Abstract
Jejunal absorption of calcium, water, and electrolytes was measured in 10 normal subjects by the triple-lumen perfusion method. During the control period, water and electrolyte movements were minimal when a bicarbonate-free test solution was infused. By contrast, bicarbonate-containing solutions were readily absorbed in the control period. Intravenous infusion of synthetic salmon calcitonin (SCT) (1 Medical Research Council U/kg wt/h) over 110-120 min resulted in a marked jejunal secretion of water, sodium, potassium, and chloride in 8 of the 10 subjects. This jejunal secretion occurred with both the bicarbonate-free and the bicarbonate-containing test solutions. Calcium absorption was not affected by SCT, and the serum calcium concentration did not fall during SCT infusion. These results suggest that diarrhea in patients with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid may be due to intestinal secretion secondary to high blood concentrations of thyrocalcitonin.
Full text
PDF
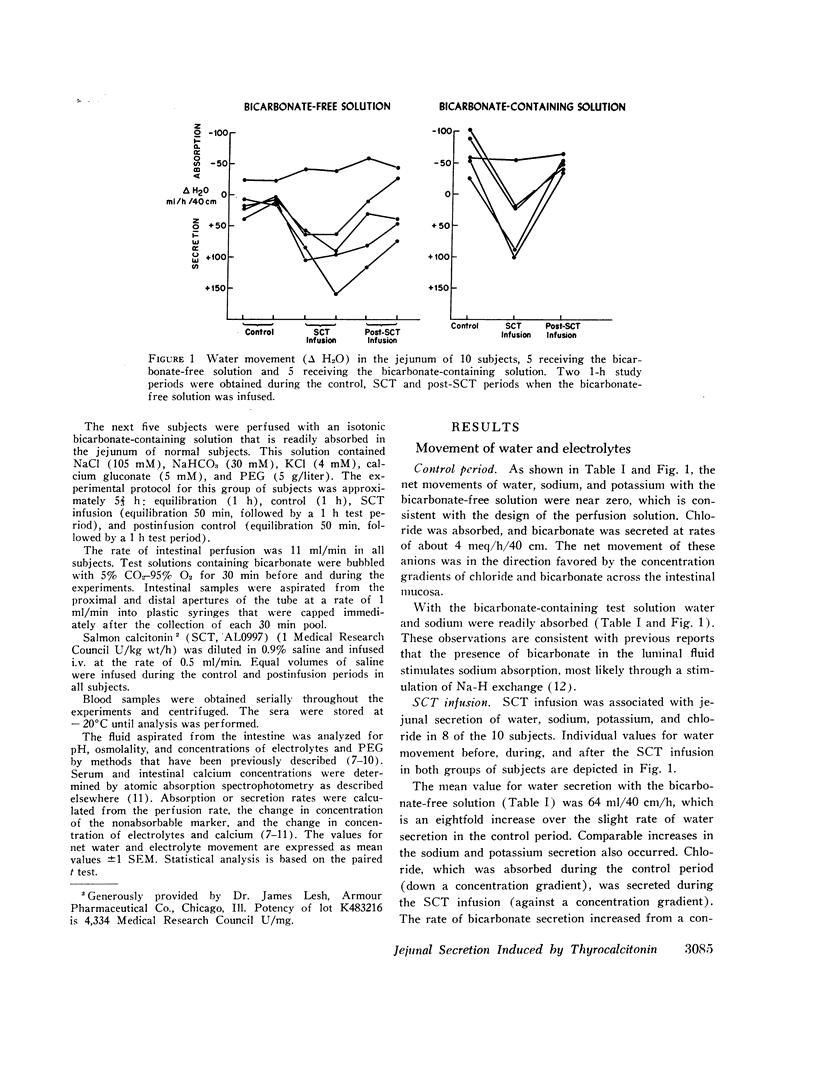
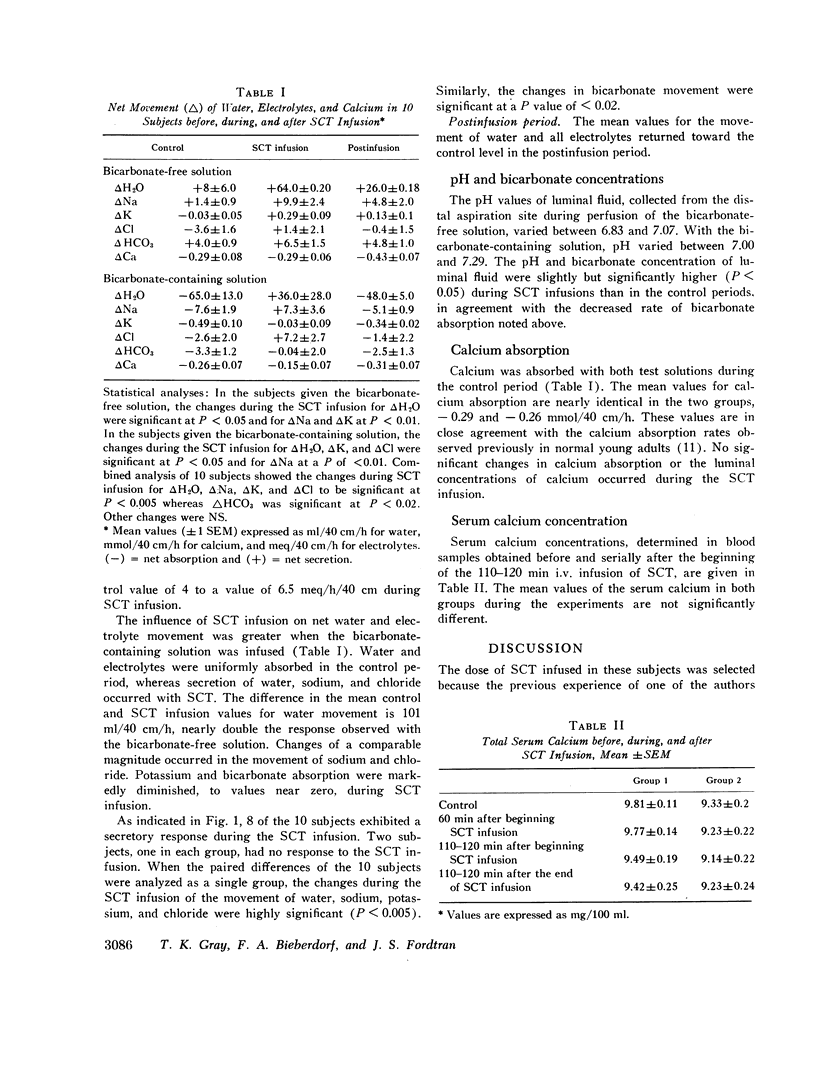


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper H., Levitan R., Fordtran J. S., Ingelfinger F. J. A method for studying absorption of water and solute from the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jan;50(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deftos L. J., Bury A. E., Habener J. F., Singer F. R., Potts J. T., Jr Immunoassay for human calcitonin. II. Clinical studies. Metabolism. 1971 Dec;20(12):1129–1137. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S. Marker perfusion techniques for measuring intestinal absorption in man. Gastroenterology. 