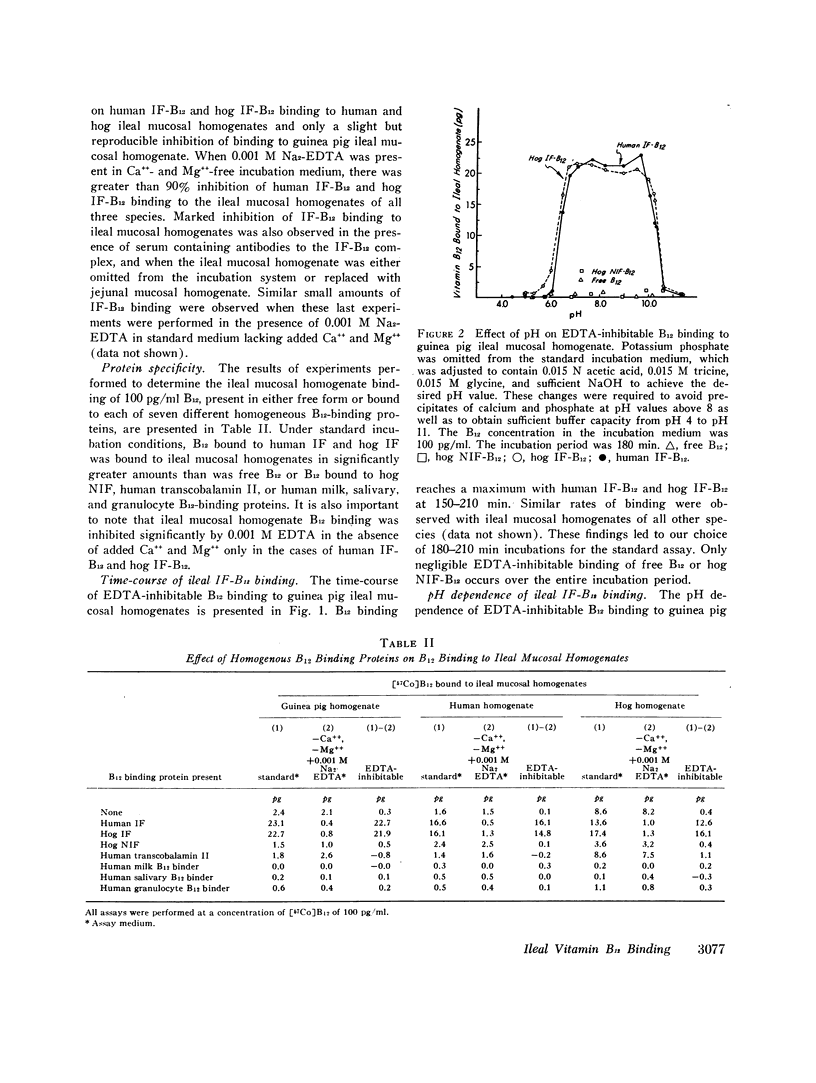
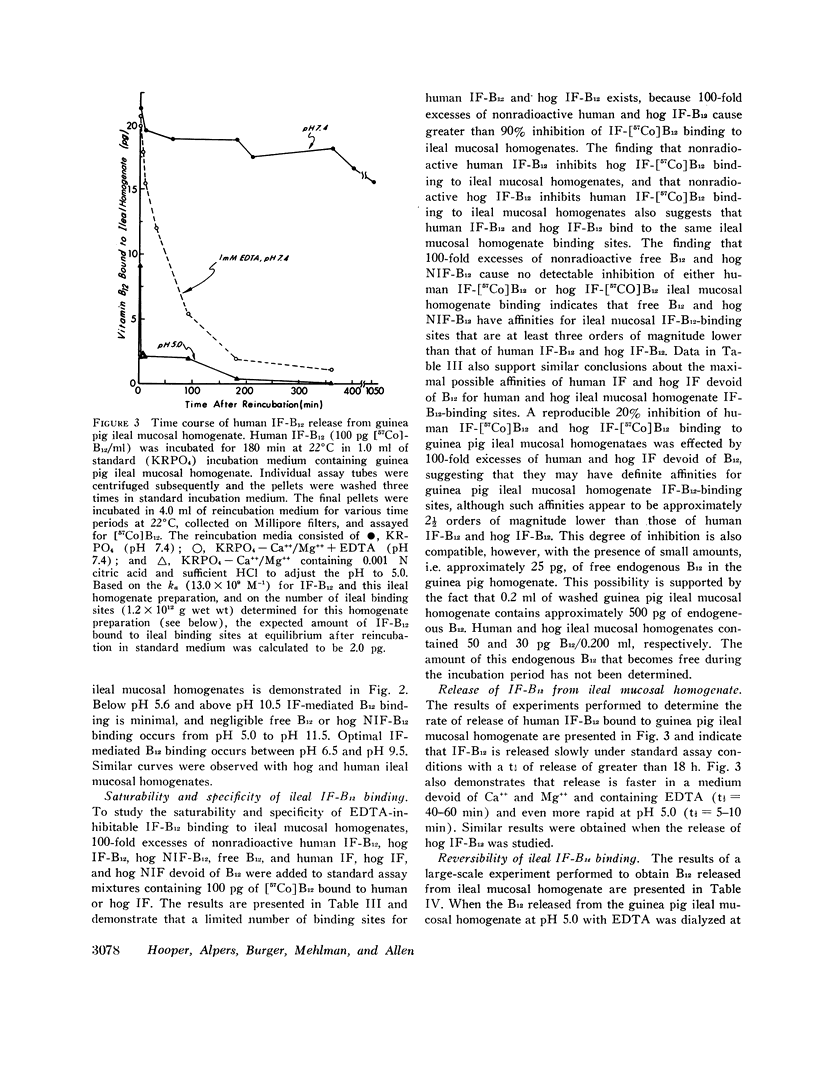
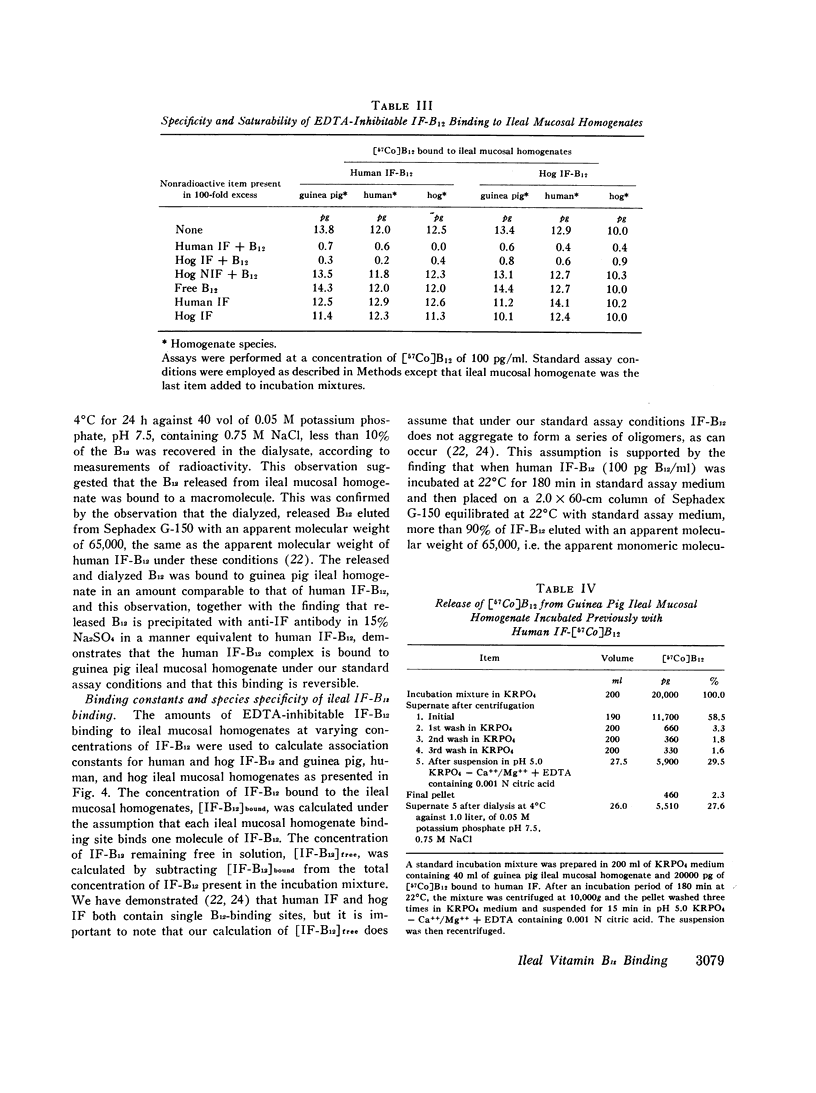
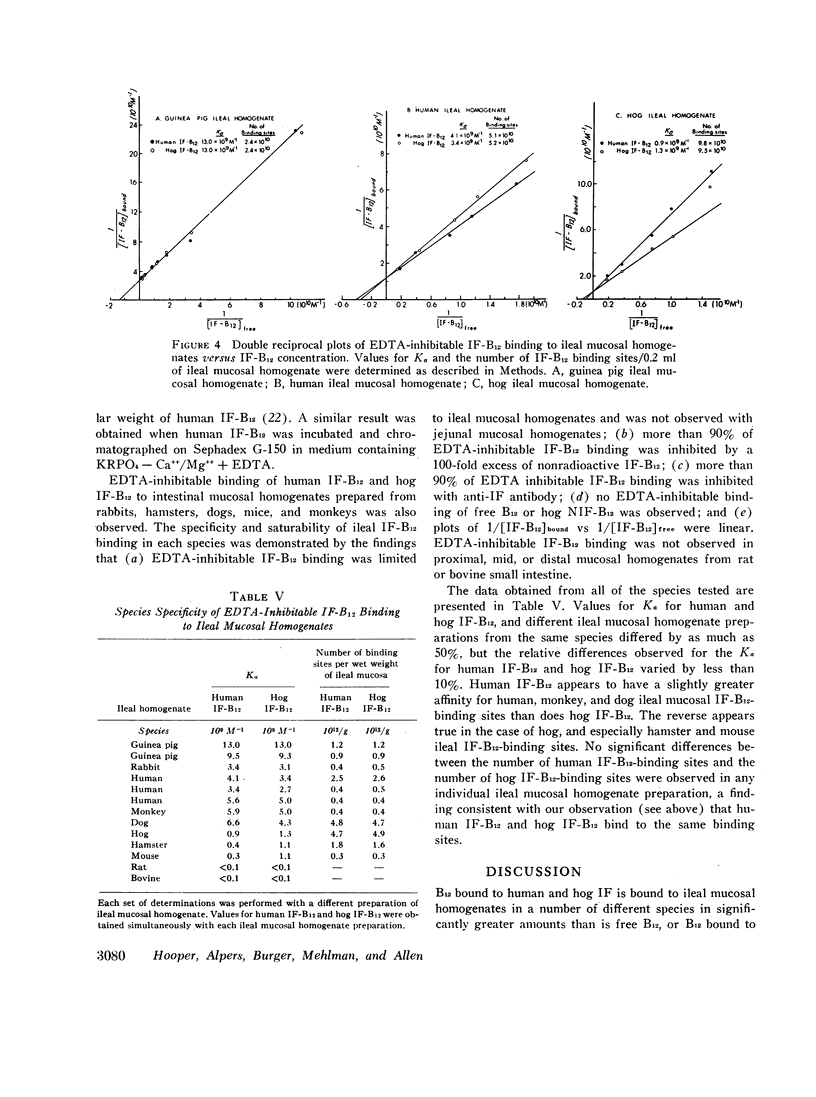
Abstract
Elucidation of the mechanism of intrinsic factor (IF)-mediated vitamin B12 (B12) binding to ileal binding sites has been hampered by the use of crude or only partially purified preparations of IF in previous studies. We have used homogeneous human IF and hog IF isolated by affinity chromatography to study [57Co]B12 binding to ileal mucosal homogenates. The following observations were made: (a) Human IF-B12 and hog IF-B12 were bound to human, monkey, hog, dog, rabbit, mouse, hamster, and guinea pig ileal, but not jejunal, homogenates in amounts significantly greater than free B12 or B12 bound to five other homogeneous B12-binding proteins; (b) only IF-mediated B12 binding was localized to ileal homogenates and was inhibited by EDTA; (c) values for the association constant (Ka) for the various ileal homogenates mentioned above and human IF-B12 and hog IF-B12 ranged from 0.3 × 109 M-1 to 13.0 × 109 M-1. Apparent differences in the Ka for human IF-B12 and hog IF-B12 existed in most species; (d) the number of ileal IF-B12 binding sites per gram (wet weight) of ileal mucosa ranged from 0.3 × 1012 to 4.9 × 1012. The same value was always obtained with human IF-B12 and hog IF-B12 for any given homogenate preparation; (c) 100-fold excesses of free B12 or human IF and hog IF devoid of B12 did not significantly inhibit human IF-B12 and hog IF-B12 binding to human and hog ileal homogenates.
