Abstract
Background:
In India, 67,500 infants acquire HIV infection yearly due to mother to child transmission.
Objective:
The objective was to assess the operational aspect of the Prevention of Parent to Child Transmission (PPTCT) program in a tertiary care hospital and explore its bottleneck.
Materials and Methods:
A 5-year (2004-2008) prospective evaluation study was conducted among the pregnant women attending Obstetrics Department of a rural tertiary care hospital, since the year of implementation. Indicators were used according to UNAIDS/WHO guideline.
Results:
Out of 40,140 registered pregnant women, 23,812 were counseled of which 19,794 were agreed to undergo HIV testing and 111 were found HIV positive with a prevalence of 0.56%. Overall HIV counseling and testing rates were 59.32% and 83.13%, respectively. The nevirapine (NVP) dispensing rate of the mother and newborn were 29.72% and 85.4%, respectively. At 18 months of age, 85% babies were found HIV negative in the mother baby pair who received NVP with absolutely formula feeding but it was 42.8% without such intervention.
Conclusion:
Majority of the pregnant women who came to the labor room directly were deprived of the program (PPTCT) coverage. Although the HIV testing rate reached the WHO target which was excellent, but the NVP dispensing rate lagged far behind.
Keywords: Evaluation, PPTCT program, pregnant women, rural tertiary care hospital
Introduction
In India, 25 million births take place yearly and overall estimated prevalence of HIV infection among pregnant women of 0.9% yields 225,000 HIV infected pregnant women deliver every year. Using a conservative vertical transmission rate of 30%, about 67,500 infants acquire HIV infection every year. Apart from posing the burden of HIV positive children on the society, mother to child transmission (MTCT) is causing a great social problem by producing orphans after the death of one or both parents due to AIDS.(1)
National AIDS Control Organization of India initiated phase 1 feasibility study on the prevention of mother to child transmission using the short course regimen of AZT and phase 2 of this project using nevirapine (NVP) has been done from year 1999 at 11 centers. The results of the feasibility study indicate that the Prevention of Parent to Child Transmission (PPTCT) program of HIV can be implemented within the existing framework of Reproductive and Child Health Programme. It is proposed to introduce this intervention in six high prevalence states on priority basis. In West Bengal, the PPTCT program started in January 2004 in most of the Medical College Hospitals including North Bengal Medical College and Hospital which is a rural tertiary care hospital.Recent data from the UNGASS study in India demonstrated that the full range of PPTCT services, including actually taking NVP, varied greatly ranging from a low of 17% to 69%, with an average of ~50% overall across sites.(2,3)
In view of the above facts, the present study has been undertaken to assess the operational aspects of the PPTCT program in a tertiary care hospital and explore its bottlenecks.
Materials and Methods
This 5-year prospective follow-up study was conducted from the year of implementation (January 2004) of the program to the end of December 2008 among the pregnant women attending the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, North Bengal Medical College, after getting necessary approval from the institutional ethical committee and West Bengal State AIDS Prevention and Control Society.
The desk evaluation of the PPTCT program was performed in relation to the propose activity which includes monthly reports of the program along with PPTCTP counseling and laboratory register. All HIV positive mothers and those who refused to test and health personals involved were interviewed with pretested semistructured questionnaires after obtaining informed consent. The information regarding PPTCT services was also obtained by periodical focused group discussion among health workers, pregnant women, and representatives of local positive people network.
Indicators were used according to the UNAIDS/WHO guideline for program evaluation.(4)
Results and Observations
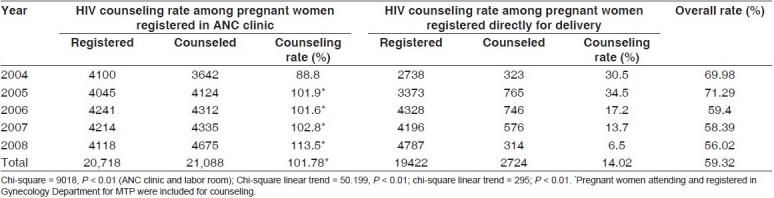
During the study periods, total 40,140 pregnant women were registered in North Bengal Medical College and among them 23,812 pregnant women were counseled for HIV testing. The overall HIV counseling rate among the pregnant women was 59.32%.
