Abstract
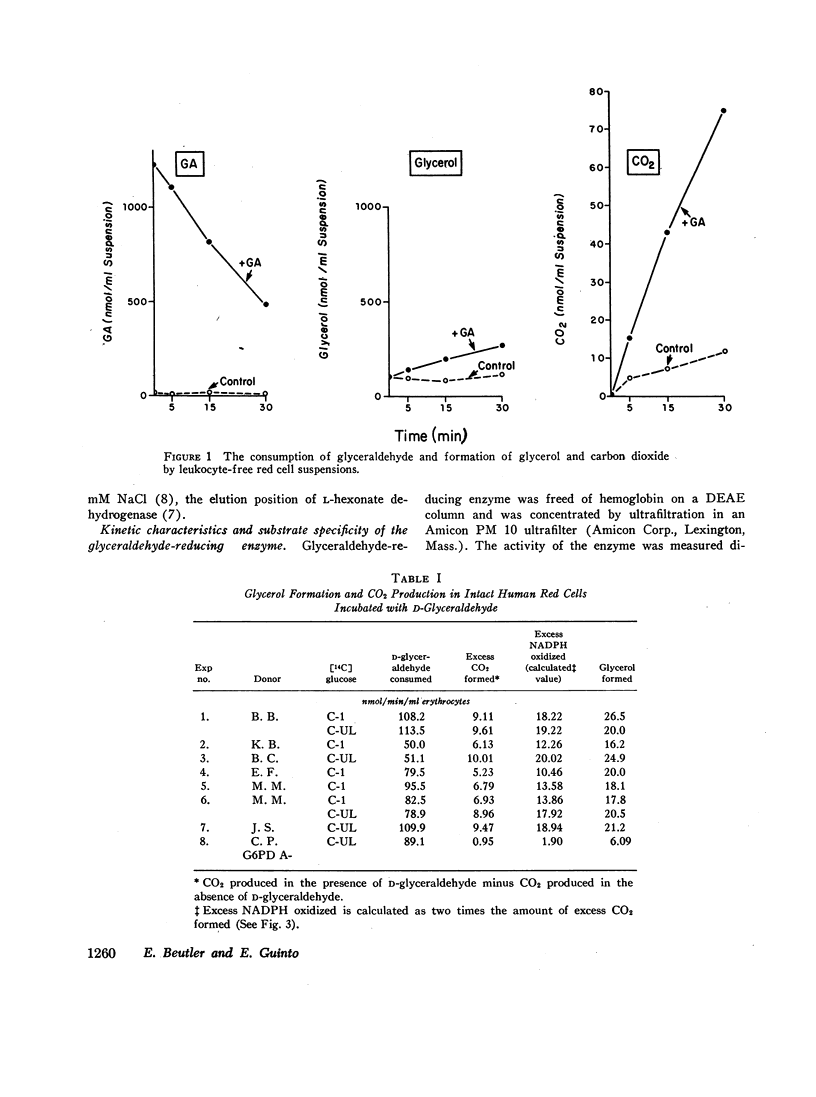
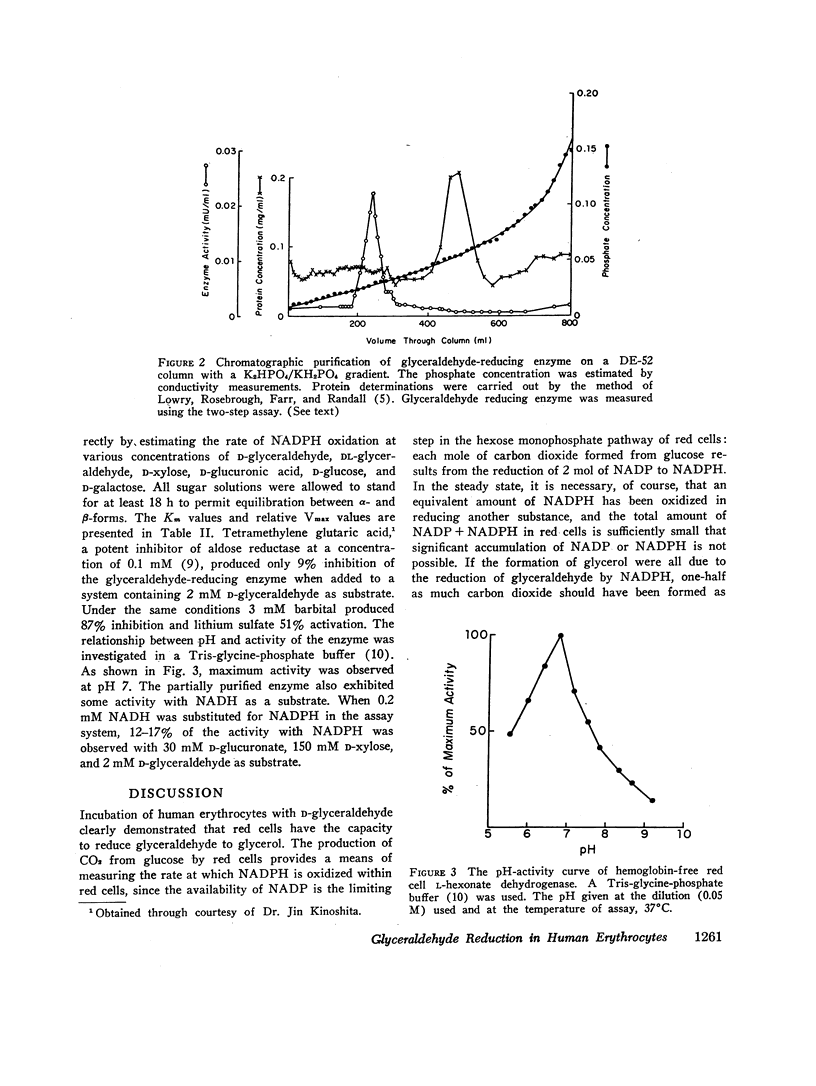
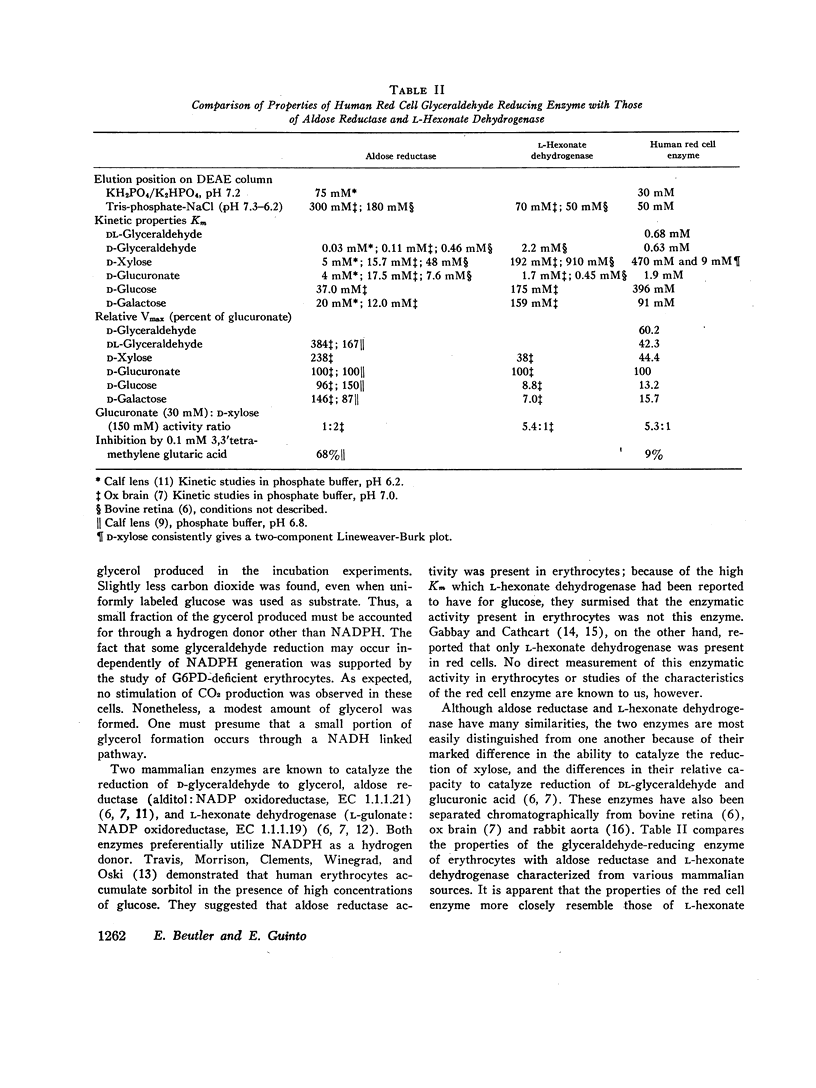
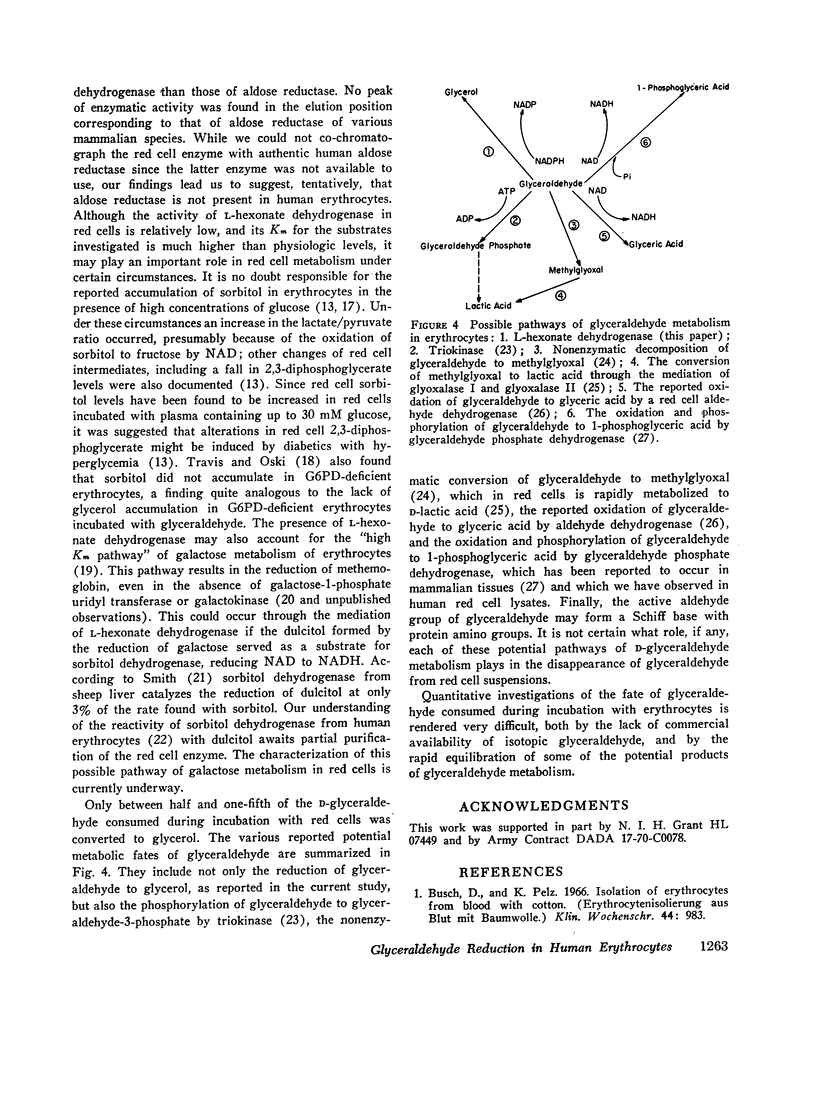
Incubation of red cell suspensions with D-glyceraldehyde resulted in disappearance of glyceraldehyde and appearance of glycerol. Concomitantly, there was an increase of CO2 formation from glucose. This indicated that the reduction of glyceraldehyde to glycerol occurred through a NADPH-linked system. Studies in hemolysates revealed the presence of an enzyme with the capacity to catalyze the reduction of glyceraldehyde to glycerol by NADPH. This enzyme was partially purified by DEAE chromatography. The elution pattern of the enzyme and its kinetic characteristics indicated that the enzyme was L-hexonate dehydrogenase (L-gulonate: NADP oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.1.19), not aldose reductase (Alditol: NADP oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.1.21), which had previously been thought present in erythrocytes. The reduction of glyceraldehyde to glycerol is one of a number of pathways for the metabolism of glyceraldehyde that have been found in red cells and/or other mammalian tissues.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler E., Guinto E. Dihydroxyacetone metabolism by human erythrocytes: demonstration of triokinase activity and its characterization. Blood. 