Abstract
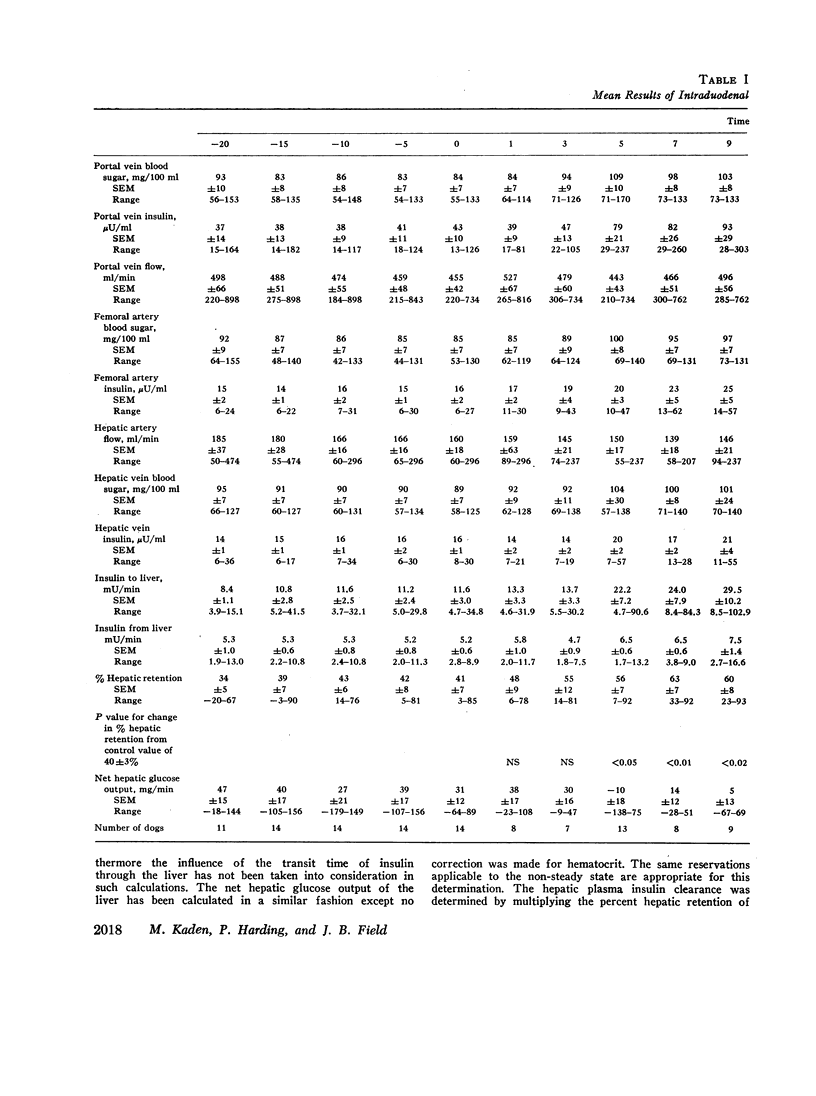
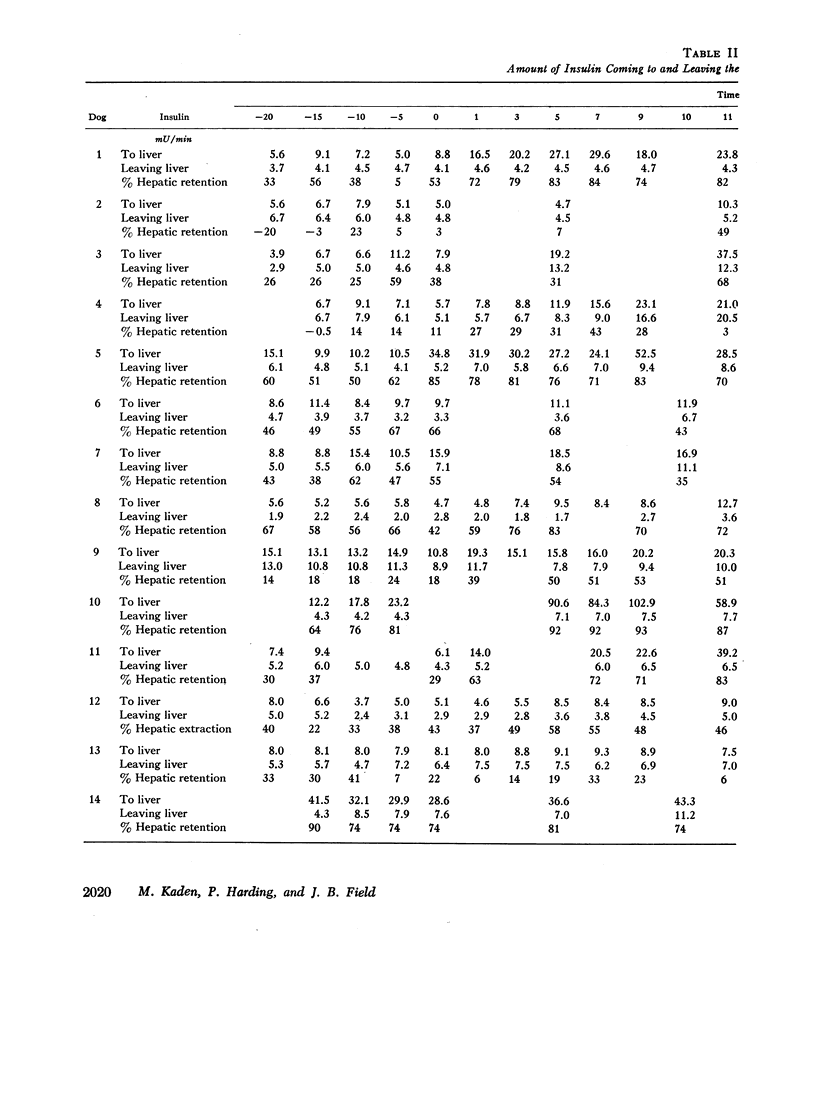
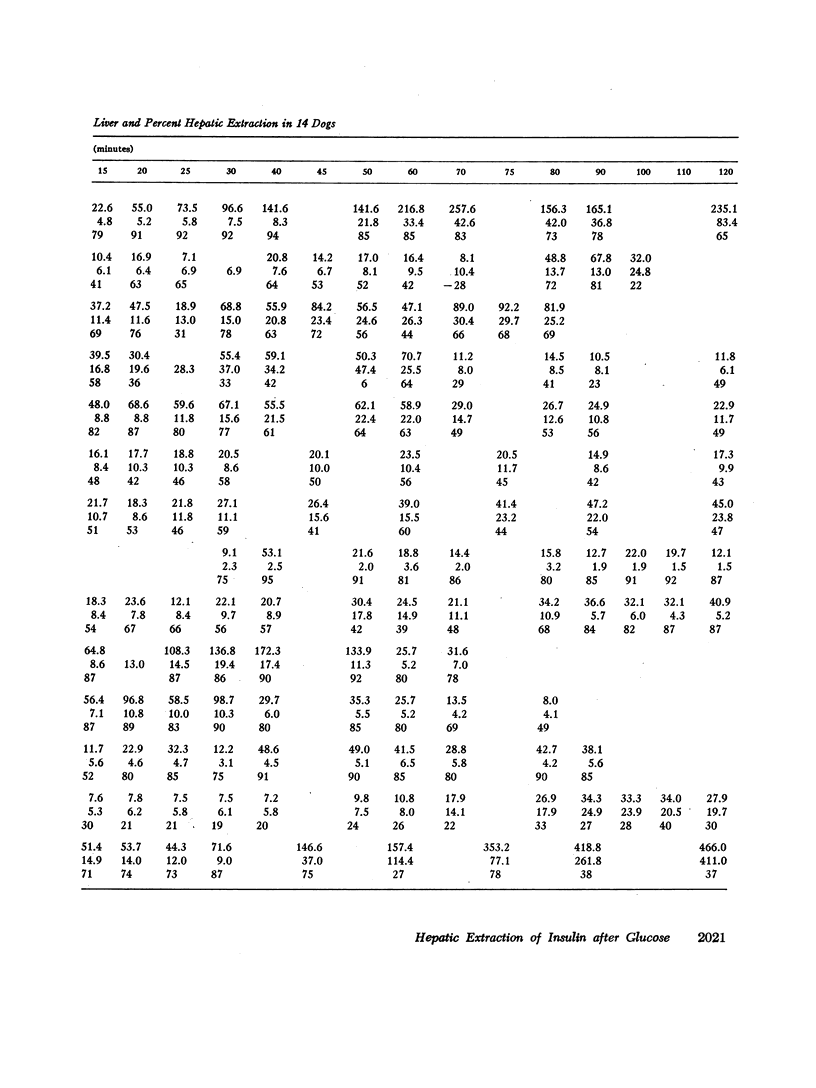
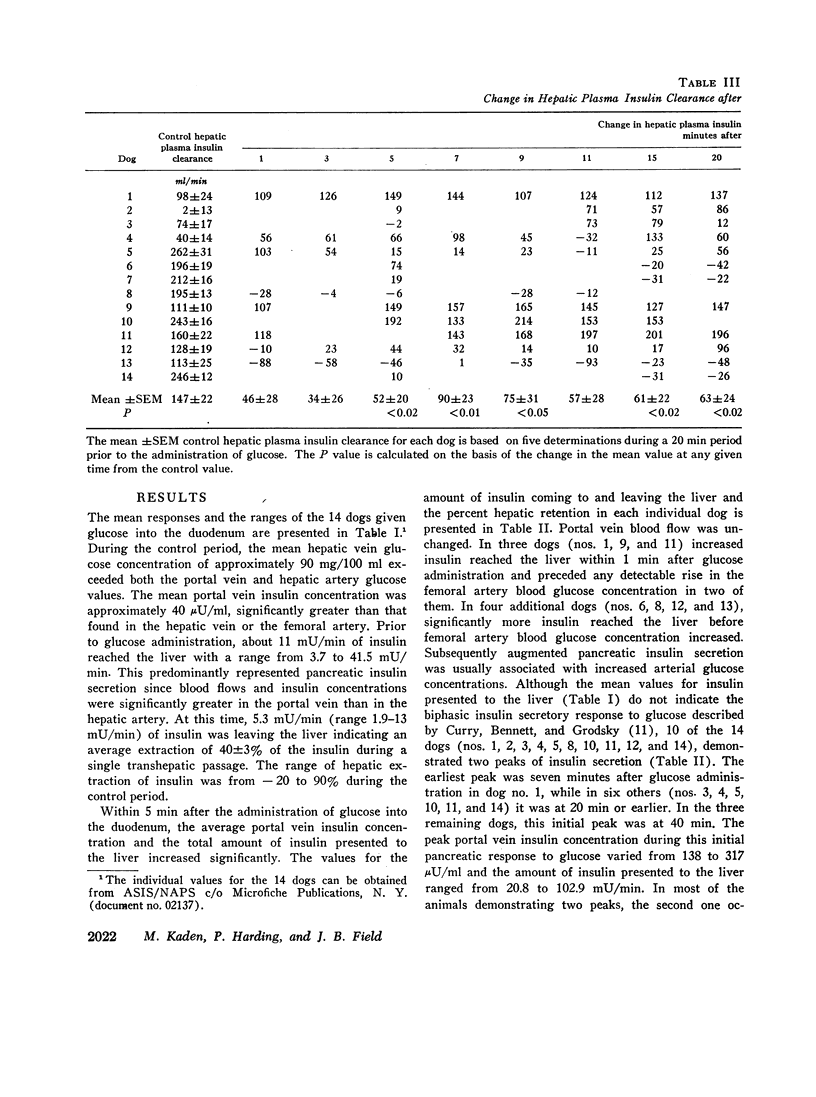
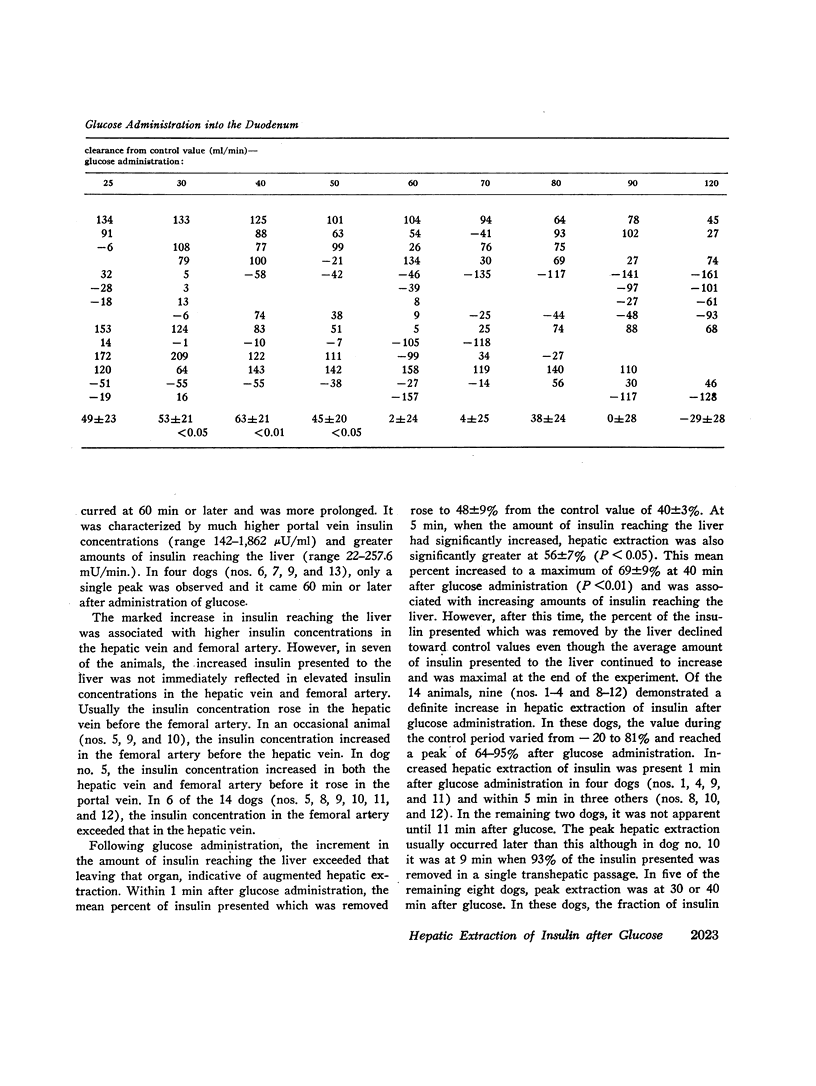
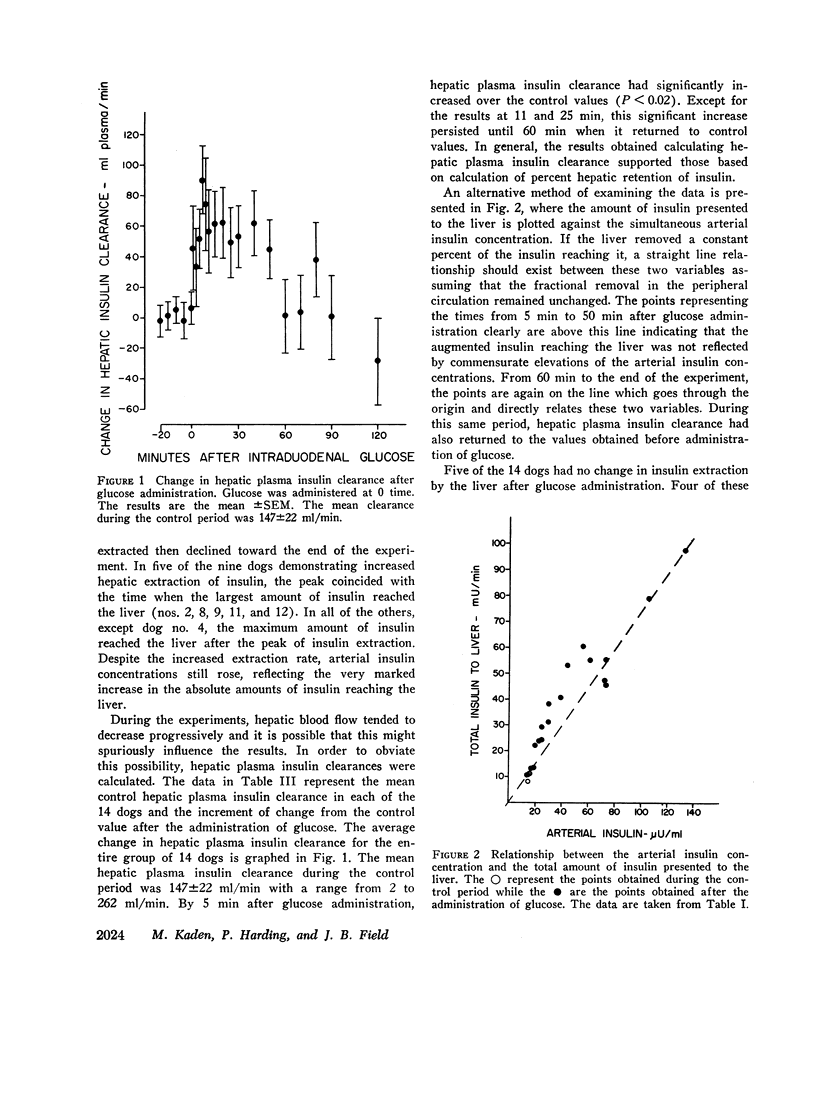
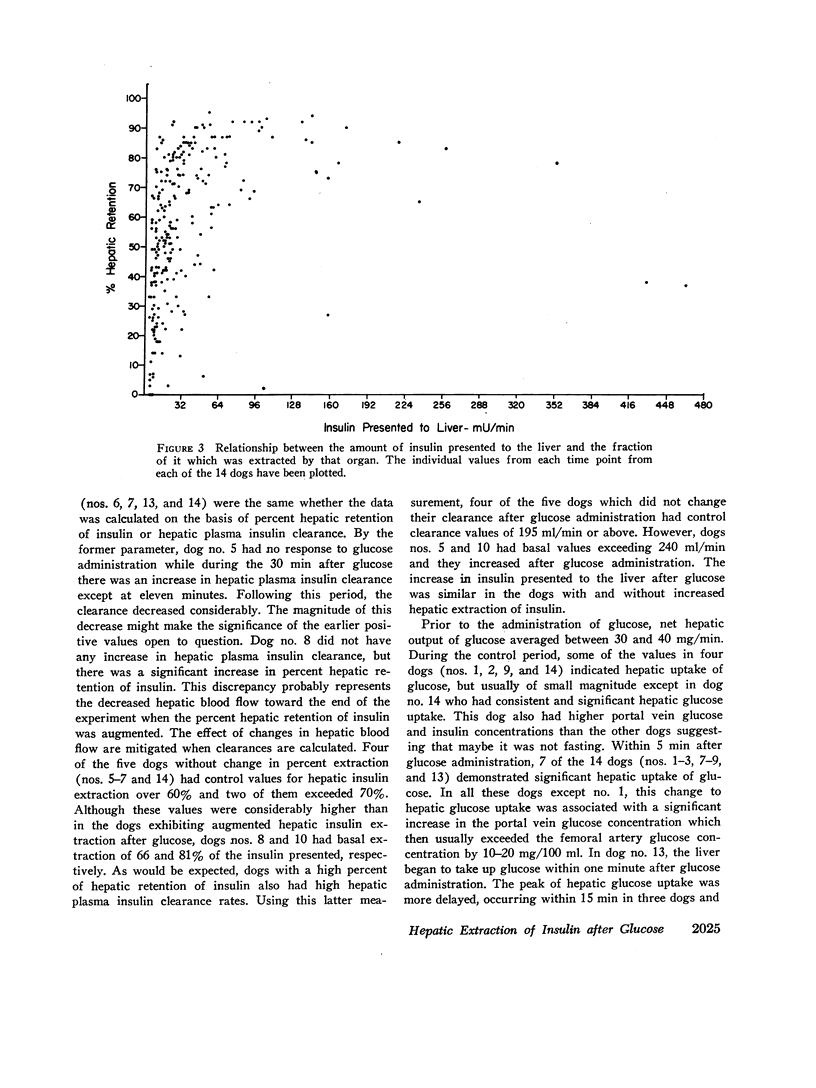
Extraction of insulin by the liver after administration of glucose in the duodenum has been studied in fourteen anesthetized dogs. Plasma insulin and glucose were measured in the portal vein hepatic vein and hepatic artery. During the control period 40±3% of the approximately 11 mU of insulin presented to the liver/min was removed during a single transhepatic passage. Within 5 min after glucose administration, the amount of insulin reaching the liver increased significantly. In some animals this increase preceded any significant increase in the glucose concentration of the femoral artery. After glucose administration, hepatic extraction of insulin remained unchanged in five animals and rose significantly in nine. In five of the latter animals, the increase may have been more apparent than real due to nonrepresentative sampling of hepatic venous blood. However, for the whole group of animals, comparison of arterial insulin levels with the amount of insulin delivered to the liver suggested a transient increase in insulin extraction between 5 and 50 min after glucose administration. In no animal was there a decrease in the proportion of insulin extracted by the liver after glucose administration. The results indicate that the extraction process is not saturable at physiological insulin levels. Prior to glucose administration, net hepatic glucose output averaged between 30 and 40 mg/min. After glucose administration, the liver began to take up glucose and there was a significant correlation between hepatic glucose uptake and the amount of insulin reaching the liver. However, since the amount of glucose presented to the liver also increased, it is not established that the insulin was responsible for the change in hepatic carbohydrate metabolism.
