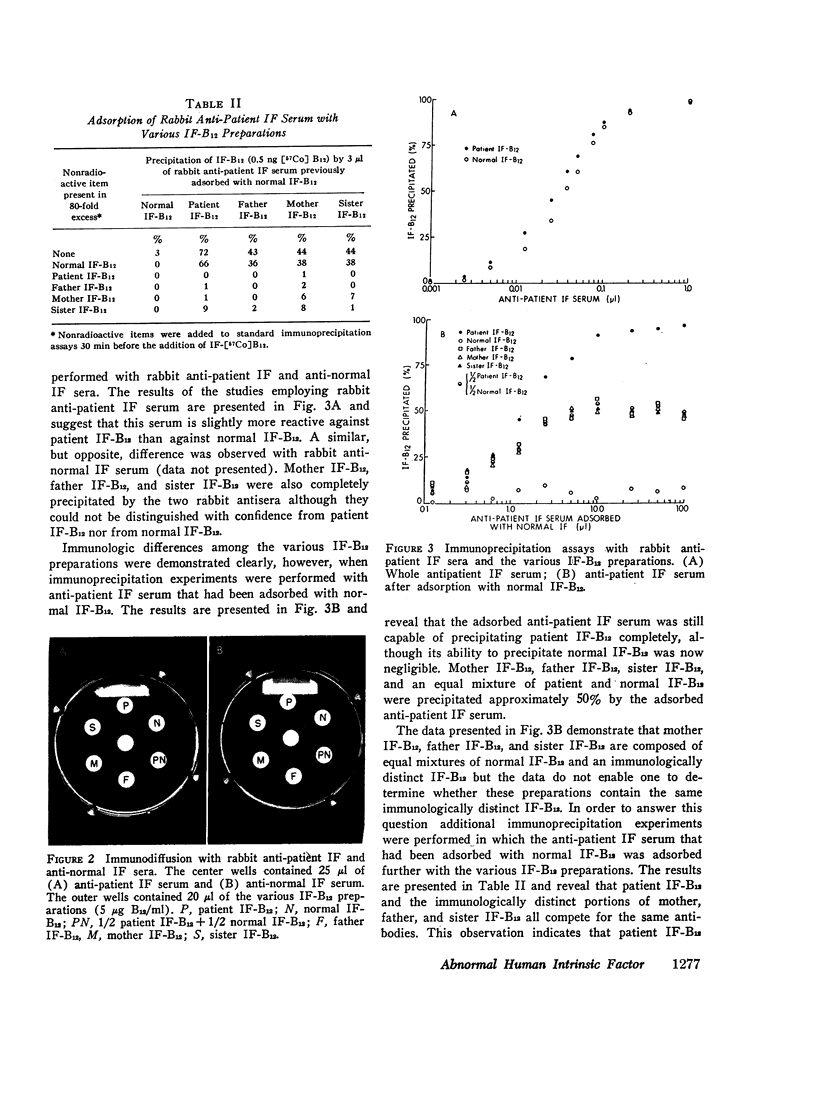
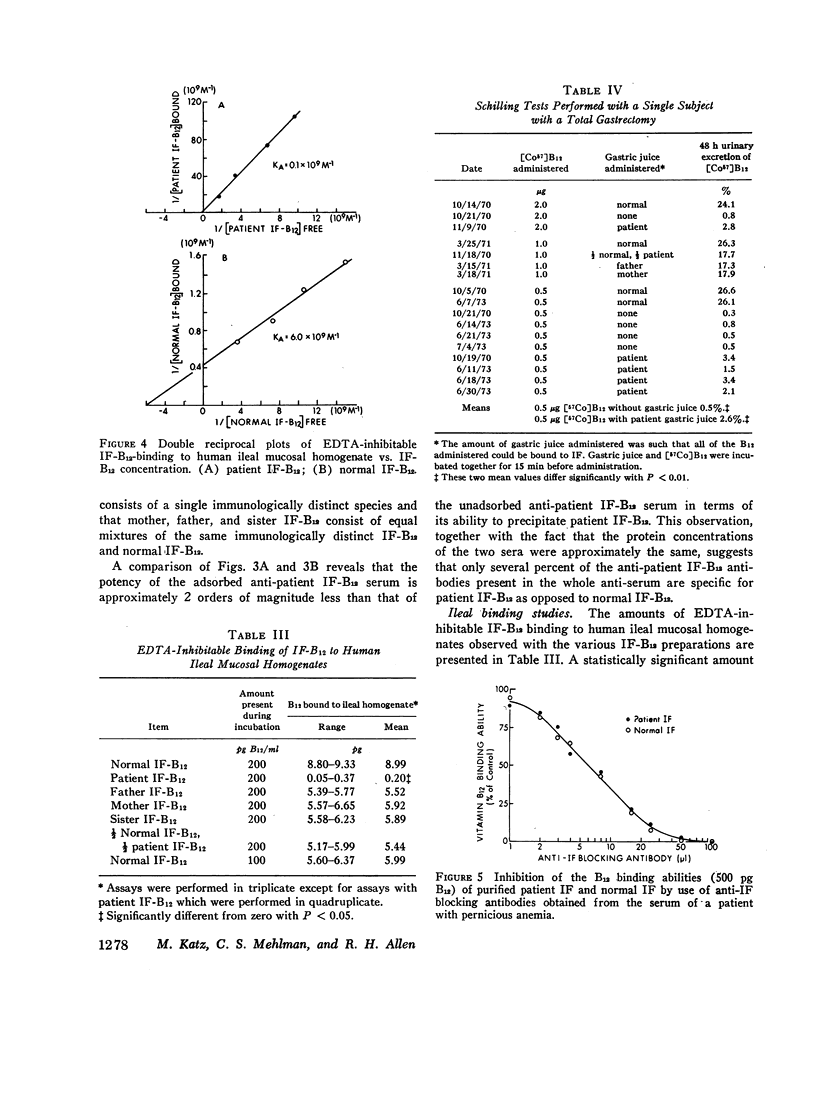
Abstract
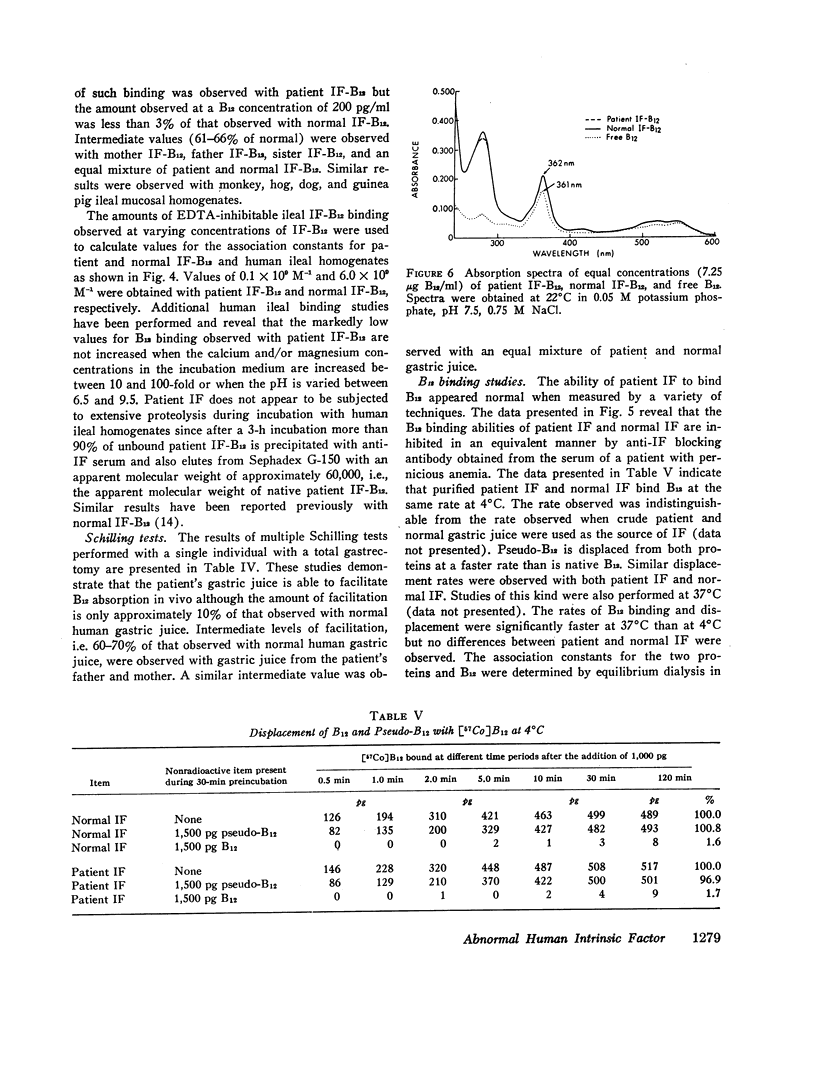
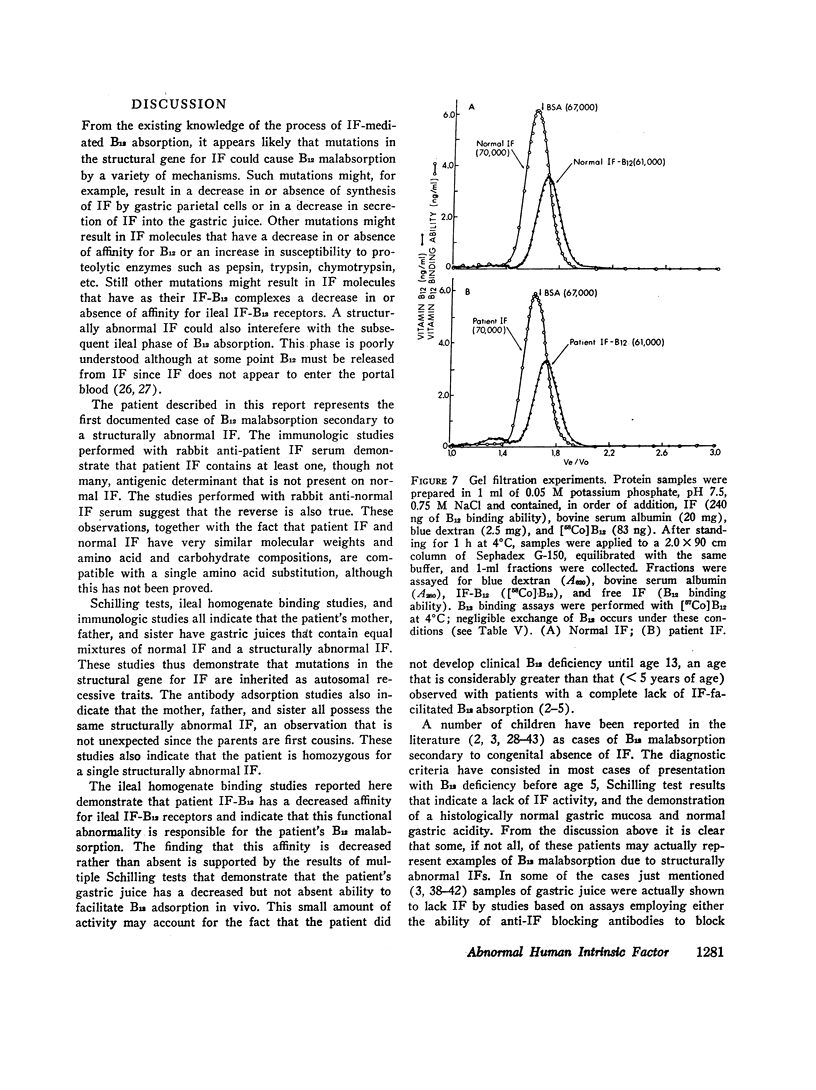
A patient has been described previously who presented at age 13 with vitamin B12 (B12) deficiency secondary to a functionally abnormal intrinsic factor (IF). IF has now been isolated from the gastric juice of the patient, his sister, and both parents, who are first cousins, by using affinity chromatography on B12-Sepharose. Patient IF appeared normal in terms of (a) B12 binding, (b) mol wt, (c) total amino acid and carbohydrate composition, and (d) immunodiffusion with rabbit anti-patient and anti-normal IF sera. After adsorption with normal IF, however, anti-patient IF serum precipitated the various IFs as follows: patient IF (> 95%); mother, father, and sister IF (50%); and normal IF (< 10%). Additional adsorption with mother, father, or sister IF completely inhibited the precipitation of patient IF. The association constant determined for patient IF-B12 and human ileal mucosal homogenates (0.1 × 109 M-1) was 60-fold lower than that determined with normal IF-B12 (6.0 × 109 M-1). Intermediate amounts of ileal IF-B12 binding were observed with mother, father, and sister IF-B12. These in vitro studies were supported by multiple Schilling tests, performed with a totally gastrectomized volunteer, that gave the following mean urinary excretions of [57Co]B12: free B12 (0.5%); + patient gastric juice (2.6%); + mother or father gastric juice (17%); and + normal gastric juice (26%). These studies demonstrate that the patient is homozygous and that the mother, father, and sister are heterozygous for a structurally abnormal IF that has a markedly decreased, but not absent, affinity for ileal IF-B12 receptors. These studies also indicate that the B12 and ileal binding sites are located on different portions of the IF molecule.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARDEMAN S., CHANARIN I., BERRY V. STUDIES ON HUMAN GASTRIC INTRINSIC FACTOR: OBSERVATIONS ON ITS POSSIBLE ABSORPTION AND ENTERO-HEPATIC CIRCULATION. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jan;11:11–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. 