1966 Dec;51(6):1089–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Carter N. W. The mechanisms of sodium absorption in the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):884–900. doi: 10.1172/JCI105781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Ewton M. F., Soter N., Kinney J. Permeability characteristics of the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1935–1944. doi: 10.1172/JCI105299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesch R. D., Hüfner M., Hasenhager B., Creutzfeldt W. Inhibition of gastric secretion by calcitonin in man. Horm Metab Res. 1971 Mar;3(2):140–140. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1096771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland P., Fordtran J. S. Effect of dietary calcium and age on jejunal calcium absorption in humans studied by intestinal perfusion. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2672–2681. doi: 10.1172/JCI107461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melvin K. E., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Miller H. H. Studies in familial (medullary) thyroid carcinoma. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1972;28:399–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. B., Jr, Deluca H. F., Potts J. T., Jr Calcitonin inhibition of vitamin D-induced intestinal calcium absorption. Endocrinology. 1972 Jan;90(1):151–157. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-1-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Wong M., Bikle D., Goodman D. B. Hormonal control of the renal conversion of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2502–2504. doi: 10.1172/JCI107065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shai F., Baker R. K., Wallach S. The clinical and metabolic effects of porcine calcitonin on Paget's disease of bone. J Clin Invest. 1971 Sep;50(9):1927–1940. doi: 10.1172/JCI106685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnberg L. A., Fordtran J. S., Carter N. W., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of bicarbonate absorption and its relationship to sodium transport in the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):548–556. doi: 10.1172/JCI106265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



