Abstract
The effects of acute volume expansion and of intraluminal administration of cholera toxin have been examined in rabbit jejunum.
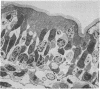
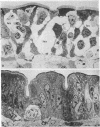
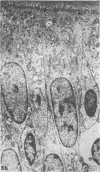
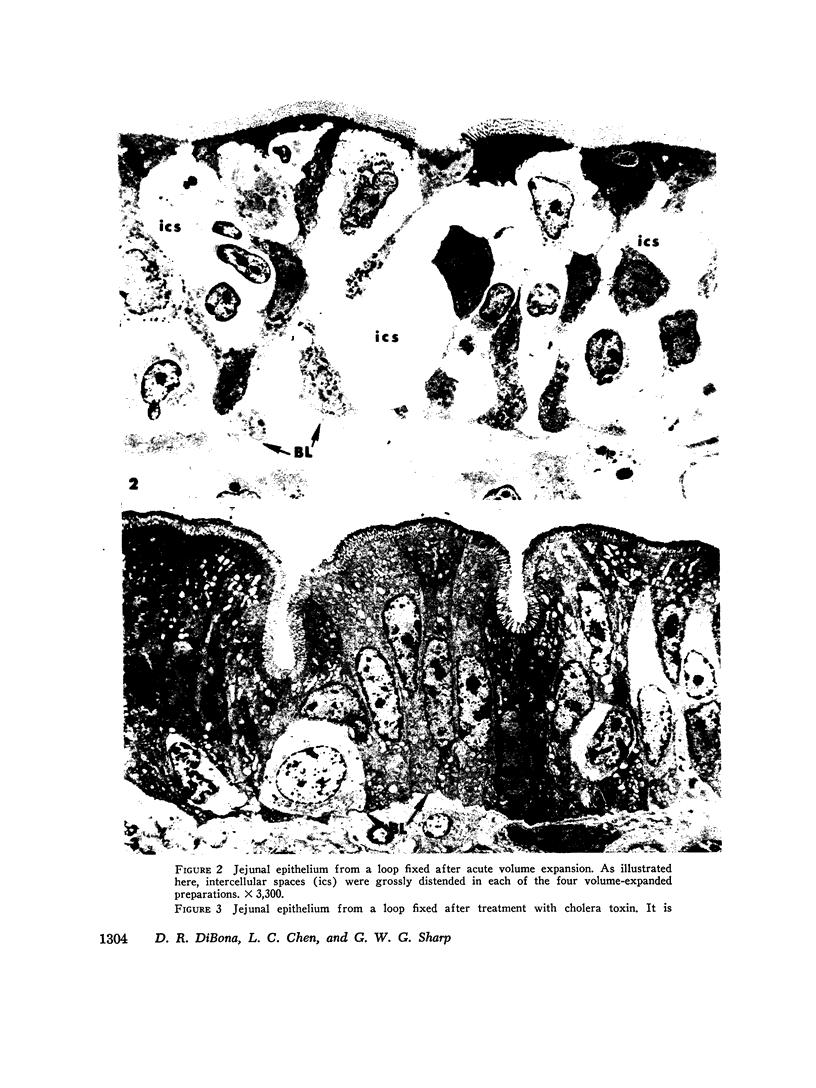
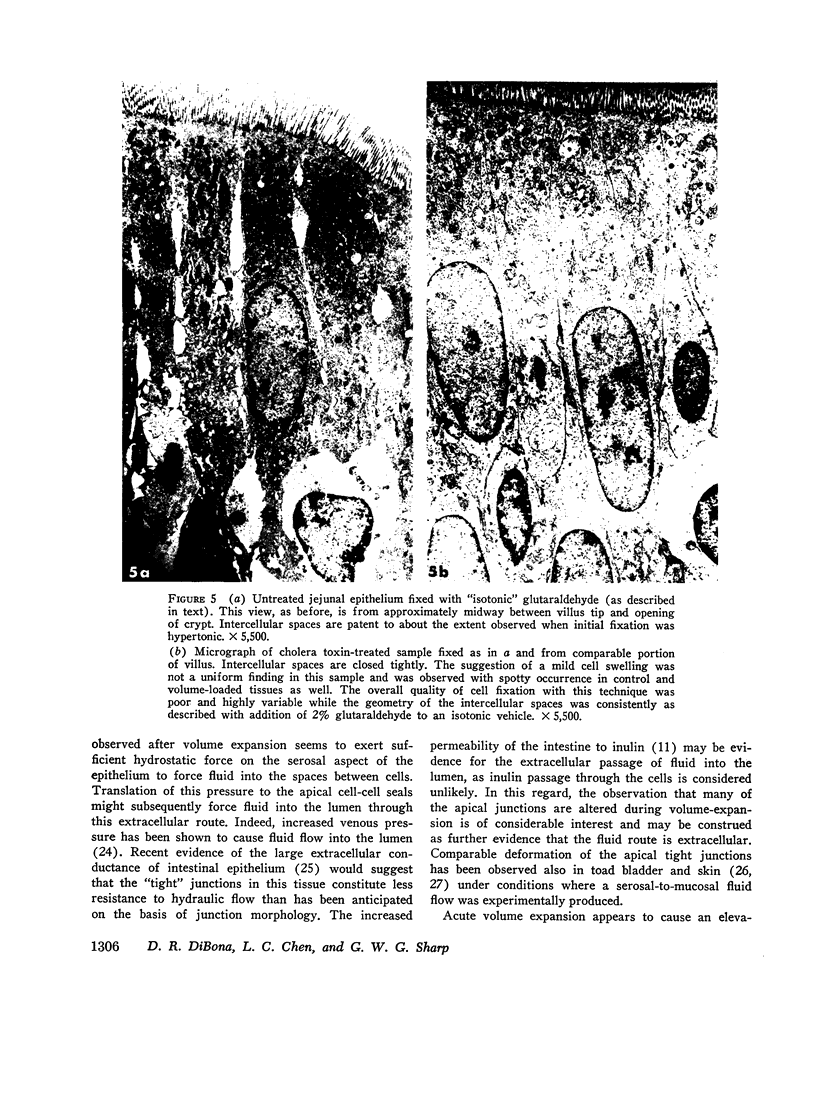
Acute volume expansion was shown to reverse the normal reabsorptive flux of water and cause significant fluid secretion. Phase and electronmicroscopic examination of the jejunal epithelium showed that marked distension of the intercellular spaces had occurred. Examination of the jejunal epithelium after treatment with cholera toxin showed that, in association with high rates of fluid secretion, the intercellular spaces were extremely small and lateral membranes of adjacent cells were in close apposition to one another. Thus the mechanisms of fluid secretion in these two situations would appear to be quite different. The secretion associated with volume expansion, and accompanied by a rise in venous pressure and bullous deformations of terminal junctions, could well be due to hydrostatic pressure applied through intercellular channels. The secretion of cholera appears to be unrelated to hydrostatic pressure and is more likely due to body-to-lumen active ion transport.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bone Q., Ryan K. P. Osmolarity of osmium tetroxide and glutaraldehyde fixatives. Histochem J. 1972 Jul;4(4):331–347. doi: 10.1007/BF01005008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., MACINTOSH J. R. A model system for biological water transport. Nature. 