3. Purification and properties of human plasma transcobalamin II. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7709–7717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. I. Preparation and properties of vitamin B12-sepharose. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7695–7701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Majerus P. W. Isolation of vitamin B12-binding proteins using affinity chromatography. II. Purification and properties of a human granulocyte vitamine B12-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7702–7708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Mehlman C. S. Isolation of gastric vitamin B 12 -binding proteins using affinity chromatography. I. Purification and properties of human intrinsic factor. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3660–3669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. H., Mehlman C. S. Isolation of gastric vitamin B 12 -binding proteins using affinity chromatography. II. Purification and properties of hog intrinsic factor and hog nonintrinsic factor. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3670–3680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Major human erythrocyte glycoprotein spans the cell membrane. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):229–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio231229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEMENT D. H., NICHOL C. A., WELCH A. D. A case of juvenile pernicious anemia: study of the effects of folic acid and vitamin B12. Blood. 1961 May;17:618–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper B. A., White J. J. Absence of intrinsic factor from human portal plasma during 57CoB12 absorption in man. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jan;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimson S. B. Juvenile pernicious anaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Apr;41(216):216–220. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.216.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTLIEBLAU K. S., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. RAPID CHARCOAL ASSAY FOR INTRINSIC FACTOR (IF), GASTRIC JUICE UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY, ANTIBODY TO IF, AND SERUM UNSATURATED B12 BINDING CAPACITY. Blood. 1965 Jun;25:875–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASBECK R., GORDIN R., KANTERO I., KUHLBACK B. Selective vitamin B12 malabsorption and proteinuria in young people. A syndrome. Acta Med Scand. 1960 Jul 15;167:289–296. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1960.tb03549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gräsbeck R. Intrinsic factor and the transcobalamins with reflections on the general function and evolution of soluble transport proteins. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1967;95:7–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS-JONES J. N., SWAN H. T., TUDHOPE G. R. Pernicious anemia without gastric atrophy and in the presence of free hydrochloric acid; report of a case. Blood. 1957 May;12(5):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., STREIFF R. R., SULLIVAN L. W. NOTES ON VITAMIN B12 ABSORPTION; AUTOIMMUNITY AND CHILDHOOD PERNICIOUS ANEMIA; RELATION OF INTRINSIC FACTOR TO BLOOD GROUP SUBSTANCE. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 Nov;43:679–687. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196411000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakami N., Neiman P. E., Canellos G. P., Lazerson J. Neonatal megaloblastic anemia due to inherited transcobalamin II deficiency in two siblings. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov 18;285(21):1163–1170. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111182852103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippe E. Changes in Stokes radius on binding of vitamin B12 to human intrinsic factor and transcobalamins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 12;208(2):337–339. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90255-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Alpers D. H., Burger R. L., Mehlman C. S., Allen R. H. Characterization of ileal vitamin B12 Binding using homogeneous human and hog intrinsic factors. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3074–3083. doi: 10.1172/JCI107506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IMERSLUND O. Idiopathic chronic megaloblastic anemia in children. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1960 Jan;49(Suppl 119):1–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., Cullen D. R., Scarth L., Simpson J. D. Intrinsic-factor secretion assessed by direct radioimmunoassay and by total-body counting in patients with achlorhydria and in acid secretors. Lancet. 1968 Jul 27;2(7561):184–188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92620-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M., Lee S. K., Cooper B. A. Vitamin B 12 malabsorption due to a biologically inert intrinsic factor. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 31;287(9):425–429. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208312870902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBERT H. P., PRANKERD T. A., SMELLIE J. M. Pernicious anaemia in childhood. A report of two cases in one family and their relationship to the aetiology of pernicious anaemia. Q J Med. 1961 Jan;30:71–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGLEY L., LITTLE J. A., STEVENSON T. D. Pernicious anemia in childhood. N Engl J Med. 1956 Dec 27;255(26):1219–1223. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195612272552603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIKIN S. L. Pernicious anemia in childhood. Pediatrics. 1960 Jan;25:91–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampkin B. C., Mauer A. M. Congenital pernicious anemia with coexistent transitory intestinal malabsorption of vitamin B12. Blood. 1967 Oct;30(4):495–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE O. R., SULLIVAN L. W., JEFFRIES G. H., SILVER R. H. PERNICIOUS ANEMIA IN CHILDHOOD. N Engl J Med. 1965 May 13;272:981–986. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196505132721901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLIN D. L., BAKER S. J., DONLACH I. Addisonian pernicious anaemia without gastric atrophy in a young man. Br J Haematol. 