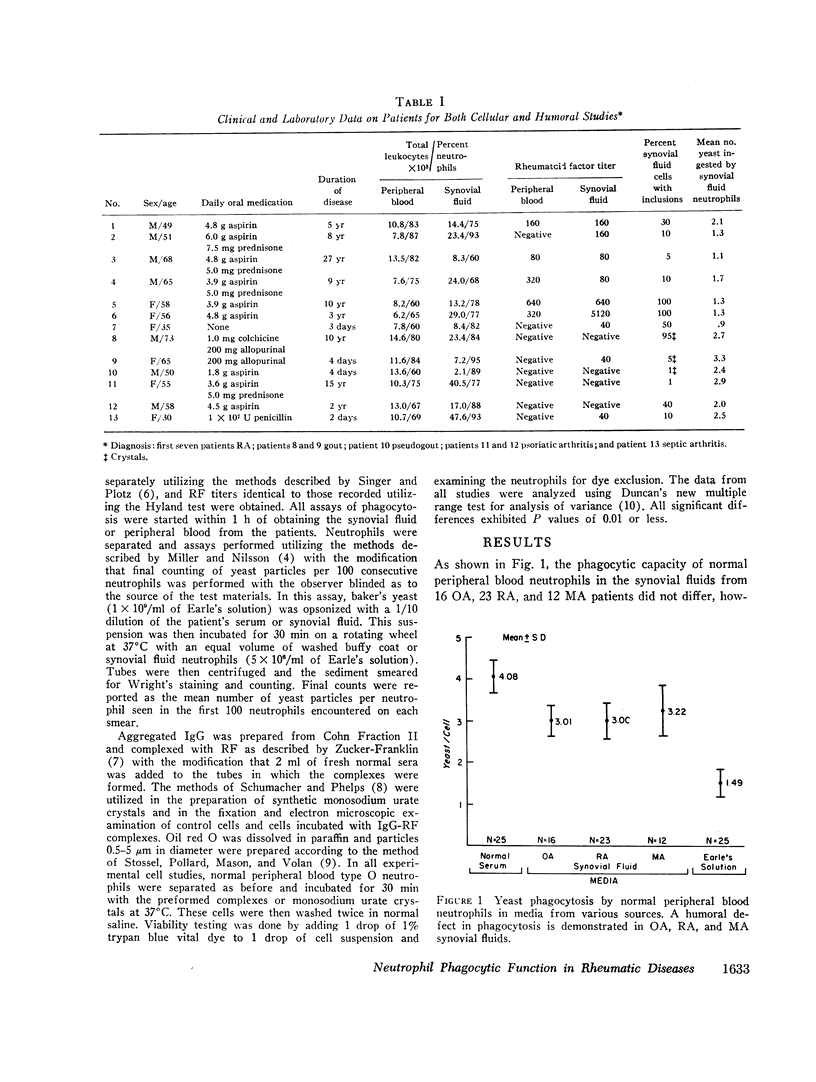
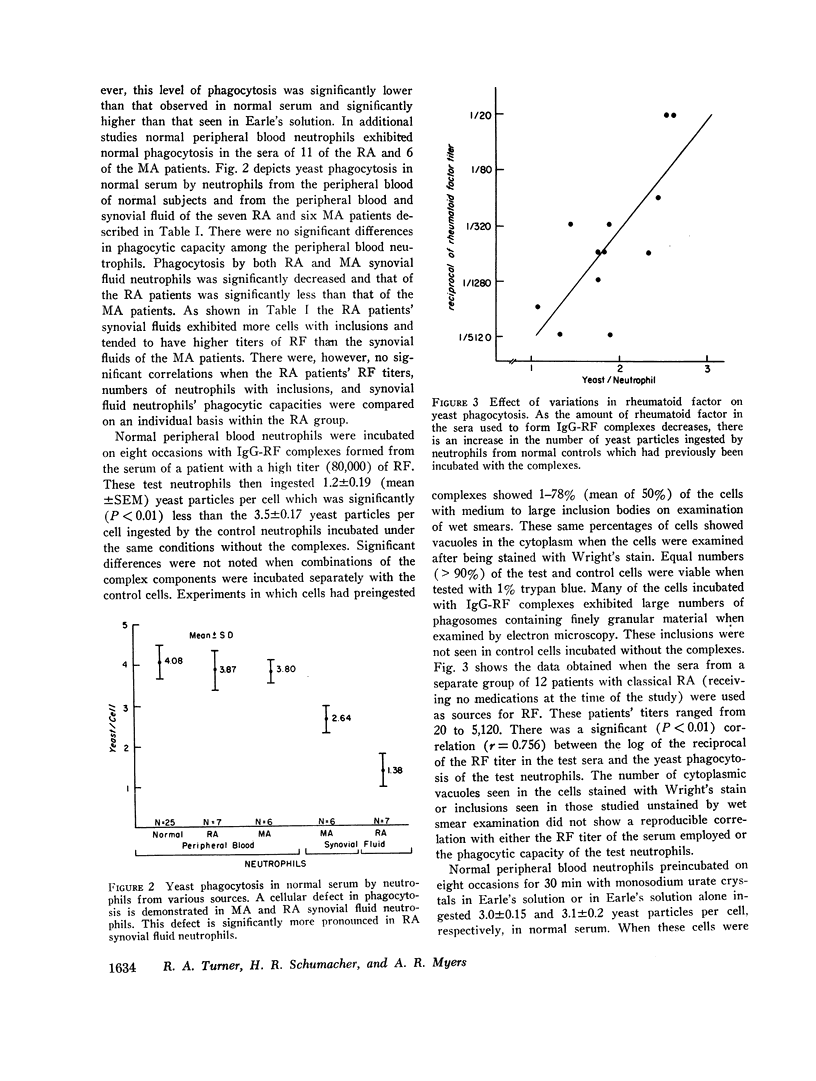
Phagocytosis of yeast particles by peripheral blood and synovial fluid neutrophils was compared in the sera and synovial fluids from 16 osteoarthritis, 23 rheumatoid arthritis, and 12 miscellaneous arthritis patients. Phagocytosis by normal peripheral blood neutrophils was decreased equally and significantly in all synovial fluids. All synovial fluid neutrophils demonstrated decreased phagocytic capacity in all media. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid neutrophils showed significantly less phagocytosis than miscellaneous arthritis synovial fluid neutrophils. Normal peripheral blood neutrophils which in vitro had previously ingested monosodium urate crystals or oil red O, subsequently exhibited a normal yeast phagocytic capacity. Normal peripheral blood neutrophils, which had ingested preformed immunoglobulin G-rheumatoid factor complexes exhibited significantly less yeast phagocytic capacity than control cells or cells preincubated with the individual complex components. There was a significant correlation between the log of the reciprocal of the rheumatoid factor titer in sera used to produce complexes and the phagocytic capacity exhibited by test neutrophils. Ingestion of immunoglobulin G-rheumatoid factor complexes may be important in the production of the cellular phagocytic defect which this study has demonstrated in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid neutrophils.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodel P. T., Hollingsworth J. W. Comparative morphology, respiration, and phagocytic function of leukocytes from blood and joint fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):580–589. doi: 10.1172/JCI105372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLANDER J. L., MCCARTY D. J., Jr, ASTORGA G., CASTRO-MURILLO E. STUDIES ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID JOINT INFLAMMATION. I. THE "R.A. CELL" AND A WORKING HYPOTHESIS. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Feb;62:271–280. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLGREN J. H., BALL J., FAIRBROTHER R. W., BARNES K. L. Suppurative arthritis complicating rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1958 May 24;1(5081):1193–1200. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5081.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E., Nilsson U. R. A familial deficiency of the phagocytosis-enhancing activity of serum related to a dysfunction of the fifth component of complement (C5). N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 12;282(7):354–358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002122820702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. G., Baum J. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2541–2549. doi: 10.1172/JCI106754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Phelps P. Sequential changes in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes after urate crystal phagocytosis. An electron microscopic study. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Jul-Aug;14(4):513–526. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Pollard T. D., Mason R. J., Vaughan M. Isolation and properties of phagocytic vesicles from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1745–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI106664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. The phagosomes in rheumatoid synovial fluid leukocytes: a light, fluorescence, and electron microscope study. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Feb;9(1):24–36. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


