Abstract
The glucose turnover rate in maturity-onset diabetes in man has been variously reported as increased, normal, and decreased. The present experiments suggest that these discrepancies may have been due to methodology, and to nonrecognition of a circadian cycle in the glucose turnover rate that is present in health, and marked in diabetes.
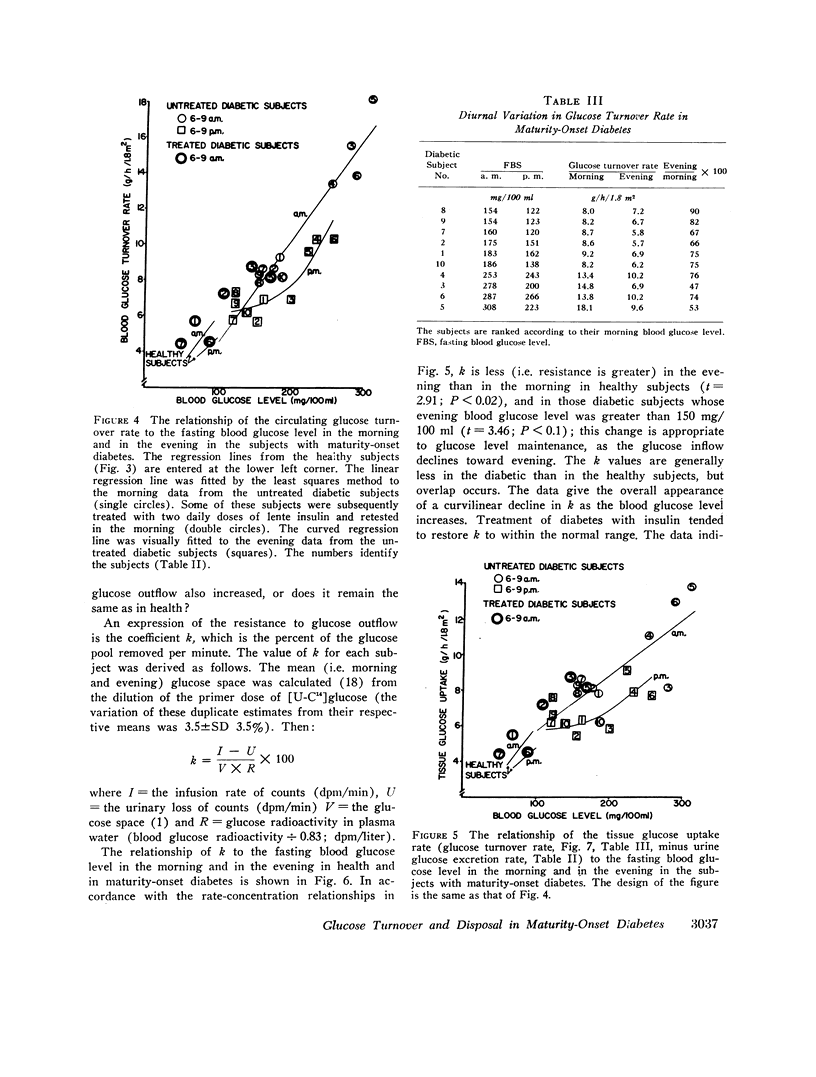
During the early morning hours the glucose turnover rate in maturity-onset diabetes is increased in proportion to the fasting blood glucose level. It may reach three to four times the rate found in health. During the evening hours the increments are about one-half as great.
The glucose outflow rate constant, k, lower in diabetes than in health, is also lower in both groups in the evening than in the morning.
