Abstract
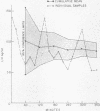
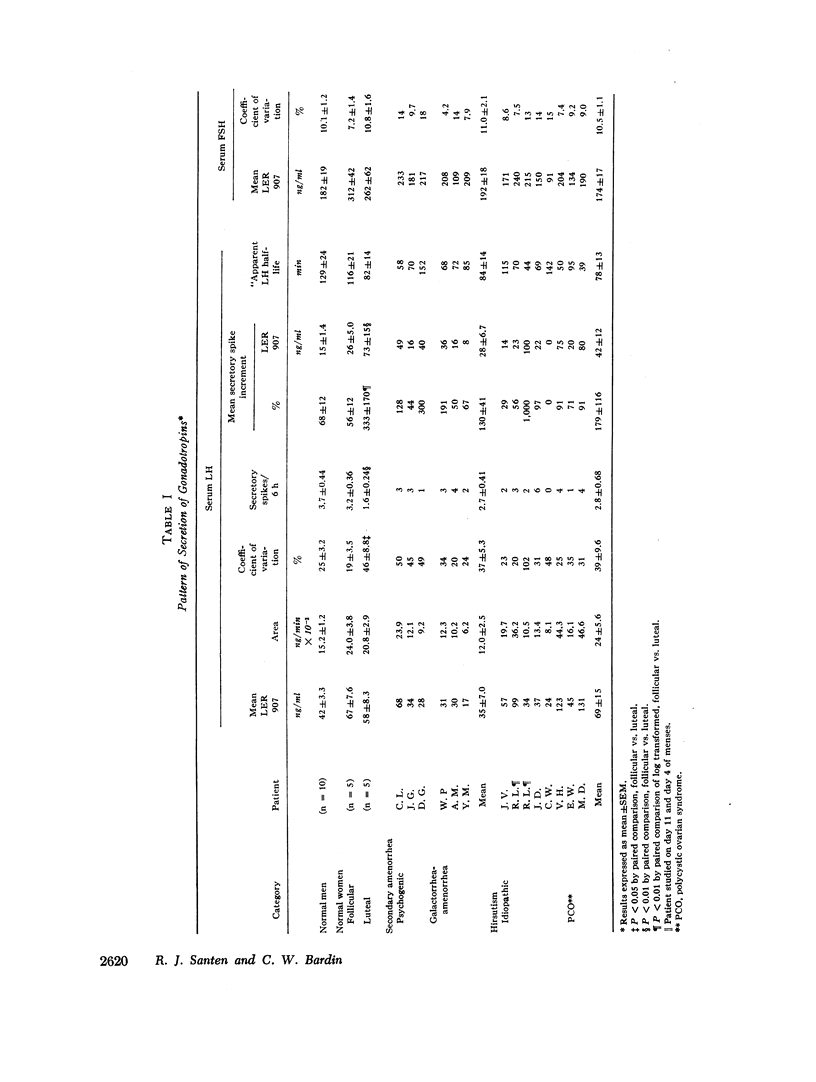
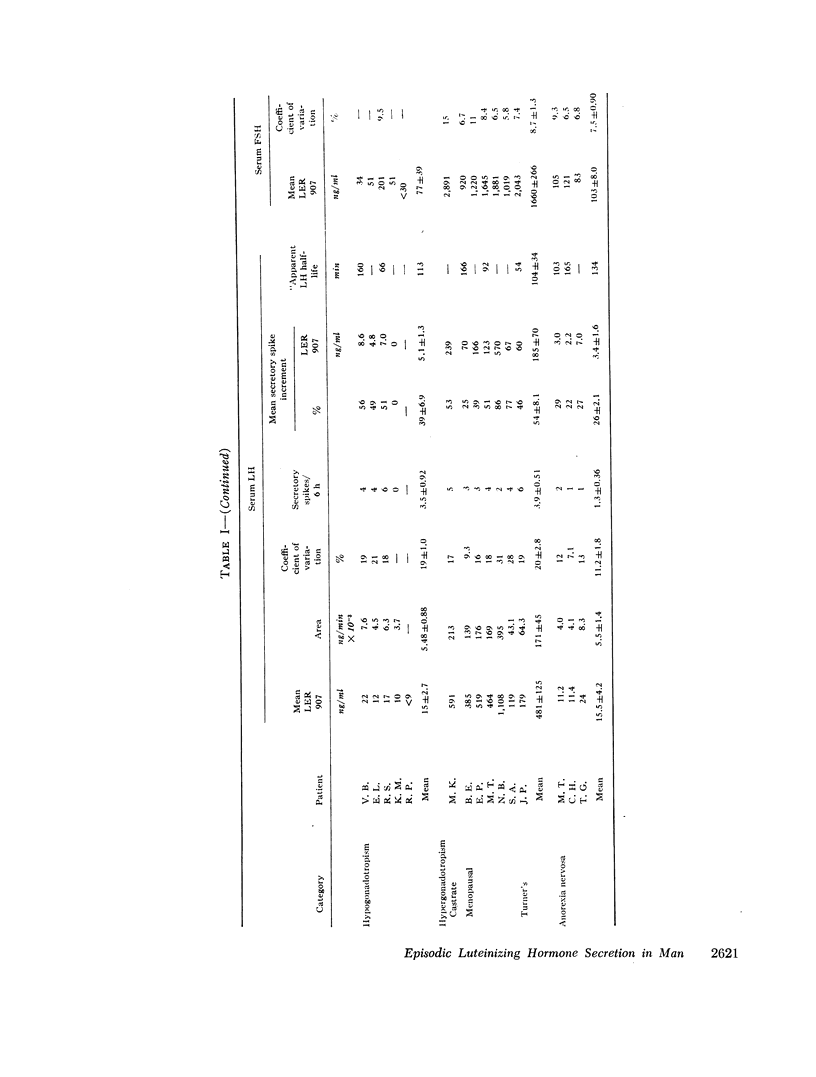
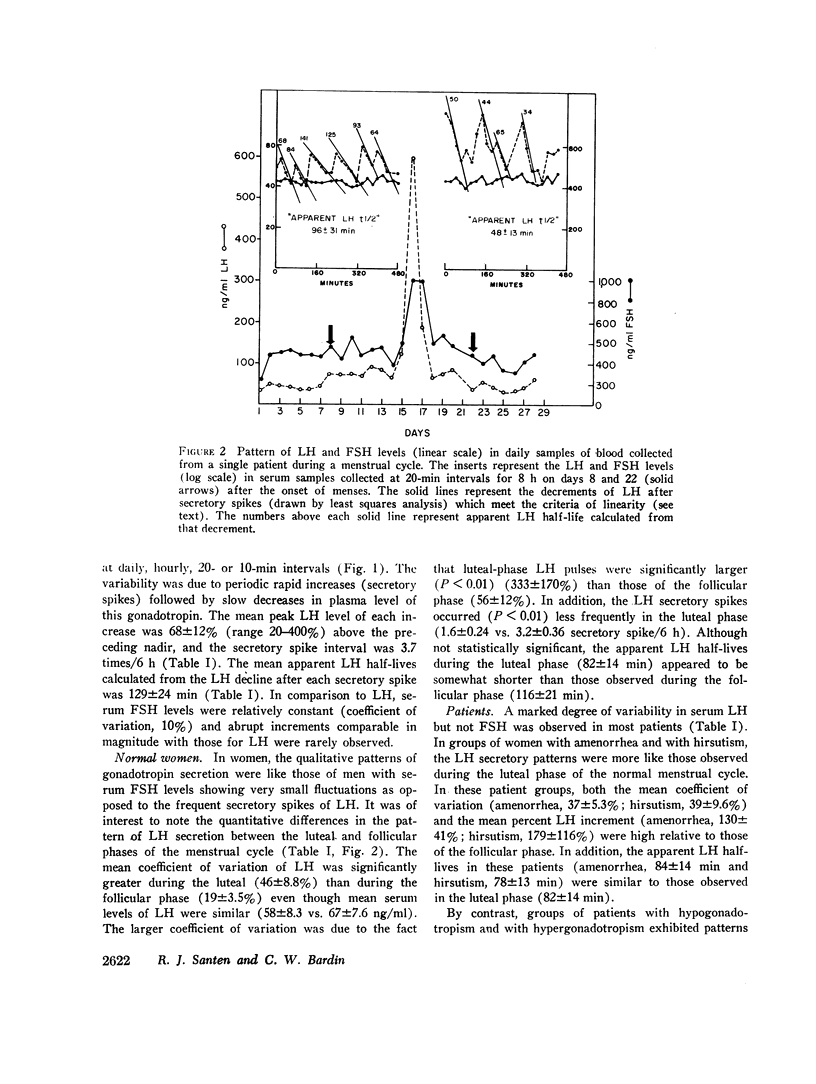
The demonstration that luteinizing hormone (LH) release from the pituitary is episodic rather than constant raises fundamental questions regarding the physiologic control of pulsatile LH secretion and its possible alteration in patients with gonadal disorders. To evaluate this mode of LH secretion, quantitative means of analyzing LH pulse amplitude, frequency, shape, and