Abstract
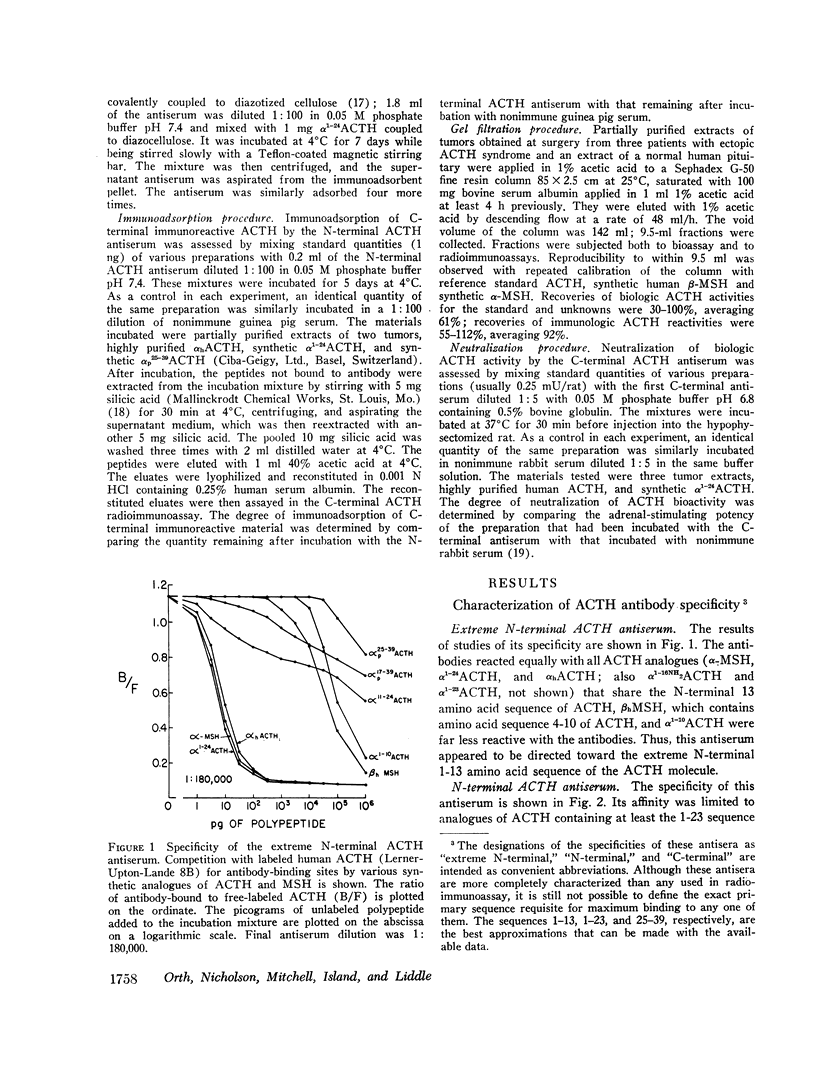
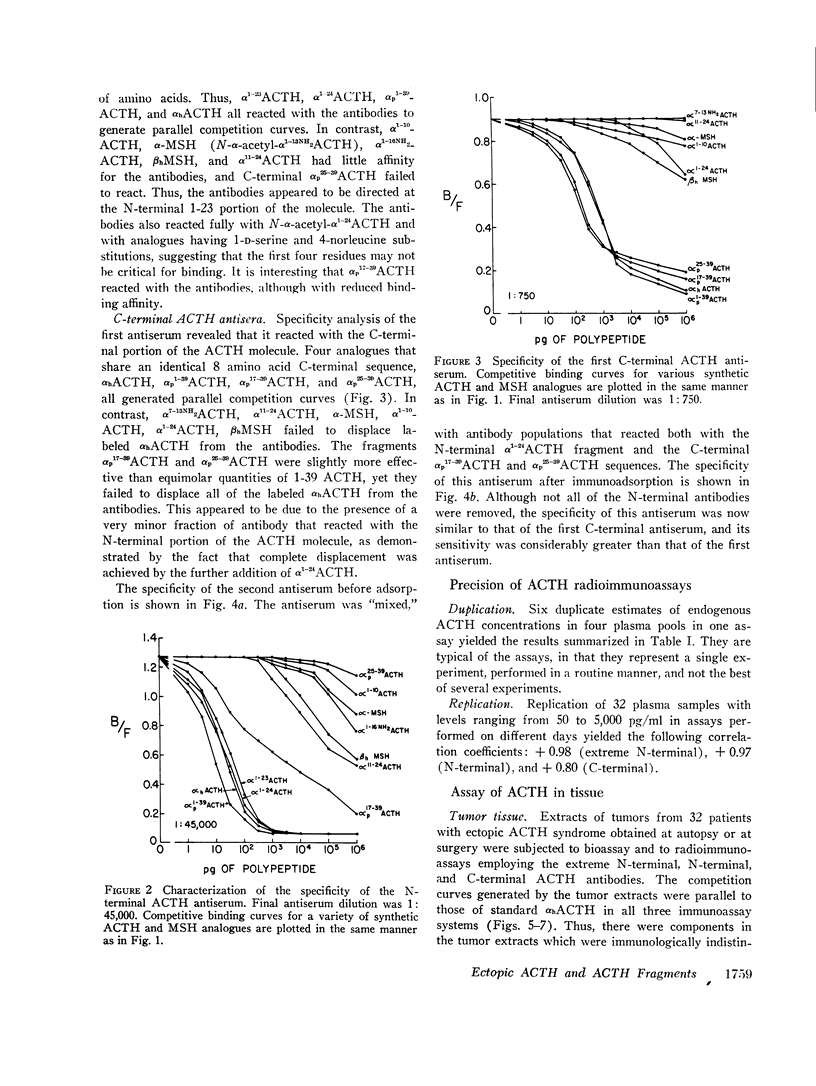
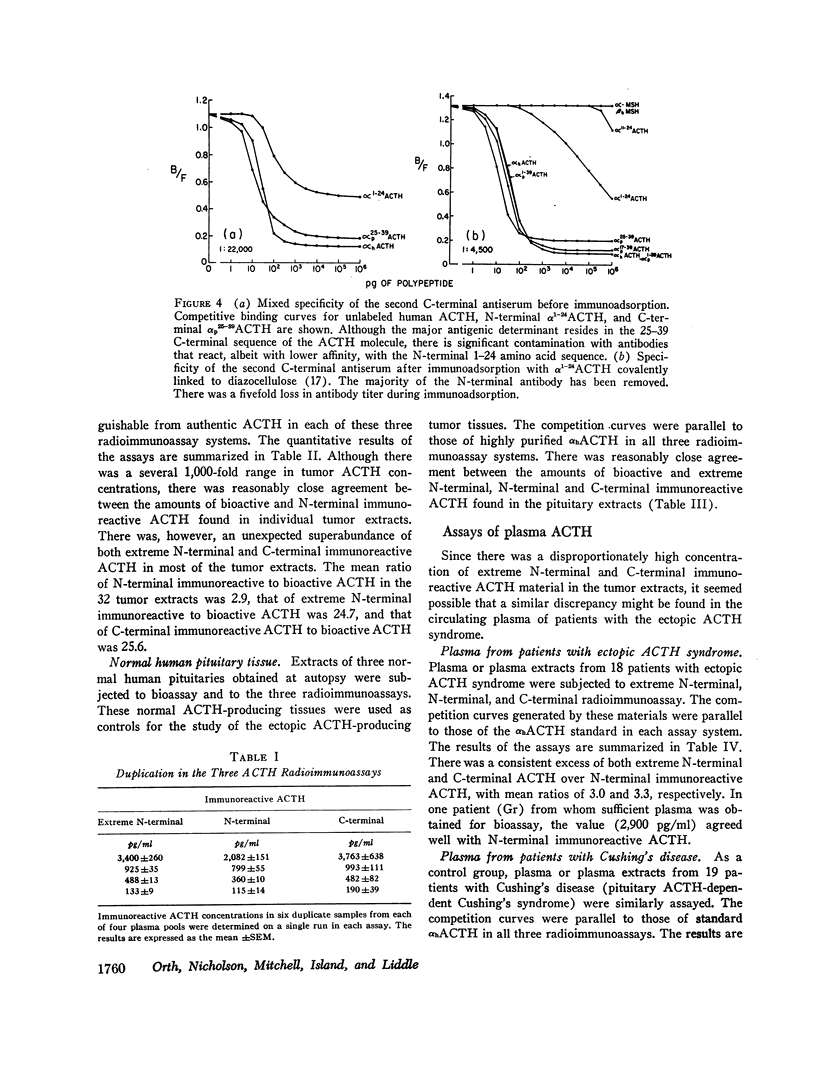
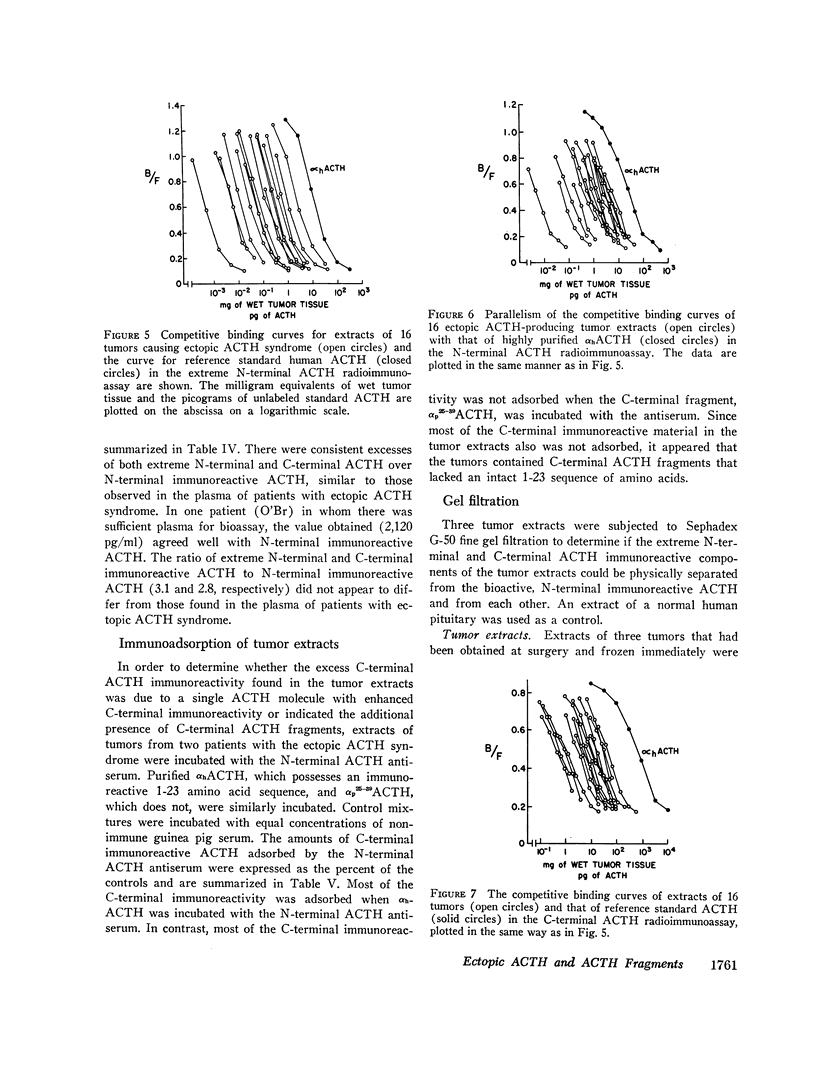
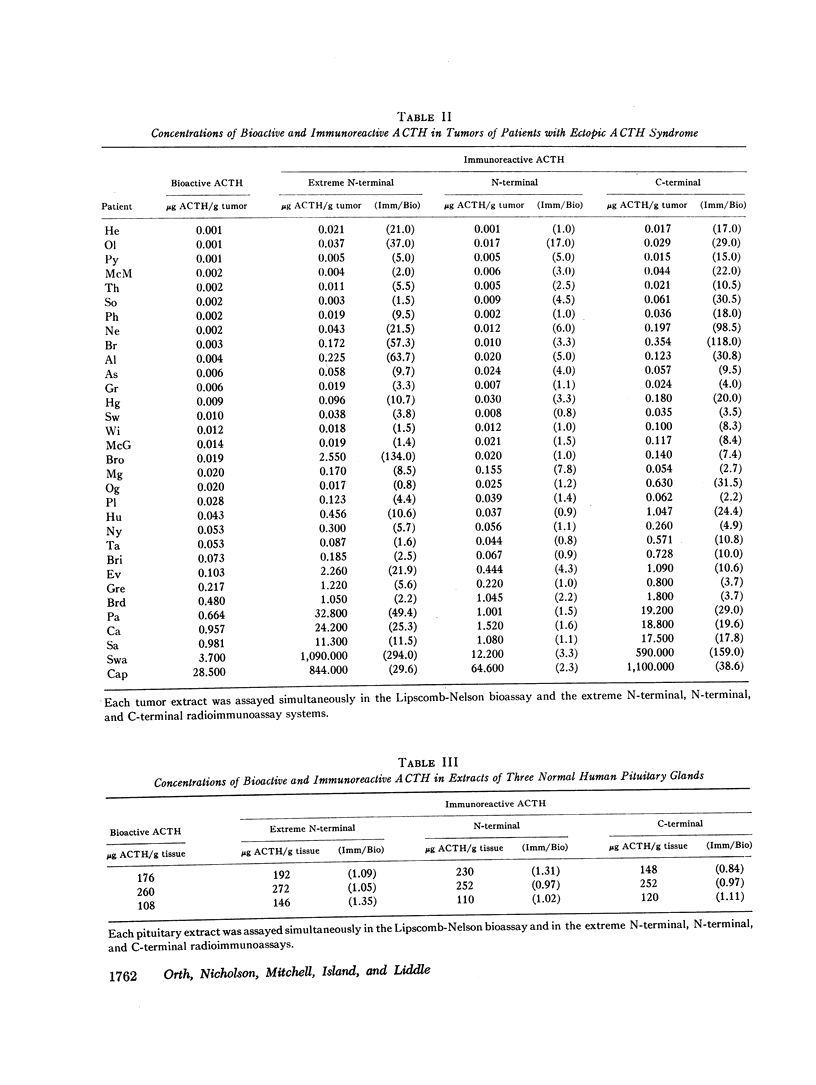
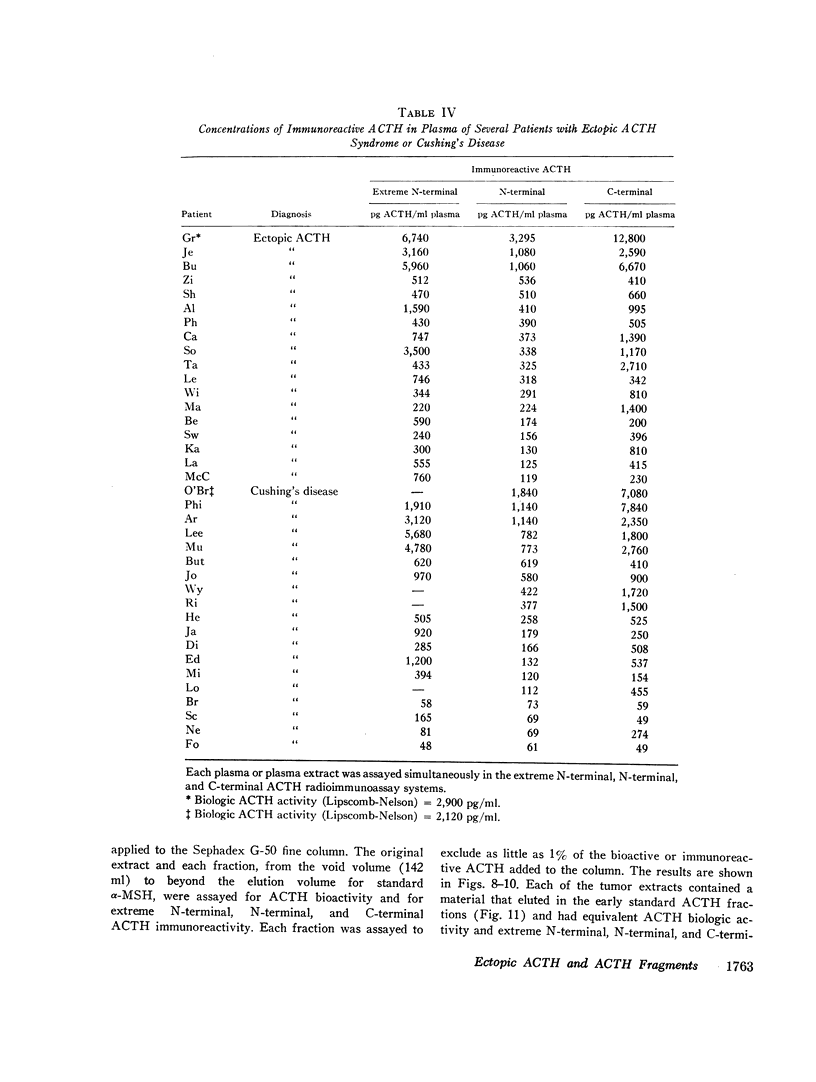
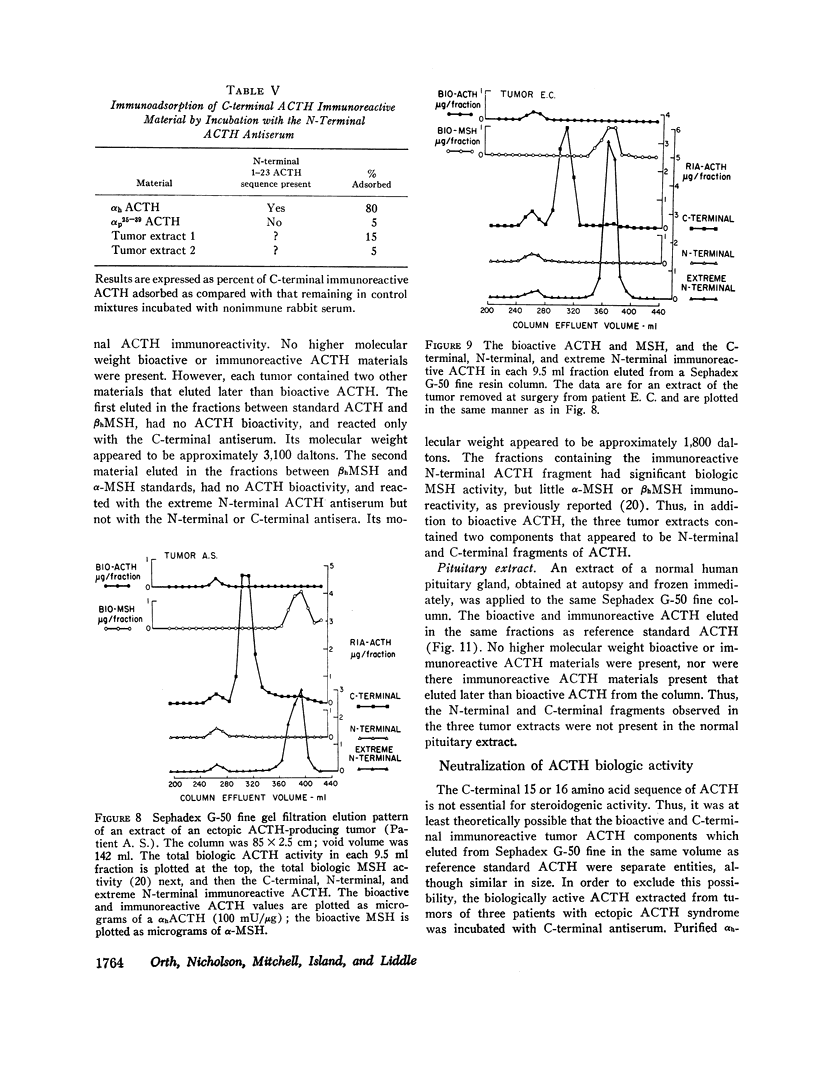
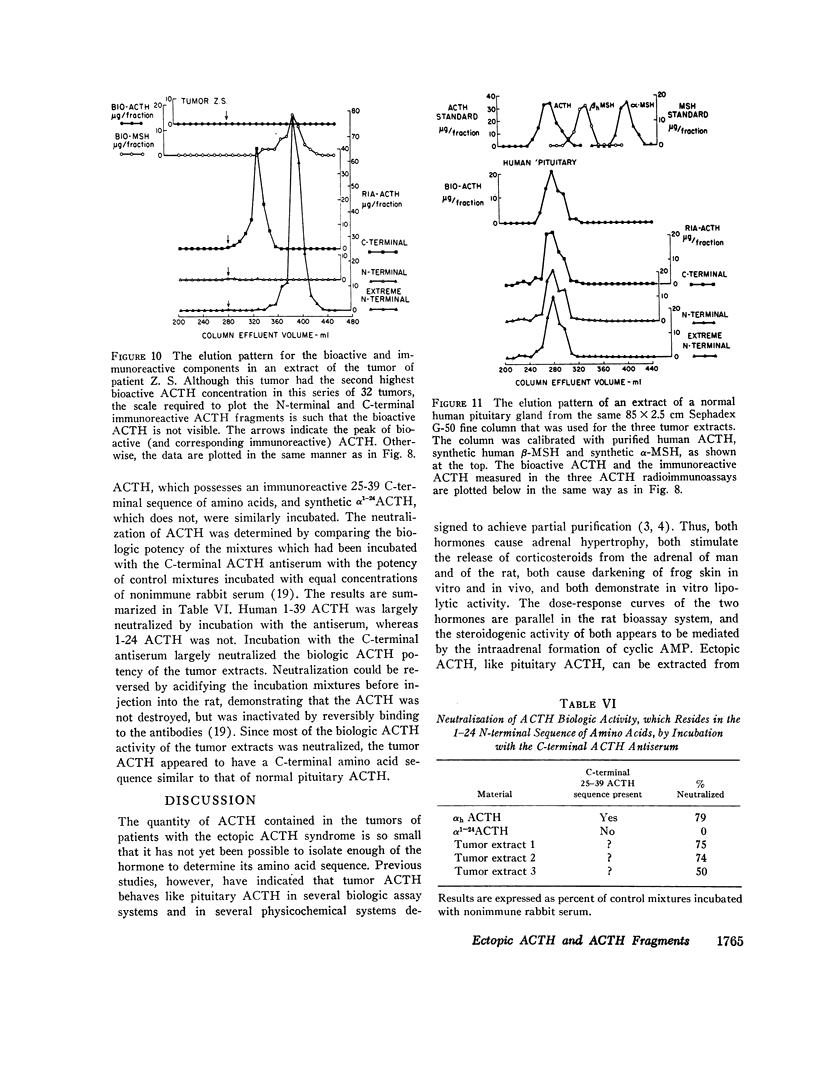
Extracts of tumors from 32 patients with the ectopic ACTH syndrome were subjected to simultaneous bioassay and radioimmunoassays for ACTH. Radioimmunoassays were performed using three antisera, one of which reacts with the extreme N-terminal 1-13 amino acid sequence of ACTH, the second with the N-terminal 1-23 sequence of the ACTH molecule, and the third with the C-terminal 25-39 amino acid sequence of ACTH. There was, in general, good correlation between bioactivity and N-terminal ACTH immunoreactivity. However, there were large excesses of both extreme N-terminal and C-terminal immunoreactive materials in most tumor extracts, which were not found in extracts of three human pituitaries. Three tumor extracts were subjected to molecular sieve chromatography on Sephadex G-50 fine resin. The bioactive ACTH eluted in the same fractions as pituitary