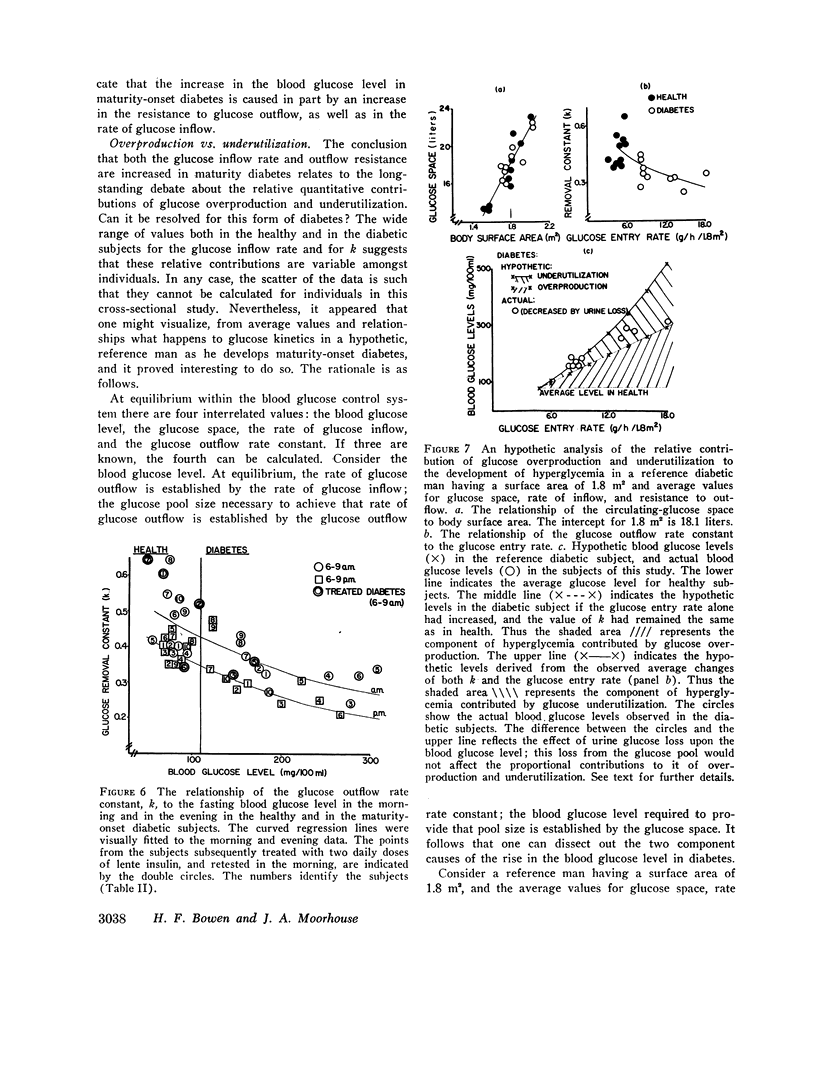
An analysis of the relative contributions of glucose overproduction and underutilization to the development of hyperglycemia in maturity-onset diabetes indicates that overproduction is the greater factor. The relative role of underutilization appears to increase as the fasting blood glucose level increases.