area were established and utilized to study normal subjects and patients with disorders of gonadotropin secretion. Similar patterns of LH secretion were observed in normal men, in women during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, and in patients with hyper- and hypogonadotropism, hirsuitism, and amenorrhea (mean pulse amplitude 39-179% from nadir to peak, frequency 2.7-3.9 secretory spikes/6 h). These observations suggested that the pattern of LH secretion is similar in both normal individuals and in those with a variety of pathologic conditions. By contrast, the pattern of pulsatile secretion appeared to differ in the following conditions. LH pulses of higher amplitude (333±170%) and lower frequency (1.6±0.24 SEM/6 h) characterized the secretory patterns of women during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, suggesting that gonadal steroids may modulate LH pulses. LH pulses of low amplitude (26±2.1%) and frequency (1.3±0.36/6 h) were observed in women with anorexia nervosa.
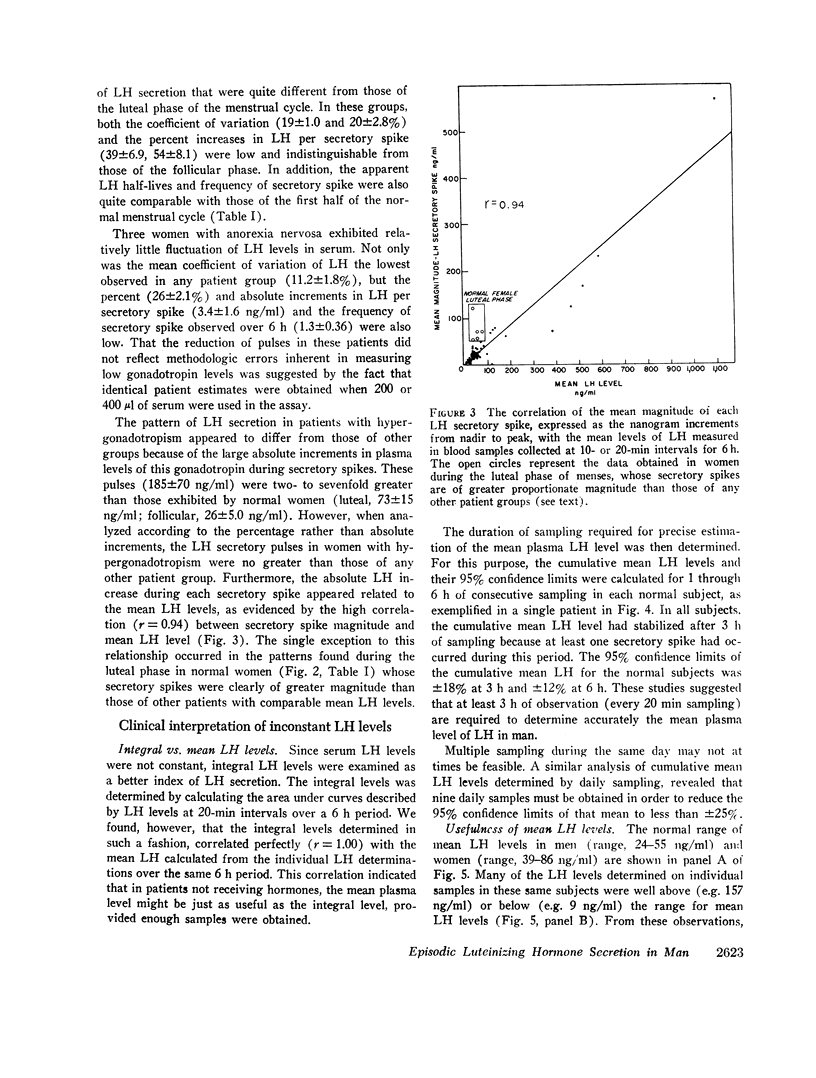