These experiments performed with homogeneous IF indicate that: (a) gastric factors other than IF are not required for B12 binding to ileal IF-B12-binding sites: (b) the mechanism of ileal IF-B12 binding is different from that of free B12 or of B12 bound to non-IF-B12-binding proteins; (c) human IF and hog IF have different structures; (d) human IF-B12 and hog IF-B12 bind to the same ileal binding sites; and (c) human and hog ileal IF-B12 binding sites bind free B12 and human and hog IF devoid of B12 poorly, if at all.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARDEMAN S., CHANARIN I., BERRY V. STUDIES ON HUMAN GASTRIC INTRINSIC FACTOR: OBSERVATIONS ON ITS POSSIBLE ABSORPTION AND ENTERO-HEPATIC CIRCULATION. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jan;11:11–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. 3. Purification and properties of human plasma transcobalamin II. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7709–7717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. II. Purification and properties of a human granulocyte vitamine B12-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7702–7708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Mehlman C. S. Isolation of gastric vitamin B 12 -binding proteins using affinity chromatography. I. Purification and properties of human intrinsic factor. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3660–3669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Mehlman C. S. Isolation of gastric vitamin B 12 -binding proteins using affinity chromatography. II. Purification and properties of hog intrinsic factor and hog nonintrinsic factor. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3670–3680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOASS A., WILSON T. H. An assay for gastric intrinsic factor. Am J Physiol. 1963 Jan;204:97–100. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., CASTLE W. B. Sequential mechanisms in the enhanced absorption of vitamin B12 by intrinsic factor in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:199–214. doi: 10.1172/JCI104019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., PARANCHYCH W., LOWENSTEIN L. Studies on the absorption by guinea pig intestine of cyanocobalamin incubated with intrinsic factor. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:370–377. doi: 10.1172/JCI104491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A. THE UPTAKE OF CO57-LABELED VITAMIN B12 BY EVERTED SACS OF INTESTINE IN VITRO. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 Nov;43:689–696. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196411000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel R., Rosenberg A. H., Lau K. S., Streiff R. R., Herbert V. Vitamin B12 uptake by human small bowel homogenate and its enhancement by intrinsic factor. Gastroenterology. 1969 Mar;56(3):548–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper B. A., White J. J. Absence of intrinsic factor from human portal plasma during 57CoB12 absorption in man. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jan;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr, Mackenzie I. L., Trier J. S. Intrinsic factor-mediated attachment of vitamin B12 to brush borders and microvillous membranes of hamster intestine. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jul;46(7):1215–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI105615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenbogen L., Highley D. R. Hog intrinsic factor. I. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding fractions from hog pylorus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):1004–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTLIEBLAU K. S., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. RAPID CHARCOAL ASSAY FOR INTRINSIC FACTOR (IF), GASTRIC JUICE UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY, ANTIBODY TO IF, AND SERUM UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY. Blood. 1965 Jun;25:875–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräsbeck R. Intrinsic factor and the other vitamin B12 transport proteins. Prog Hematol. 1969;6:233–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. Divalent cation and pH dependence of rat intrinsic factor action in everted sacs and mucosal homogenates of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1978–1983. doi: 10.1172/JCI104423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Mechanism of intrinsic factor action in everted sacs of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):102–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI103779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH E. S., COATES M. E. The absorption of vitamin B12 in animals. I. The effect of different binding and intrinsic factors. Clin Chim Acta. 1960 Nov;5:853–861. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(60)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH E. S. The isolation and properties of intrinsic factor and vitamin B12 binding substances from pig pylorus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Aug 5;51:295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippe E., Schwartz M. Intrinsic factor activity of stomach preparations from various animal species. Scand J Haematol. 1971;8(4):276–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1971.tb00876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J. Immunoassay of gastric intrinsic factor and the titration of antibody to intrinsic factor. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jan;1(1):99–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAU K. S., GOTTLIEB C., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. MEASUREMENT OF SERUM VITAMIN B12 LEVEL USING RADIOISOTOPE DILUTION AND COATED CHARCOAL. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:202–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie I. L., Donaldson R. M., Jr Effect of divalent cations and pH on intrinsic factor-mediated attachment of vitamin B 12 to intestinal microvillous membranes. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2465–2471. doi: 10.1172/JCI107060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg S. P. Identification of a macromolecular factor in the ileum which binds intrinsic factor and immunologic identification of intrinsic factor in ileal extracts. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):913–923. doi: 10.1172/JCI105783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STECK T. L., HOELZLWALLACH D. F. THE BINDING OF KIDNEY-BEAN PHYTOHEMAGGLUTININ BY EHRLICH ASCITES CARCINOMA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 8;97:510–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS E. W., WILSON T. H. Factors controlling B12 uptake by intestinal sacs in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1960 Jan;198:103–107. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SULLIVAN L. W., HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. IN VITRO ASSAY FOR HUMAN INTRINSIC FACTOR. J Clin Invest. 1963 Sep;42:1443–1458. doi: 10.1172/JCI104829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toskes P. P., Deren J. J., Conrad M. E. Trypsin-like nature of the pancreatic factor that corrects vitamin B12 malabsorption associated with pancreatic dysfunction. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1660–1664. doi: 10.1172/JCI107346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toskes P. P., Deren J. J. The role of the pancreas in vitamin B 12 absorption: studies of vitamin B 12 absorption in partially pancreatectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):216–223. doi: 10.1172/JCI106806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toskes P. P., Hansell J., Cerda J., Deren J. J. Vitamin B 12 malabsorption in chronic pancreatic insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 1971 Mar 25;284(12):627–632. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197103252841202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UKYO S., COOPER B. A. INTRINSIC FACTOR-LIKE ACTIVITY IN EXTRACTS OF GUINEA PIG INTESTINE. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jan;208:9–13. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