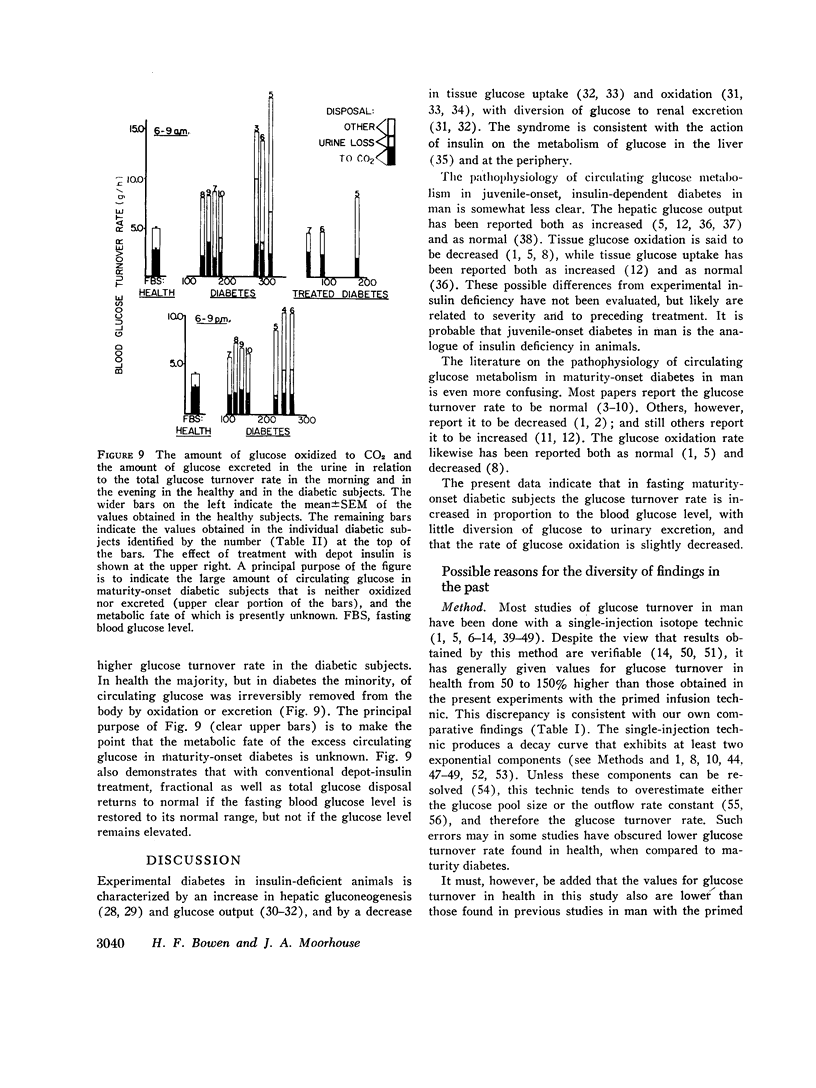
The circulating glucose oxidation rate in maturity-onset diabetes is only slightly lower than in health, but the fraction oxidized is markedly lower, and only a small fraction is excreted.
The principal conclusion is that in maturity-onset diabetes there is a hypertrophied flux of endogenous glucose, most of which is neither oxidized nor excreted. The precursors and the qualitative and quantitative metabolic fates of this excess glucose are unknown.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER N., SHIPLEY R. A., CLARK R. E., INCEFY G. E. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism: glucose pool size and rate of turnover in the normal rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Feb;196(2):245–252. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER N., SHREEVE W. W., SHIPLEY R. A., INCEFY G. E., MILLER M. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism. I. The oxidation of glucose in normal human subjects. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):575–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEARN A. G., BILLING B. H., SHERLOCK S. Hepatic glucose output and hepatic insulin sensitivity in diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1951 Oct 20;2(6686):698–701. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)91476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMAN E. N. GLUCOSE TURNOVER RATES IN PREGNANT AND NON-PREGNANT SHEEP. Nature. 1964 Jun 27;202:1333–1333. doi: 10.1038/2021333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR A., SEGAL S. The isolation of blood glucose as potassium gluconate. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Jun;55:959–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barter P. J., Nestel P. J., Carroll K. F. Precursors of plasma triglyceride fatty acid in humans. Effects of glucose consumption, clofibrate administration, and alcoholic fatty liver. Metabolism. 1972 Feb;21(2):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90063-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisswenger P. G., Spiro R. G. Human glomerular basement membrane: chemical alteration in diabetes mellitus. Science. 1970 May 1;168(3931):596–598. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3931.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Dyke R. Diurnal variation of oral glucose tolerance in volunteers and laboratory animals. Diabetologia. 1971 Jun;7(3):156–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01212547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B., Reis D. J. Central neural regulation by adrenergic nerves of the daily rhythm in hepatic tyrosine transaminase activity. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):267–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy P. K., Bloom W. L., Whitner V. S., Farrar B. W. STUDIES OF THE ROLE OF THE LIVER IN HUMAN CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM BY THE VENOUS CATHETER TECHNIC. II. PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC KETOSIS, BEFORE AND AFTER THE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN. J Clin Invest. 1949 Sep;28(5 Pt 2):1126–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI102146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen A. J., Reeves R. L. Diurnal variation in glucose tolerance. Arch Intern Med. 1967 Mar;119(3):261–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brech W. J., Glennon J. A., Gordon E. S. Kinetische Untersuchungen des Glucosestoffwechsels. I. Glucosepool, Glucoseumssatz und Cori-Cyclus bei normalen Versuchspersonen. Klin Wochenschr. 