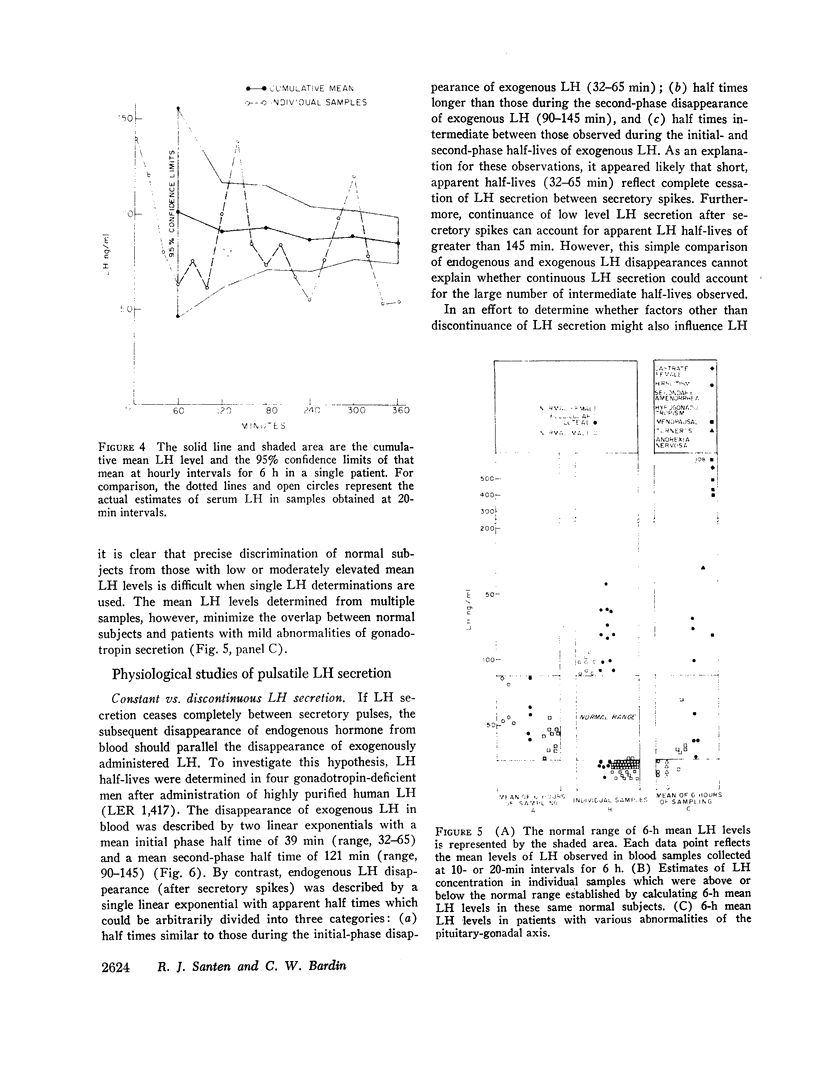
Either integrated LH levels or a mean LH level determined from multiple samples provided a more accurate reflection of gonadotropin secretion than the use of single LH measurements. With multiple sampling over 6 h, it was possible to reduce the 95% confidence limit of LH estimates from ±50-90 to ±12%. This allowed normal subjects to be distinguished from patients with low or moderately elevated LH levels in whom gonadotropin levels in single samples were often in the “normal range.”