Major proportion (85.98%) of pregnant women reporting directly to the labor room for delivery without prior ANC registration were deprived from PPTCT services. The counseling rate among the pregnant women registered in ANC clinic was 101.78%, which is significantly higher (P < 0.01) than pregnant women registered directly for delivery (14.02%) [Table 1].
Table 1.
HIV counseling rate among the pregnant women from year 2004 to 2008
Out of total 23,812 pregnant women counseled, 19,7 94 individuals (83.13%) agreed for HIV testing. In ANC clinic, the HIV testing rate was 87.6% which is significantly higher (P < 0.01) than pregnant women in labor room (47.87%)[Table 2].
Table 2.
HIV testing rate among the pregnant women from year 2004 to 2008
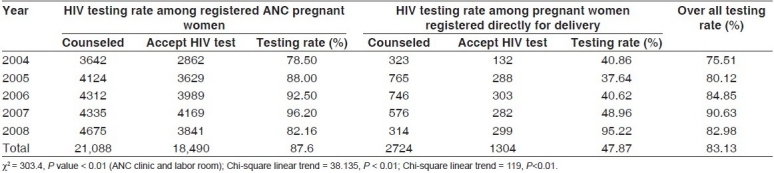
The nonavailablity of HIV testing kits (50%), inadequate lab. technicians (30%), and refusal for testing by the husbands (20%) were the main reasons for the failure of HIV testing among the pregnant women counseled.
Throughout the study periods, 19,794 pregnant women tested for HIV of which 111 pregnant women were found to be HIV positive. Only 33 HIV positive pregnant women received NVP with an overall NVP dispensing rate of 29.72%. It gradually increased from 15.8% to 37.5% from 2004 to 2006 but sharply decreased to 22.22% in 2007 and again sharply increased to 70.58% in the year of 2008. The overall NVP dispensing rate among the newborns of HIV positive mothers was 85.4% which was gradually increased from 75% to 100% during this period [Table 3].
Table 3.
NVP dispensing rate among HIV positive mother and their new born
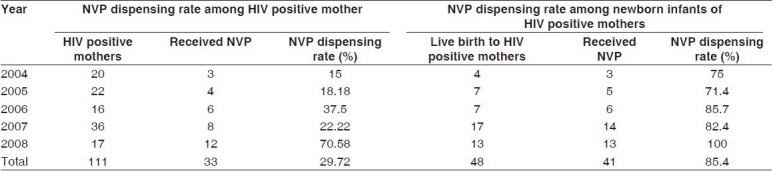
Women opting for home delivery (40%), delivering their baby in institutions where PPTCT services were not available (32%), nonavailability of NVP (20%), and lack of awareness among the health workers (8%) were the major reasons for failure to provide NVP. Out of 50 deliveries among HIV positive mothers in this hospital, 48 were live births and 2 stillbirths and most of them opted for formula feeding (73%).
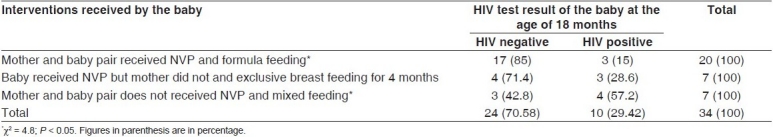
At the end of study period it was found that out of 48 babies, 34 babies crossed the age of 18 months among which 24 (70.58%) and 10 (29.42%) were sero-negative and sero-positive, respectively. Among the babies of HIV positive mothers who received full coverage of the PPTCT program, i.e., mother and baby pair received NVP and formula feeding, there was 85% HIV negative status which was significantly higher (P < 0.05) than the babies who did not received such intervention [Table 4].
Table 4.