The data demonstrate an increase in the absolute amount of insulin extracted by the liver after glucose administration and an important role for the liver in regulating peripheral insulin concentrations.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal and peripheral vein immunoreactive insulin concentrations before and after glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1970 May;19(5):302–306. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.5.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMBES B., ADAMS R. H., STRICKLAND W., MADISON L. L. The physiological significance of the secretion of endogenous insulin into the portal circulation. IV. Hepatic uptake of glucose during glucose infusion in non-diabetic dogs. J Clin Invest. 1961 Sep;40:1706–1718. doi: 10.1172/JCI104393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata K., Hetenyi G., Jr, Vranic M. Effect of D-glucose or D-ribose on the turnover of glucose in pancreatectomized dogs maintained on a matched intraportal infusion of insulin. Diabetes. 1969 Dec;18(12):820–827. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.12.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa Y., Kuzuya T., Ide T. Insulin output via the pancreatic vein and plasma insulin response to glucose in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1968 Sep;215(3):620–626. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.3.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa Y., Kuzuya T., Ide T., Kosaka K. Plasma insulin responses to glucose in femoral, hepatic, and pancreatic veins in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1966 Aug;211(2):442–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.2.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY I. A. THE METABOLISM OF INSULIN. Diabetes. 1964 May-Jun;13:225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E., TIETZE F., STETTEN D., Jr Metabolism of insulin-I 131; studies in isolated, perfused rat liver and hindlimb preparations. Diabetes. 1959 Jul-Aug;8(4):307–314. doi: 10.2337/diab.8.4.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. L. Role of insulin in the hepatic handling of glucose. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport A. M., Davidson J. K., Kawamura T., Lin B. J., Zelin S., Henderson J., Haist R. E. Quantitative determination of insulin output following an intravenous glucose tolerance test in the dog. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1968 May;46(3):373–381. doi: 10.1139/y68-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMOLS E., RYDER J. A. Studies on tissue uptake of insulin in man using a differential immunoassay for endogenous and exogenous insulin. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:2092–2102. doi: 10.1172/JCI104435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvers A., Farquhar J. W., Lerner R. L., Reaven G. M. Evaluation of the dog as an experimental model for the study of insulin distribution and degradation in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Feb;75(2):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. P., Farquhar J. W., Silvers A., Reaven G. M. Insulin delivery rate into plasma in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):1947–1957. doi: 10.1172/JCI105884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. C., Grayburn J. A., Newman G. B., Nabarro J. D. Measurement of the insulin delivery rate in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):279–286. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranic M., Wrenshall G. A. Matched rates of insulin infusion and secretion and concurrent tracer-determined rates of glucose appearance and disappearance in fasting dogs. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1968 May;46(3):383–390. doi: 10.1139/y68-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. R., Sussman K. E. Plasma insulin after diversion of portal and pancreatic venous blood to vena cava. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Apr;22(4):808–812. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.4.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. H. Measurement of insulin secretion. A review of current methods. Diabetes. 1968 Oct;17(10):641–645. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.10.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