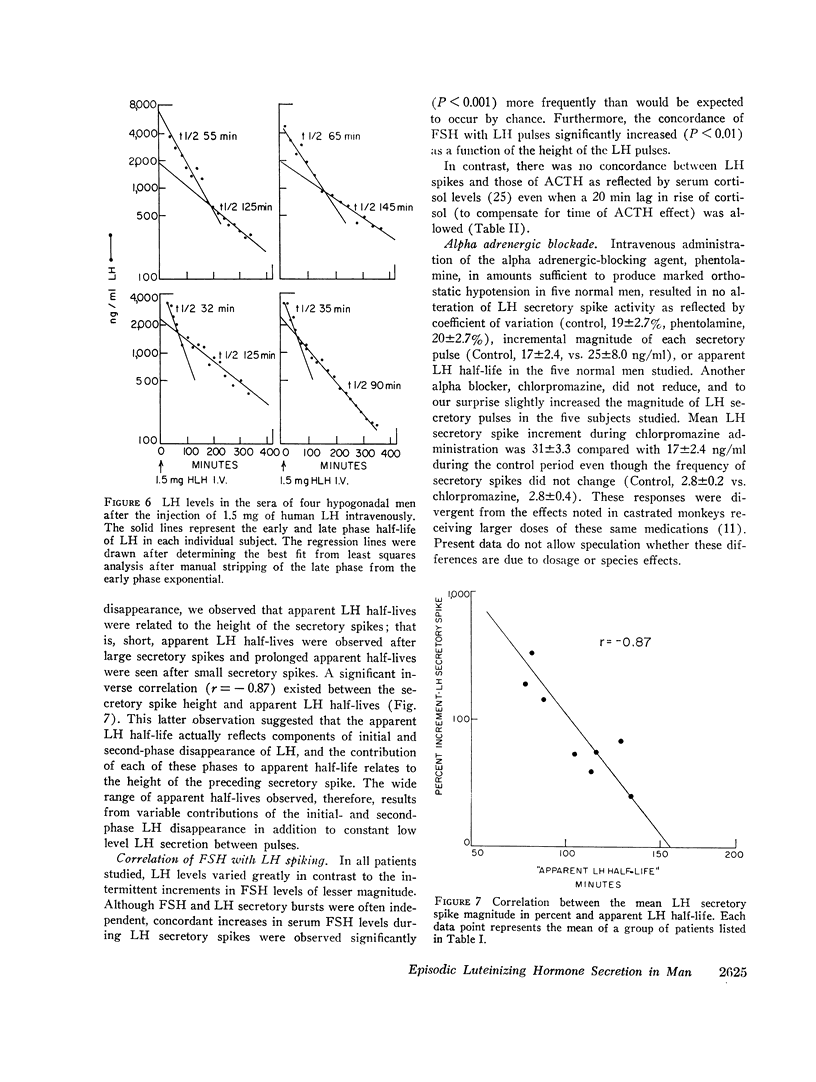
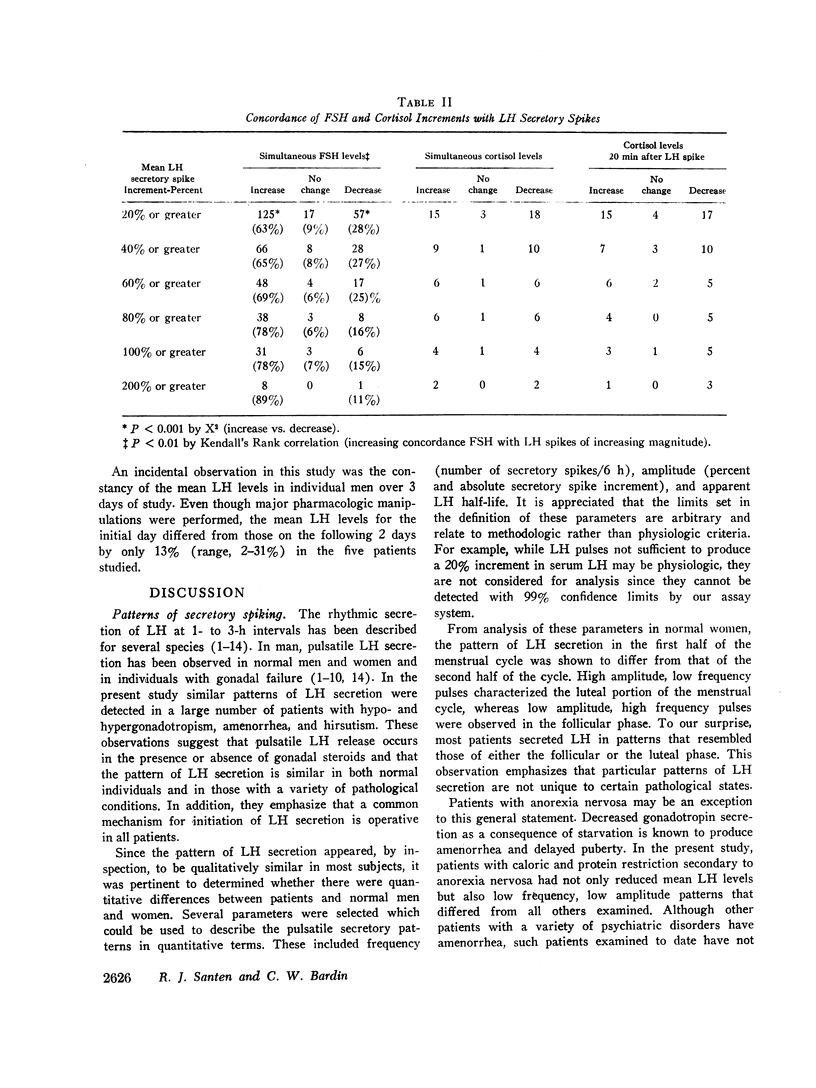
Several aspects of the physiologic control of pulsatile LH secretion were studied. The concordance of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) with LH pulses progressively increased as LH pulse height increased (P < 0.01) suggesting possible hypothalamic mediation of gonadotropin pulses. Measurement of the “apparent half-life” of LH after secretory spikes revealed half times of 34-233 min. It is likely that this variability was attributable to at least two phenomena: (a) constant low level LH secretion that continued after certain secretory episodes but not others; (b) variable mixing of newly secreted LH into at least two pools. The alpha adrenergic-blocking agents, chlorpromazine and phentolamine, failed to block LH secretory spikes at doses sufficient to result in a 30 mm drop in systolic blood pressure in normal men.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G. E., Swerdloff R., Tulchinsky D., Odell W. D. Radioimmunoassay of plasma progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):619–624. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardin C. W., Lipsett M. B. Testosterone and androstenedione blood production rates in normal women and women with idiopathic hirsutism or polycystic ovaries. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):891–902. doi: 10.1172/JCI105588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Radioimmunoassay of ACTH in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2725–2751. doi: 10.1172/JCI105955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya A. N., Dierschke D. J., Yamaji T., Knobil E. The pharmacologic blockade of the circhoral mode of LH secretion in the ovariectomized rhesus monkey. Endocrinology. 1972 Mar;90(3):778–786. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-3-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyar R., Finkelstein J., Roffwarg H., Kapen S., Weitzman E., Hellman L. Synchronization of augmented luteinizing hormone secretion with sleep during puberty. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 21;287(12):582–586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209212871203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyar R., Perlow M., Hellman L., Kapen S., Weitzman E. Twenty-four hour pattern of luteinizing hormone secretion in normal men with sleep stage recording. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jul;35(1):73–81. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay V. L., Sheth N. A. Evidence for a periodic release of LH in castrated male and female rats. Endocrinology. 1972 Jan;90(1):158–162. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-1-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job J. C., Garnier P. E., Chaussain J. L., Milhaud G. Elevation of serum gonadotropins (LH and FSH) after releasing hormone (LH-RH) injection in normal children and in patients with disorders of puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Sep;35(3):473–476. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-3-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jubiz W., Meikle A. W., West C. D., Tyler F. H. Single-dose metyrapone test. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Mar;125(3):472–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. T., Ossowski R., Fogel M., Allen W. Lack of circaidan periodicity of human serum FSH and LH levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Oct;35(4):619–623. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-4-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY B. P., ENGELBERG W., PATTEE C. J. Simple method for the determination of plasma corticoids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Mar;23:293–300. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Rabinowitz D., Riggs L., Burgess J. A., Rimoin D. L., McKusick V. A. Plasma growth hormone after arginine infusion. Clinical experiences. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 23;276(8):434–439. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702232760803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley A. R., Jr, Jaffe R. B. Regulation of human gonadotropins. X. Episodic fluctuation of LH during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):962–969. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhaud G., Rivaille P., Garnier P., Chaussain J. L., Binet E., Job J. C. Synthèse de la LH-RH et effet sélectif sur la libération de l'hormone lutéotrophique chez l'homme adulte. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Nov 15;273(20):1858–1861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada E. Familial study of hirsutism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Nov;31(5):556–564. doi: 10.1210/jcem-31-5-556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naftolin F., Yen S. S., Tsai C. C. Rapid cycling of plasma gonadotrophins in normal men as demonstrated by frequent sampling. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 22;236(64):92–93. doi: 10.1038/newbio236092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nankin H. R., Troen P. Overnight patterns of serum luteinizing hormone in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Nov;35(5):705–710. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-5-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nankin H. R., Troen P. Repetitive luteinizing hormone elevations in serum of normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Sep;33(3):558–560. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-3-558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr A receptor mechanism for the inhibition of insulin release by epinephrine in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):86–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI105514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root A., DeCherney A., Russ D., Duckett G., Garcia C. R., Wallach E. Epidosic secretion of luteinizing and follicle stimulating hormones in agonadal and hypogonadal adolescents and adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Nov;35(5):700–704. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-5-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. T., Cargille C. M., Lipsett M. B., Rayford P. L., Marshall J. R., Strott C. A., Rodbard D. Pituitary and gonadal hormones in women during spontaneous and induced ovulatory cycles. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:1–62. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. T., Kales A., Adler R., Fagan T., Odell W. Gonadotropin secretion during sleep in normal adult men. Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):196–198. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santen R. J., Leonard J. M., Sherins R. J., Gandy H. M., Paulsen C. A. Short- and long-term effects of clomiphene citrate on the pituitary-testicular axis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):970–979. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. P., Dahlen H. G. Studies with synthetic LH-releasing hormone in the human. I. Continuous recording of plasma gonadotropins in women following intravenous LRH. Life Sci I. 1972 Jul 1;11(13):623–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaji T., Dierschke D. J., Bhattacharya A. N., Knobil E. The negative feedback control by estradiol and progesterone of LH secretion in the ovariectomized rhesus monkey. Endocrinology. 1972 Mar;90(3):771–777. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-3-771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. S., Rebar R., Van den Berg G., Naftolin F., Ehara Y., Engblom S., Ryan K. J., Benirschke K., Rivier J., Amoss M. Synthetic luteinizing hormone-releasing factor. A potent stimulator of gonadotropin release in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jun;34(6):1108–1111. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-6-1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. S., Tsai C. C., Naftolin F., Vandenberg G., Ajabor L. Pulsatile patterns of gonadotropin release in subjects with and without ovarian function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Apr;34(4):671–675. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-4-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. S., Tsai C. C., Vandenberg G., Rebar R. Gonadotropin dynamics in patients with gonadal dysgenesis: a model for the study of gonadotropin regulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Dec;35(6):897–904. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-6-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. S., VandenBerg G., Rebar R., Ehara Y. Variation of pituitary responsiveness to synthetic LRF during different phases of the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Dec;35(6):931–934. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-6-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]