HIV status of the baby at the age of 18 months (N = 34)
Discussion
In this study, the overall counseling rate observed was 59.32% of which 101.78% women registered in ANC clinic where as 14.02% among the pregnant women came to the labor room directly. The counseling rate was higher in ANC clinic in this study compared to different studies reported in India and Africa(2,3,5–7) whereas the overall counseling rate was lagging behind. Main reasons behind the low counseling rate were round-the-clock (24 h) unavailability of counseling and testing services.
The overall testing rate found in this study was 83.13% among the counseled mothers which meets the WHO-suggested target >80% counseling rate which is considered very well. The testing rate was higher compared to most of the studies conducted in India and South Africa except Welty et al.′s work and UNGASS India report by NACO. The major reason for the failure of HIV testing was inadequate supply of HIV kits whereas in most of the studies from India and Africa, it was due to refusal for HIV testing by the couple.(2,3,6,7)
The NVP dispensing rates were 29.72% for HIV positive mothers and 85.4% for their children which were lagging behind most of the studies from South Africa, Cameroon, Thailand, and India. The main reason for the low NVP dispensing rate was HIV positive mothers opting for home delivery and delivering their child where ART facility was not available. Majority of cases were deprived of PPTCT services due to unavailability of NVP and lack of awareness among the health workers. Among the babies of HIV positive mothers who received full coverage of the PPTCT program, 85% HIV negative status was achieved which indicates the protective role of NVP in MTCT. A similar observation was also found by Doherty et al. and Welty et al.(6,7)
Conclusion
Majority of the pregnant women who came to the labor room directly were deprived of the program (PPTCT) coverage. Although the HIV testing rate met the WHO target which was excellent but the NVP dispensing rate lagged far behind.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very much grateful to WBSACS, technicians and Councilor of the PPTCT unit of North Bengal Medical College for their full cooperation.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.Report on the global AIDS epidemic, year 2008. UNAIDS/WHO; 2006. [Last accessed on 2009 Nov 09]. unaids.org. [Internet] Available from: http://www.unaids.org/en/KnowledgeCentre /HIVData/ GlobalReport/2008/default.asp . [Google Scholar]
- 2.Progress Report on the Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS; United Nations General Assembly Special Session (UNGASS) on HIV/AIDS. NACO, GOI; 2005. [Last accessed on 2009 Nov 09]. unaids.org. [Internet] Available from: http://www.data.unaids.org/.../Report/.../2006_country_progress_report_india_en.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- 3.nacoonline.org. [internet] Feasibility study of administering short-term AZT intervention among HIV infected mothers to prevent mother- to- child transmission of HIV in India. 2001. [Last accessed on 2009 Nov 09]. Available from: http://www.naco.nic.in/nacp/pmtct.htm .
- 4.National guideline to monitoring and evaluating programmes for the prevention of HIV in infant and young children. UNAIDS, WHO, CDC, UNICEF, NACO; 2004. [Last accessed on 2009 Nov 09]. who.int-[internet] Available from: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/prev_care/en/nationalguide young children.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rutenberg N, Baek C, Kalibala S, Rosen J. UNICEF. New York: HIV/AIDS Working Paper; 2003. Evaluation of United Nations supported Pilot Projects for the Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV: Overview of Findings.HIV/AIDS Working Paper. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Welty TK, Bulterys M, Welty ER, Tih PM, Ndikintum G, Nkuoh G, et al. Integrating Prevention of Mother-to-Child HIV Transmission Into Routine Antenatal Care: The Key to Program Expansion in Cameroon. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;40:486–93. doi: 10.1097/01.qai.0000163196.36199.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Doherty T, Basser M, Donohue S, Kamoga N, Stoop N, Williamson L, et al. Childrencount.ci.org.za. An Evaluation of the Prevention of Mother-to-child Transmission (PMTCT) of HIV Initiative in South Africa: Lessons and Key Recommendations. 2003. Sep, [Last accessed on 2009 Nov 09]. Available from: from:http://www.childrencount.ci.org.za/uploads/NSP-PMTCT-access-to-HIV-testing-inpregnant-women.pdf .