1970 May 1;48(9):521–529. doi: 10.1007/BF01488566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brech W. J., Glennon J. A., Gordon E. S. Kinetische Untersuchungen des Glucosestoffwechsels. II. Glucosepool, Glucoseumsatz und Cori-Cyclus bei Adipositas. Klin Wochenschr. 1970 May 1;48(9):529–536. doi: 10.1007/BF01488567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan J. S., Schachter D., Hetenyi G., Jr Validity of a tracer-injection method for studying glucose turnover in normal dogs. J Nucl Med. 1969 Feb;10(2):98–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MEUTTER R. C., SHREEVE W. W. Conversion of DL-lactate-2-C14 or -3-C14 or pyruvate-2-C14 to blood glucose in humans: effects of diabetes, insulin, tolbutamide, and glucose load. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:525–533. doi: 10.1172/JCI104741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaCosta F., Moorhouse J. A. Protein nutrition in aged individuals on self-selected diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969 Dec;22(12):1618–1633. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/22.12.1618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Jefferson L. S., Jr, Butcher R. W., Park C. R. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused liver. The effects of fasting, alloxan diabetes, glucagon, epinephrine, adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and insulin. Am J Med. 1966 May;40(5):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELLER D. D., CHAIKOFF I. L., STRISOWER E. H., SEARLE G. L. Glucose utilization in the diabetic dog, studied with C14-glucose. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):865–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKSON D. S., ONO K. An improved technique for assay of C14O2 in expired air using the liquid scintillation counter. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Jan;51(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
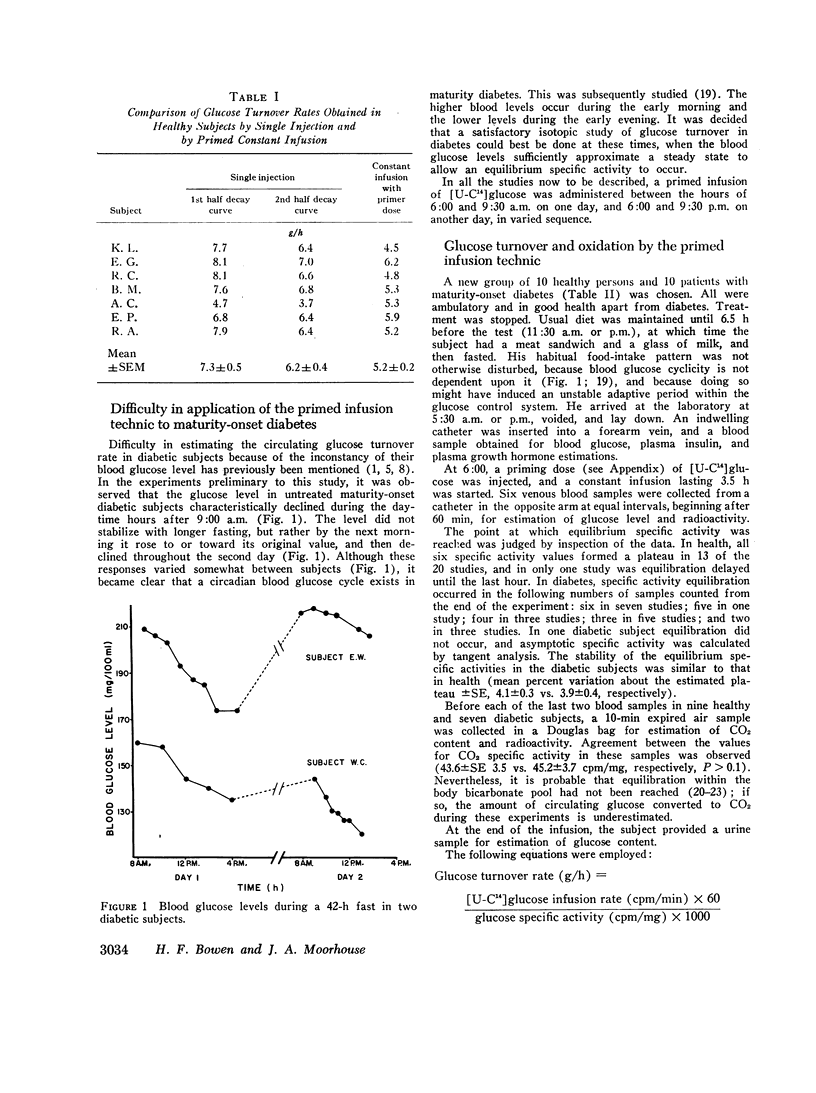
- Faiman C., Moorhouse J. A. Diurnal variation in the levels of glucose and related substances in healthy and diabetic subjects during starvation. Clin Sci. 1967 Feb;32(1):111–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbath N., Hetenyi G., Jr Glucose dynamics in normal subjects and diabetic patients before and after a glucose load. Diabetes. 1966 Nov;15(11):778–789. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.11.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbath N., Kenshole A. B., Hetenyi G., Jr Turnover of lactic acid in normal and diabetic dogs calculated by two tracer methods. Am J Physiol. 1967 May;212(5):1179–1184. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.5.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franckson J. R., Malaise W., Arnould Y., Rasio E., Ooms H. A., Balasse E., Conard V., Bastenie P. A. Glucose kinetics in human obesity. Diabetologia. 1966 Sep;2(2):96–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00423017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel N., Mager M., Vinnick L. Cyclicity in the interrelationships between plasma insulin and glucose during starvation in normal young men. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jan;71(1):171–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T., Jarrett R. J. Diurnal variation in insulin sensitivity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 4;2(7784):947–948. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92472-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
