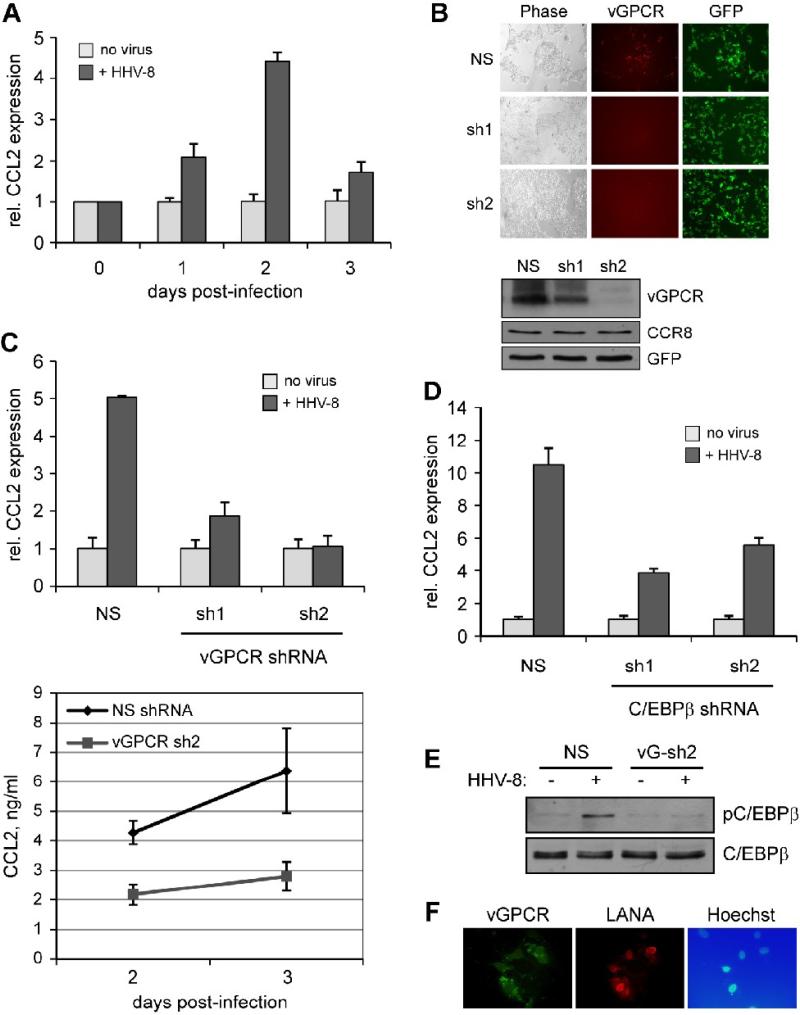
Figure 6.
Relevance of vGPCR and C/EBPβ to CCL2 induction in the context of HHV-8 infection. (A) Induction of CCL2 by HHV-8 infection. Cultures of TIME cells were infected with BCBL-1 cell-derived HHV-8 virus (see Materials and Methods). Infected and mock infected cultures were harvested at different times (0 to 3 days) after infection/mock infection, and extracted RNA analyzed by qRT-PCR to quantify relative mRNA levels (normalized to 18S RNA). (B) Testing of vGPCR-directed shRNAs for vGPCR depletion. First, two different vGPCR-specific shRNAs, cloned into GFP+ lentiviral vectors, were tested by cotransfection with a vGPCR-RFP expression plasmid to determine their efficacies. Visualization of RFP by UV microscopy verified that each shRNA effectively depleted vGPCR-RFP expression, relative to non-silencing (NS) control. RFP fields for the vGPCR shRNAs (sh1, sh2) have been deliberately overexposed to demonstrate very weak expression of vGPCR-RFP. vGPCR depletion by the receptor-directed lentiviral-cloned shRNAs was further tested using immunoblotting of transfected cell extracts; the results demonstrated significant depletion of vGPCR by both sh1 and sh2. (C) Stably-transduced TIME cultures expressing the vGPCR-specific shRNAs or NS control were infected or mock-infected with HHV-8 and cells harvested at 48 h for RNA extraction and qRT-PCR analysis of CCL2 mRNA and media collected at 48 h and 72 h for ELISA detection and quantitation of secreted CCL2 protein. In cells expressing the vGPCR shRNAs, the ability of HHV-8 de novo infection to induce CCL2 mRNA and protein expression was markedly reduced. (D) A similar, qRT-PCR-based experiment was undertaken in C/EBPβ-depleted TIME cells (Fig.5A). These cells, in contrast to NS-transduced TIME cells, were deficient in their ability to support CCL2 induction upon HHV-8 infection, confirming the importance of C/EBPβ for this response. (E) The role of vGPCR in C/EBPβ activation in HHV-8 infected cells was verified by comparison of C/EBPβ phosphorylation (on Thr235) in the absence and presence of shRNA-mediated vGPCR depletion. Western blotting of extracts from NS (control) and vGPCR shRNA-transduced cells revealed depleted phospho-C/EBPβ for the latter. (F) Detection of HHV-8 infection and vGPCR expression in de novo infected TIME cultures. TIME cultures, infected using identical conditions as before, were analyzed by IFA for detection of latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) and vGPCR. The results revealed high infection efficiency (LANA+) and widespread expression of vGPCR in this population, consistent with functional data indicating the central role of vGPCR in CCL2 induction by de novo HHV-8 infection. In panels A, C and D, error bars indicate deviations of values from duplicate PCR reactions, or duplicate ELISA tests (panel C, bottom).