1973 Apr;41(4):559–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Guinto E. The metabolism of dihydroxyacetone by intact erythrocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Oct;82(4):534–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Mathai C. K., Smith J. E. Biochemical variants of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase giving rise to congenital nonspherocytic hemolytic disease. Blood. 1968 Feb;31(2):131–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonsignore A., Leoncini G., Ricci D., Siri A. Aminic compounds tested as catalysts for glyceraldehyde conversion into methylglyoxal. Ital J Biochem. 1972 Jul-Aug;21(4):169–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch D., Pelz K. Erythrocytenisolierung aus Blut mit Baumwolle. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Aug 15;44(16):983–984. doi: 10.1007/BF01711475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements R. S., Jr, Morrison A. D., Winegrad A. I. Polyol pathway in aorta: regulation by hormones. Science. 1969 Nov 21;166(3908):1007–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3908.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H. Purification and immunological identification of bovine retinal aldose reductase. Isr J Med Sci. 1972 Aug-Sep;8(8):1626–1629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H. The sorbitol pathway and the complications of diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 19;288(16):831–836. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304192881609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYMAN S., KINOSHITA J. H. ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF LENS ALDOSE REDUCTASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:877–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedziniak J. A., Kinoshita J. H. Activators and inhibitors of lens aldose reductase. Invest Ophthalmol. 1971 May;10(5):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANO Y., SUZUKI K., YAMADA K., SHIMAZONO N. Enzymic studies on TPN L-hexonate dehydrogenase from rat liver. J Biochem. 1961 Jun;49:618–634. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHIES H. Untersuchungen über eine Aldehyd-dehydrogenase in kernlosen Erythrocyten. Biochem Z. 1957;329(5):421–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE B. W., MCGREGOR D. CHROMATOGRAPHIC AND ELECTROPHORETIC FRACTIONATION OF SOLUBLE PROTEINS OF BRAIN AND LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1647–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moonsammy G. I., Stewart M. A. Purification and properties of brain aldose reductase and L-hexonate dehydrogenase. J Neurochem. 1967 Dec;14(12):1187–1193. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb06166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. D., Clements R. S., Jr, Travis S. B., Oski F., Winegrad A. I. Glucose utilization by the polyol pathway in human erythrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morsches B., Holzmann H., Bettingen C. Zum Nachweis der Sorbit-Dehydrogenase in menschlichen Erythrocyten. Klin Wochenschr. 1969 Jun 15;47(12):672–673. doi: 10.1007/BF01884363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter J. K., Hayashi J. A., Watson J. A. Enzymic assay of glycerol, dihydroxyacetone, and glyceraldehyde. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Aug;121(2):404–414. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. G. Polyol dehydrogenases. 4. Crystallization of the L-iditol dehydrogenase of sheep liver. Biochem J. 1962 Apr;83:135–144. doi: 10.1042/bj0830135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis S. F., Morrison A. D., Clements R. S., Jr, Winegrad A. I., Oski F. A. Metabolic alterations in the human erythrocyte produced by increases in glucose concentration. The role of the polyol pathway. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2104–2112. doi: 10.1172/JCI106704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine W. N., Paglia D. E., Neerhout R. C., Konrad P. N. Erythrocyte glyoxalase II deficiency with coincidental hereditary elliptocytosis. Blood. 1970 Dec;36(6):797–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


