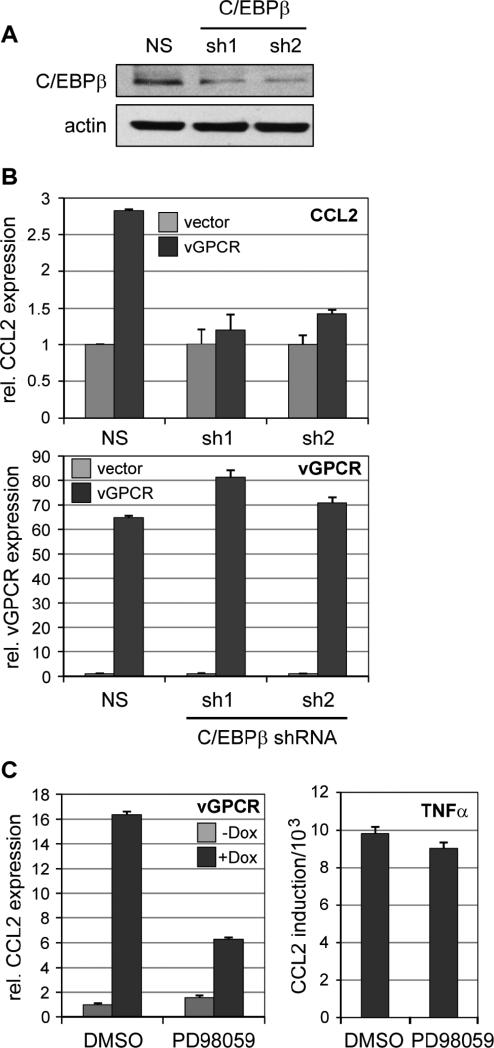
Figure 5.
C/EBPβ as a mediator of CCL2 induction by vGPCR. (A) Immunoblot-based analysis of C/EBPβ depletion in TIME-vGPCR cells transduced with either of two lentiviral vector-delivered shRNAs specific for C/EBPβ mRNA (sh1, sh2) as compared with control cells transduced with non-silencing (NS) shRNA. Actin antibody was used as a protein load control. (B) Dependency of vGPCR-induced CCL2 expression on C/EBPβ. NS or C/EBPβ shRNA-transduced TIME cells infected subsequently with vGPCR-encoding or empty lentivirus vectors were assessed by qRT-PCR analysis of extracted RNA for CCL2 mRNA expression. The data (top panel) revealed dependence of vGPCR-mediated induction of CCL2 on C/EBPβ expression, providing evidence of direct involvement of the transcription factor in this response. Expression of vGPCR in receptor expression vector-transduced cells was verified by qRT-PCR (bottom panel). Error bars indicate deviation from mean values obtained from duplicate PCR reactions. (C) Involvement of MAPK signaling in vGPCR-mediated CCL2 induction. CCL2 mRNA expression was quantified by qRT-PCR, as before, in TIME-vGPCR cells mock treated or treated with Dox in the absence (DMSO) or presence of MEK (ERK kinase) inhibitor PD98059 (50 μM). The results (left) demonstrated substantial inhibition of CCL2 induction in the presence of PD98059. A parallel analysis of CCL2 induction by TNFα (10 ng/ml), which activates CCL2 via NF-κB signaling, showed no inhibition by the MEK inhibitor, thereby indicating the absence of non-specific effects mediated by drug treatment.