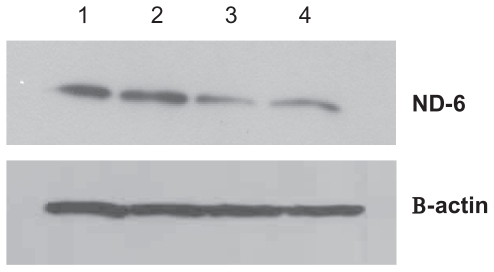
The wrong image was used in Figure 5 on page 719. The correct figure is presented below:
Figure 5.
Effect of treatment with silicon dioxide nanoparticles on expression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADh) dehydrogenase subunit 6 in human astrocytoma U87 cells. U87 cells were treated at specified concentrations of silicon dioxide nanoparticles for 48 hours. Then cell lysates of treated and untreated (ie, control) U87 cells were prepared as described in Materials and methods. The expression of NADh dehydrogenase subunit 6, encoded by mitochondrial DNA, was determined by Western blot analysis using β-actin as the loading control: Lane 1, lysate of untreated or control U87 cells; lane 2, lysate of U87 cells treated with silicon dioxide nanoparticles at 25 μg/mL; lane 3, lysate of U87 cells treated with silicon dioxide nanoparticles at 50 μg/mL; lane 4, lysate of U87 cells treated with silicon dioxide nanoparticles at 100 μg/mL. The blots were from a typical experiment. Two other experiments yielded essentially the same trend of results.