Abstract
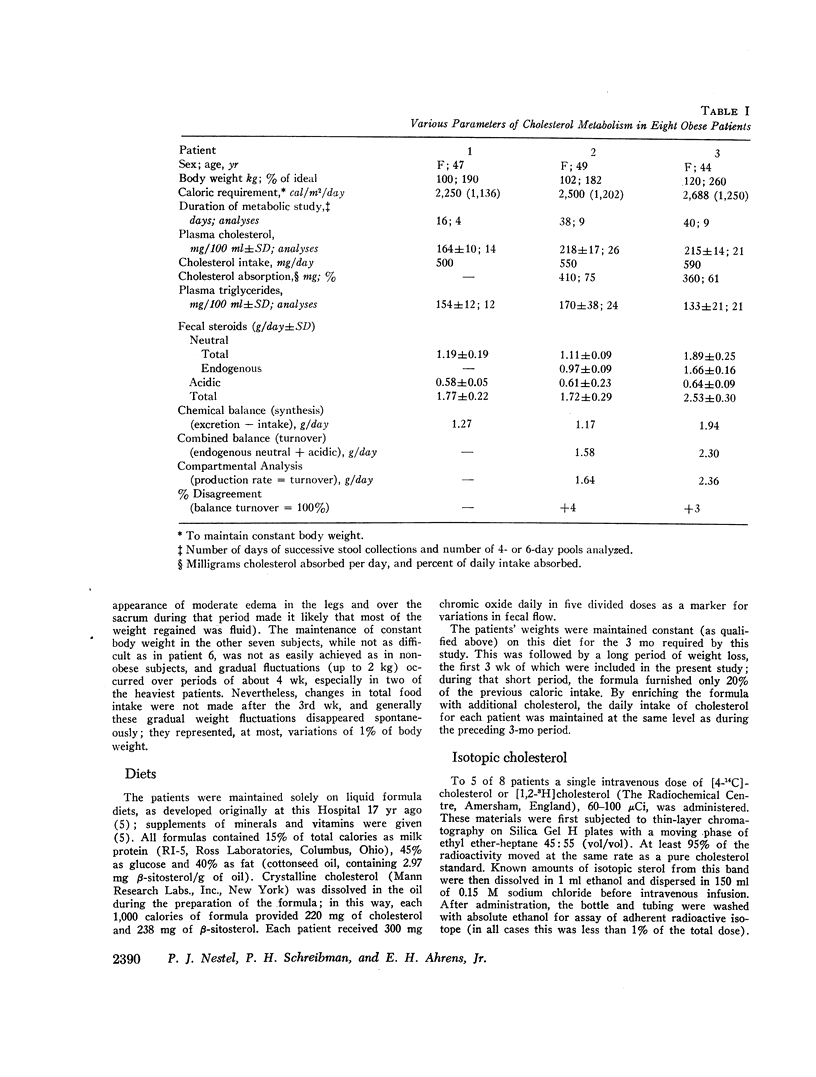
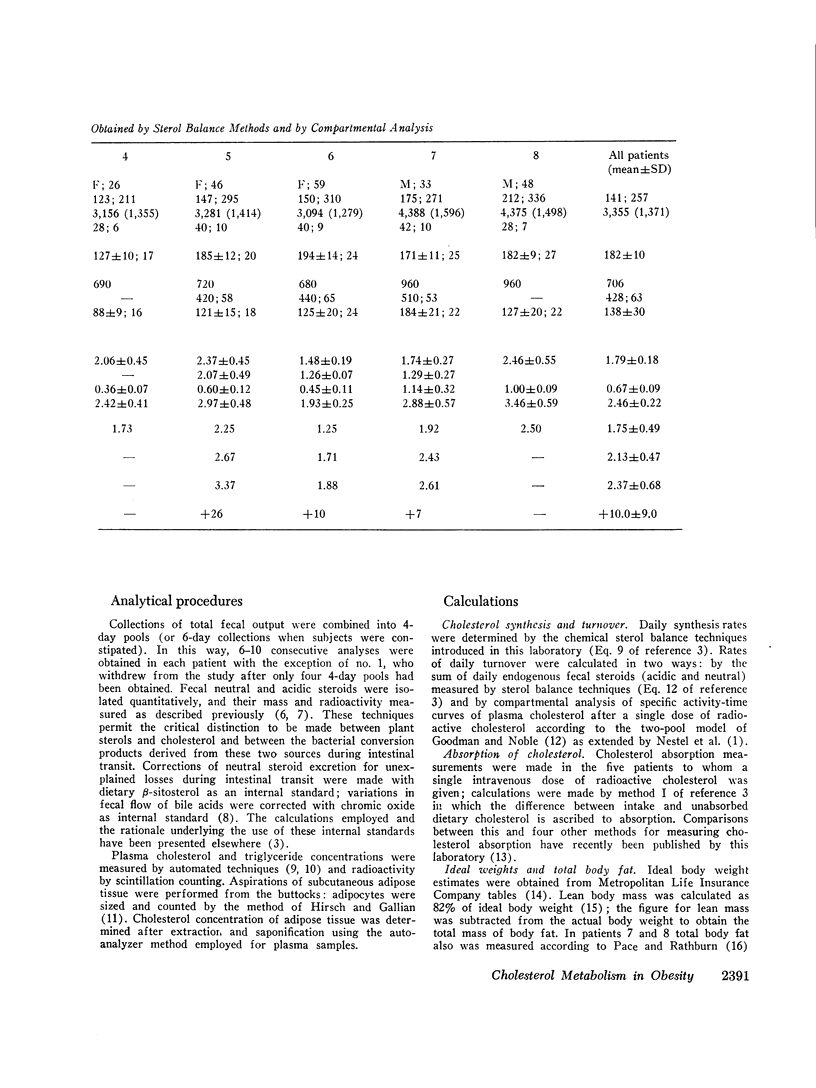
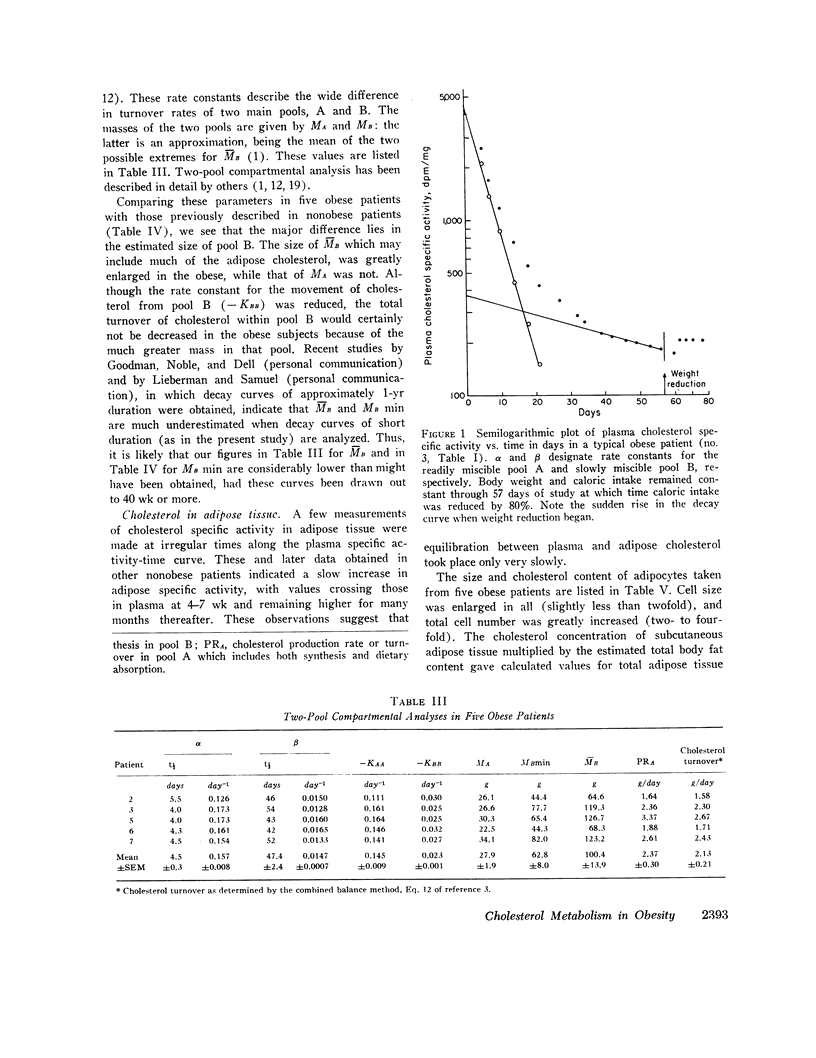
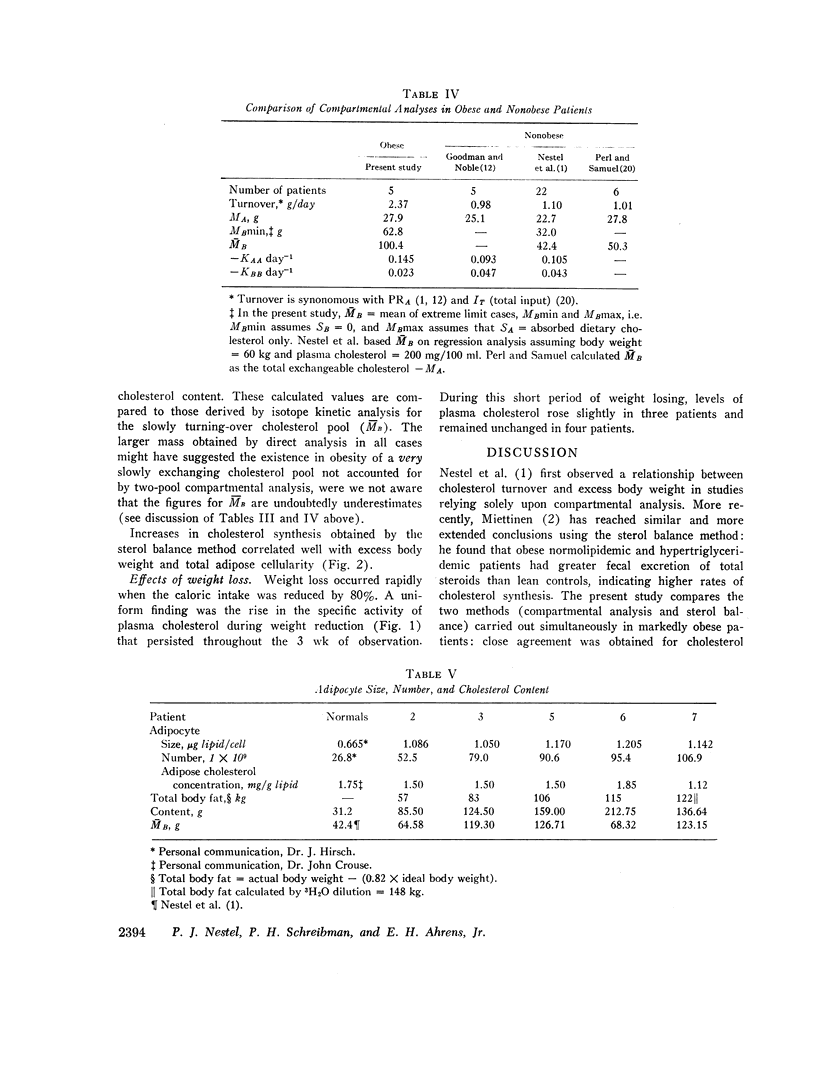
An experiment was undertaken to test whether in severe obesity cholesterol production rates obtained by isotope kinetic analysis (two-pool compartmental analysis) are comparable to those measured by chemical sterol balance techniques. Eight severely obese but normocholesterolemic patients were studied by the balance method, and five of these eight were studied by compartmental analysis. Cholesterol turnover was 10% higher by compartmental analysis.
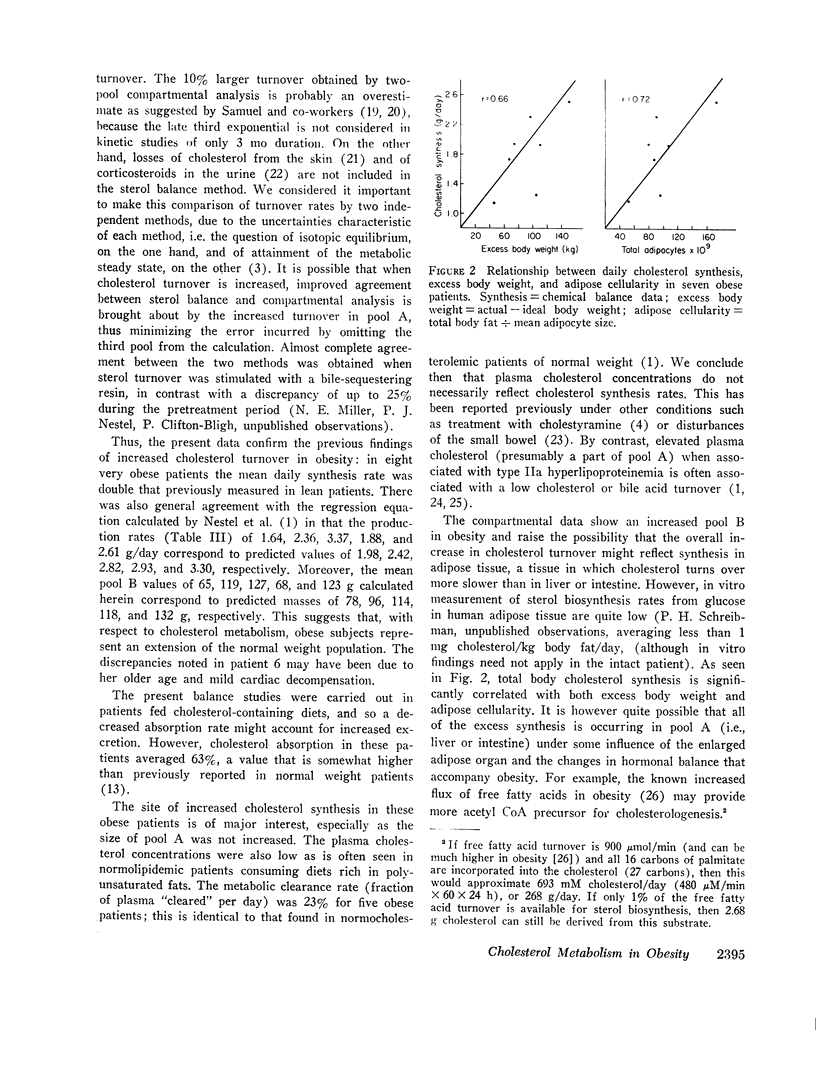
In the entire group of eight patients cholesterol turnover was greater than twice that found previously in nonobese patients studied under similar conditions with bile acids and neutral sterols both participating in the increase. This increment was directly related to excess body fat and to adipose cellularity, with correlation co-efficients of 0.66 and 0.72, respectively. The amount of cholesterol in the slowly turning over pool B was related to degree of adiposity, but that in plasma and in pool A did not differ from values in nonobese patients.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya A. K., Connor W. E., Spector A. A. Excretion of sterols from the skin of normal and hypercholesterolemic humans. Implications for sterol balance studies. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2060–2070. doi: 10.1172/JCI107012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski A., Delcroix C., Levin S. Metabolism of adrenal cholesterol in man. I. In vivo studies. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1664–1678. doi: 10.1172/JCI106968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor W. E., Witiak D. T., Stone D. B., Armstrong M. L. Cholesterol balance and fecal neutral steroid and bile acid excretion in normal men fed dietary fats of different fatty acid composition. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1363–1375. doi: 10.1172/JCI106102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Simmonds W. J., Ahrens E. H. Usefulness of chromic oxide as an internal standard for balance studies in formula-fed patients and for assessment of colonic function. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):127–138. doi: 10.1172/JCI105703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Noble R. P. Turnover of plasma cholesterol in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):231–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI105719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr Measurements of cholesterol turnover, synthesis, and absorption in man, carried out by isotope kinetic and sterol balance methods. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):91–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G. Interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in man: comparative effects of cholestyramine and ileal exclusion on cholesterol metabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):94–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr The effects of unsaturated dietary fats on absorption, excretion, synthesis, and distribution of cholesterol in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1135–1152. doi: 10.1172/JCI106329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J., Gallian E. Methods for the determination of adipose cell size in man and animals. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kottke B. A. Difference in bile acid excretion. Primary hypercholesteremia compared to combined hypercholesteremia and hypertriglyceridemia. Circulation. 1969 Jul;40(1):13–20. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.40.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIETTINEN T. A., AHRENS E. H., Jr, GRUNDY S. M. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL DIETARY AND FECAL NEUTRAL STEROIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:411–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A. Cholesterol production in obesity. Circulation. 1971 Nov;44(5):842–850. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.44.5.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A. Detection of changes in human cholesterol metabolism. Ann Clin Res. 1970 Dec;2(4):300–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A. Fecal steroid excretion during weight reduction in obese patients with hyperlipidemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Feb;19(2):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. B., Frantz I. D., Jr, Buchwald H. Changes in cholesterol pool size, turnover rate, and fecal bile acid and sterol excretion after partial ileal bypass in hypercholesteremic patients. Surgery. 1969 Jan;65(1):98–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Whyte H. M., Goodman D. S. Distribution and turnover of cholesterol in humans. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):982–991. doi: 10.1172/JCI106079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Whyte H. M. Plasma free fatty acid and triglyceride turnover in obesity. Metabolism. 1968 Dec;17(12):1122–1128. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perl W., Samuel P. Input-output analysis for total input rate and total traced mass of body cholesterol in man. Circ Res. 1969 Aug;25(2):191–199. doi: 10.1161/01.res.25.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintão E., Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr An evaluation of four methods for measuring cholesterol absorption by the intestine in man. J Lipid Res. 1971 Mar;12(2):221–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel P., Perl W., Holtzman C. M., Rochman N. D., Lieberman S. Long-term kinetics of serum and xanthoma cholesterol radioactivity in patients with hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):266–278. doi: 10.1172/JCI106811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