ACTH (mol wt≃4,500 daltons) and reacted equally in all three ACTH radioimmunoassay systems. The bioactive tumor ACTH was neutralized by incubation with the C-terminal antiserum, indicating it has an intact C-terminal sequence of amino acids. The next several fractions from the Sephadex column contained a material, mol wt≃3,100, which was biologically inactive and had C-terminal immunoreactivity but no N-terminal or extreme N-terminal immunoreactivity. Incubation with the N-terminal 1-23 ACTH antiserum did not adsorb these C-terminal fragments, indicating they lacked an intact sequence of amino acids in this region. A smaller ACTH fragment (mol wt≃1,800 daltons) eluted in still later fractions and reacted with the extreme N-terminal antiserum but not with the N-terminal or C-terminal antisera. It had no steroidogenic activity, but appeared to have significant melanocyte-stimulating activity. It is concluded that, in addition to an ACTH similar, if not identical, to pituitary ACTH, tumors of patients with the ectopic ACTH syndrome contain both N-terminal and C-terminal ACTH fragments.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Island D. P., Liddle G. W., Fleisher N., Nicholson W. E. Radioimmunologic evidence for alpha-MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone) in human pituitary and tumor tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jan;27(1):46–52. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe K., Nicholson W. E., Liddle G. W., Island D. P., Orth D. N. Radioimmunoassay of beta-MSH in human plasma and tissues. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1609–1616. doi: 10.1172/JCI105653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM D. R., MUSSET M. V., STACK-DUNNE M. P. The Third International Standard for Corticotrophin. Bull World Health Organ. 1962;27:395–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Radioimmunoassay of ACTH in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2725–2751. doi: 10.1172/JCI105955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser G. M., Landon J. Plasma levels of immunoreactive corticotrophin in patients with Cushing's syndrome. Br Med J. 1968 Nov 30;4(5630):552–554. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5630.