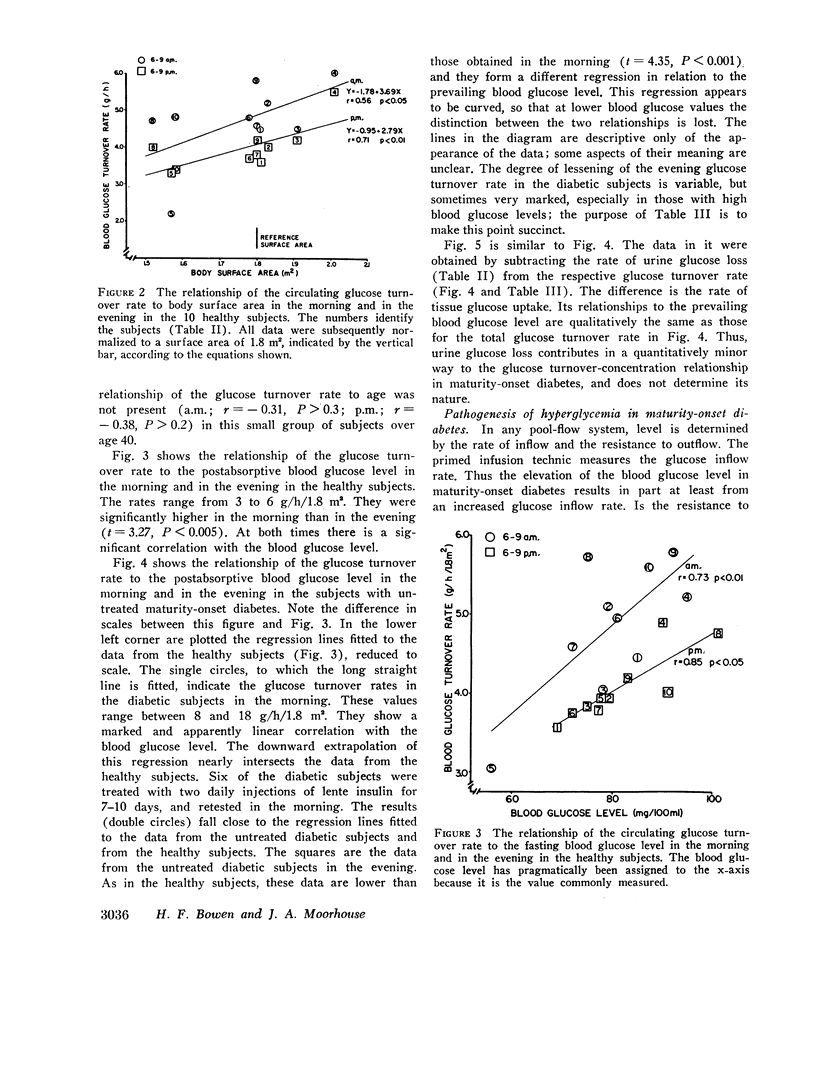
- Hansen A. P., Johansen K. Diurnal patterns of blood glucose, serum free fatty acids, insulin, glucagon and growth hormone in normals and juvenile diabetics. Diabetologia. 1970 Feb;6(1):27–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00425888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetenyi G., Jr, Wrenshall G. A. Glucose production rates in dogs determined by two different tracers and tracer methods. J Nucl Med. 1966 Jun;7(6):454–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBS G., REICHARD G., GOODMAN E. H., Jr, FRIEDMANN B., WEINHOUSE S. Action of insulin and tolbutamide on blood glucose entry and removal. Diabetes. 1958 Sep-Oct;7(5):358–364. doi: 10.2337/diab.7.5.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Baker I. A., Keen H., Oakley N. W. Diurnal variation in oral glucose tolerance: blood sugar and plasma insulin levels morning, afternoon, and evening. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 22;1(5794):199–201. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5794.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALANT N., CSORBA T. R., HELLER N. EFFECT OF INSULIN ON GLUCOSE PRODUCTION AND UTILIZATION IN DIABETES. Metabolism. 1963 Dec;12:1100–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIBLER R. F., TAYLOR W. J., MYERS J. D. THE EFFECT OF GLUCAGON ON NET SPANCHNIC BALANCES OF GLUCOSE, AMINO ACID NITROGEN, UREA, KETONES, ANS OXYGEN IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:904–915. doi: 10.1172/JCI104976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A. Glucose metabolism in normal and obese subjects. Effect of phenformin. Diabetes. 1968 Aug;17(8):481–488. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.8.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Pennington L. F., Boshell B. R. Lactate turnover and gluconeogenesis in normal and obese humans. Effect of starvation. Diabetes. 1970 Jan;19(1):53–63. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONG C. L., GEIGER J. W. LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF THE POTASSIUM GLUCONATE DERIVATIVE OF BLOOD GLUCOSE. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:253–259. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. L., Spencer J. L., Kinney J. M., Geiger J. W. Carbohydrate metabolism in normal man and effect of glucose infusion. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Jul;31(1):102–109. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS B., SIMPSON-MORGAN M. W. THE EXCRETION OF 14CO2 DURING THE CONTINUOUS INTRAVENOUS INFUSION OF NAH-14CO3 IN UNANAESTHETIZED RATS. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:713–728. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYERS J. D. Net splanchnic glucose production in normal man and in various disease states. J Clin Invest. 1950 Nov;29(11):1421–1429. doi: 10.1172/JCI102380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison L. L. Role of insulin in the hepatic handling of glucose. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Mar;123(3):284–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe C., De Gasparo M., De Hertogh R., Hoet J. J. Circadian variations of blood sugar and plasma insulin levels in man. Diabetologia. 1969 Dec;5(6):397–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00427978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. I., Pearsson M. J. Acute hypoglycemic action of insulin in insulin-dependent diabetics. Metabolism. 1971 Sep;20(9):859–869. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhouse J. A., Smithen C. S., Houston E. S. A study of glucose transport kinetics in man by means of continuous glucose infusions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Feb;27(2):256–264. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa K. Probable sleep dependency of diurnal rhythm of plasma growth hormone response to hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):854–856. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Morgan A. P., Kemp H. G., Sullivan J. M., Herrera M. G., Cahill G. F., Jr Brain metabolism during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1589–1595. doi: 10.1172/JCI105650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P., Bortz W. M. Turnover and oxidation of plasma glucose in lean and obese humans. Metabolism. 1969 Jul;18(7):570–584. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauly J. E., Scheving L. E. Circadian rhythms in blood glucose and the effect of different lighting schedules, hypophysectomy, adrenal medullectomy and starvation. Am J Anat. 1967 May;120(3):627–636. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001200312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. J., Berry L. J. Circadian rhythm of mouse liver phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Am J Physiol. 1970 May;218(5):1440–1444. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.5.1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. J., Berry L. J. Hormonal control of mouse liver phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase rhythm. Am J Physiol. 1970 Sep;219(3):697–701. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.3.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICHARD G. A., Jr, JACOBS A. G., FRIEDMANN B., KIMBEL P. R., HOCHELLA N. J., WEINHOUSE S. Effects of insulin and tolbutamide on production and utilization of blood sugar. Metabolism. 1959 Jul 2;8(4 Pt 2):486–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICHARD G. A., Jr, JACOBS A. G., KIMBEL P., HOCHELLA N. J., WEINHOUSE S. Blood glucose replacement rates in normal and diabetic humans. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Sep;16:789–795. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.5.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENOLD A. E., TENG C. T., NESBETT F. B., HASTING A. B. Studies on carbohydrate metabolism in rat liver slices. II. The effect of fasting and of hormonal deficiencies. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):533–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS H. J. AFTERNOON GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TESTING: A KEY TO THE PATHOGENESIS, EARLY DIAGNOSIS AND PROGNOSIS OF DIABETOGENIC HYPERINSULINISM. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1964 May;12:423–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1964.tb05730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON R. J., COXON R. V. Radioactivity of blood carbon dioxide in animals oxidizing glucose labelled with carbon-14 and other labelled substances. Nature. 