1955 Jul;1(3):278–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1955.tb05510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY E. A. JUVENILE PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. CASE IN AMERICAN INDIAN GIRL. Northwest Med. 1965 Mar;64:191–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholl B., Egan B. Congenital pernicious anemia: effects on growth, brain, and absorption of B12. Pediatrics. 1968 Jul;42(1):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. R., Bloom G. E., Streiff R. R., LoBuglio A. F., Diamond L. K. Juvenile "congenital" pernicious anemia. Clinical and immunologic studies. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 3;275(18):978–983. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611032751802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISNER E. H., Jr, WOLFF J. A., McKAY R. J., Jr, DOYLE E. F. Juvenile pernicious anemia. Pediatrics. 1951 Jul;8(1):88–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPURLING C. L., SACKS M. S., JIJI R. M. JUVENILE PERNICIOUS ANEMIA. N Engl J Med. 1964 Nov 5;271:995–1003. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196411052711907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SULLIVAN L. W., HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. IN VITRO ASSAY FOR HUMAN INTRINSIC FACTOR. J Clin Invest. 1963 Sep;42:1443–1458. doi: 10.1172/JCI104829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Andrews E. P., Marchesi V. T. Human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein: a re-evaluation of the molecular weight as determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UKYO S., COOPER B. A. INTRINSIC FACTOR-LIKE ACTIVITY IN EXTRACTS OF GUINEA PIG INTESTINE. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jan;208:9–13. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATERS A. H., MURPHY M. E. Familial juvenile pernicious anaemia: a study of the hereditary basis of pernicious anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1963 Jan;9:1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1963.tb05435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun D. J., Lee H., Chun G. P., Lee K. Y. Juvenile pernicious anemia in sisters. Yonsei Med J. 1967;8:71–76. doi: 10.3349/ymj.1967.8.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]