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser G. M., Orth D. N., Nicholson W. E., Byyny R. L., Abe K., Woodham J. P. Dissociation of the disappearance of bioactive and radioimmunoreactive ACTH from plasma in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):595–603. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecher A. S., Pugatch R. D., König M., Wasilauskas V. P., Jr, Suszkiw J. B., Sobel R. E. The hydrolytic activity in normal human and malignant tissue. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):828–831. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEDMAN M. L., FARMER T. H., MORRIS C. J. Studies on pituitary adrenocorticotrophin. 3. Identification of the oxidation-reduction centre. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:348–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0780348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demura H., West C. D., Nugent C. A., Nakagawa K., Tyler F. H. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for plasma ACTH levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Dec;26(12):1297–1302. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-12-1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Aurbach G. D. Use of polyethylene glycol to separate free and antibody-bound peptide hormones in radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):732–738. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. A. A rapid method for extracting corticotrophin from plasma. J Endocrinol. 1967 Nov;39(3):451–452. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer N., Givens J. R., Abe K., Nicholson W. E., Liddle G. W. Studies of ACTH antibodies and their reactions with inactive analogues of ACTH. Endocrinology. 1966 May;78(5):1067–1075. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-5-1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISLAND D. P., SHIMIZU N., NICHOLSON W. E., ABE K., OGATA E., LIDDLE G. W. A METHOD FOR SEPARATING SMALL QUANTITIES OF MSH AND ACTH WITH GOOD RECOVERY OF EACH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Jul;25:975–983. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-7-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSCOMB H. S., NELSON D. H. A sensitive biologic assay for ACTH. Endocrinology. 1962 Jul;71:13–23. doi: 10.1210/endo-71-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddle G. W., Givens J. R., Nicholson W. E., Island D. P. The ectopic ACTH syndrome. Cancer Res. 1965 Aug;25(7):1057–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddle G. W., Nicholson W. E., Island D. P., Orth D. N., Abe K., Lowder S. C. Clinical and laboratory studies of ectopic humoral syndromes. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:283–314. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEADOR C. K., LIDDLE G. W., ISLAND D. P., NICHOLSON W. E., LUCAS C. P., NUCKTON J. G., LUETSCHER J. A. Cause of Cushing's syndrome in patients with tumors arising from "nonendocrine" tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Jul;22:693–703. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-7-693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEY R. L., SHIMIZU N., NICHOLSON W. E., ISLAND D. P., LIDDLE G. W. CORRELATION OF PLASMA ACTH CONCENTRATION WITH ADRENOCORTICAL RESPONSE IN NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS, SURGICAL PATIENTS, AND PATIENTS WITH CUSHING'S DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1669–1677. doi: 10.1172/JCI104853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe J. G., Knight R. A., Besser G. M., Landon J., Stansfeld A. G. Tumor and plasma ACTH concentrations in patients with and without the ectopic ACTH syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1972 Jan;1(1):27–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1972.tb00375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYLVEN B., BOIS SVENSSON I. ON THE CHEMICAL PATHOLOGY OF INTERSTITIAL FLUID. I. PROTEOLYTIC ACTIVITIES IN TRANSPLANTED MOUSE TUMORS. Cancer Res. 1965 May;25:458–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M., Nicholson W. E., Orth D. N., Mitchell W. M., Liddle G. W. Differences between ectopic MSH and pituitary MSH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Sep;33(3):377–381. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-3-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., GLICK S. M., ROTH J., BERSON S. A. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF HUMAN PLASMA ACTH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Nov;24:1219–1225. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-11-1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Size heterogeneity of immunoreactive human ACTH in plasma and in extracts of pituitary glands and ACTH-producing thymoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90620-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