1957 Dec 7;180(4597):1279–1281. doi: 10.1038/1801279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Silvers A., Farquhar J. W. Study of the relationship between plasma insulin concentration and efficiency of glucose uptake in normal and mildly diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1970 Aug;19(8):571–578. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.8.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKS W. Cerebral metabolism of isotopic glucose in normal human subjects. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Jan;10(1):37–44. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.10.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARLE G. L., MORTIMORE G. E., BUCKLEY R. E., REILLY W. A. Plasma glucose turnover in humans as studied with C14 glucose: influence of insulin and tolbutamide. Diabetes. 1959 May-Jun;8(3):167–173. doi: 10.2337/diab.8.3.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARLE G. L., STRISOWER E. H., CHAIKOFF I. L. Determination of rates of glucose oxidation in normal and diabetic dogs by a technique involving continuous injection of C14-glucose. Am J Physiol. 1956 Jun;185(3):589–594. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.185.3.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARLE G. L., STRISOWER E. H., CHAIKOFF I. L. Glucose pool and glucose space in the normal and diabetic dog. Am J Physiol. 1954 Feb;176(2):190–194. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.176.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLLBERGER A. THE CONTROL OF CIRCADIAN GLYCOGEN RHYTHMS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Sep 10;117:519–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb48204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., ALTSZULER N., WALL J. S., DUNN A., DE BODO R. C. Influence of adrenalectomy on glucose turnover and conversion to CO2: studies with C14 glucose in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1959 Feb;196(2):221–230. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. REFLECTIONS ON POOLS. Fed Proc. 1964 May-Jun;23:671–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STETTEN D., Jr, WELT I. D., INGLE D. J., MORLEY E. H. Rates of glucose production and oxidation in normal and diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):817–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle G. L., Cavalieri R. R. Determination of lactate kinetics in the human analysis of data from single injection vs. continuous infusion methods. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Mar;139(3):1002–1006. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle G. L., Gulli R., Cavalieri R. R. Effect of Phenformin in nondiabetic humans. Estimation of glucose turnover rate and Cori cycle activity. Metabolism. 1969 Feb;18(2):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(69)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle G. L., Schilling S., Porte D., Barbaccia J., De Grazia J., Cavalieri R. R. Body glucose kinetics in nondiabetic human subjects after phenethylbiguanide. Diabetes. 1966 Mar;15(3):173–178. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.3.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman I., Horland A. A., Teebor G. W. Hepatic glycolytic and gluconeogenic enzymes of the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;146(2):600–603. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shames D. M., Berman M., Segal S. Effects of thyroid disease on glucose oxidative metabolism in man. A compartmental model analysis. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):627–641. doi: 10.1172/JCI106533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley R. A., Chudzik E. B., Gibbons A. P., Jongedyk K., Brummond D. O. Rate of glucose transformation in the rat by whole-body analysis after blucose-14-C. Am J Physiol. 1967 Nov;213(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.5.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley R. A., Chudzik E. B., Gibbons A. P. Rate of disposal of glucose carbon to CO2, fat, protein, and glycogen in the diabetic rat. Am J Physiol. 1970 Aug;219(2):364–373. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.2.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Spiro M. J. Effect of diabetes on the biosynthesis of the renal glomerular basement membrane. Studies on the glucosyltransferase. Diabetes. 1971 Oct;20(10):641–648. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.10.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. The influences of insulin on the hepatic metabolism of glucose. Ergeb Physiol. 1966;57:91–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R., Winkler B., Rathgeb I., Bjerknes C., Altszuler N. Plasma glucose and free fatty acid metabolism in normal and long-fasted dogs. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):313–319. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Glucagon and the insulin: glucagon ratio in diabetes and other catabolic illnesses. Diabetes. 1971 Dec;20(12):834–838. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.12.834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRENSHALL G. A., HETENYI G., Jr, BEST C. H. The validity of rates of glucose appearance in the dog calculated by the method of successive tracer injections. II. The influence of intermixing time following tracer injection. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Feb;39:267–278. doi: 10.1139/o61-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRENSHALL G. A., RAPPAPORT A. M., BEST C. H., COWAN J. S., HETENYI G., Jr ABSOLUTE RATES OF GLUCOSE PRODUCTION, ACCUMULATION, AND UTILIZATION IN THE DOG AT PANCREATECTOMY AND THEREAFTER. Diabetes. 1964 Sep-Oct;13:500–508. doi: 10.2337/diab.13.5.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Cerasi E., Luft R. Splanchnic and peripheral glucose and amino acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1870–1878. doi: 10.1172/JCI106989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse C., Keilson J. Cori cycle activity in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2359–2366. doi: 10.1172/JCI106202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse C., Kemperman J. H. Changes in oxidative metabolism with glucose ingestion. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Aug;68(2):250–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. R., Pelligra R., Shapira J., Adachi R. R., Skrettingland K. Glucose oxidation and replacement during prolonged exercise in man. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Nov;23(5):734–741. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.5.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]