1962 Jan 27;193:347–348. doi: 10.1038/193347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. C., Jr Cholera enterotoxin--recent investigations yield insights into transport processes. Am J Med. 1971 Jan;50(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Rohde J. E., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in human cholera. Lancet. 1971 May 8;1(7706):939–941. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Rohde J. E., Sharp G. W. Properties of adenyl cyclase from human jejunal mucosa during naturally acquired cholera and convalescence. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):731–740. doi: 10.1172/JCI106867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R., Civan M. M., Leaf A. The anatomic site of the transepithelial permeability barriers of toad bladder. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):1–7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R., Civan M. M. Pathways for movement of ions and water across toad urinary bladder. I. Anatomic site of transepithelial shunt pathways. J Membr Biol. 1973;12(2):101–128. doi: 10.1007/BF01869994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R., Civan M. M. The effect of smooth muscle on the intercellular spaces in toad urinary bladder. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):235–244. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R. Passive intercellular pathway in amphibian epithelia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 9;238(84):179–181. doi: 10.1038/newbio238179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Bossert W. H. Functional consequences of ultrastructural geometry in "backwards" fluid-transporting epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):694–702. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Bossert W. H. Standing-gradient osmotic flow. A mechanism for coupling of water and solute transport in epithelia. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Sep;50(8):2061–2083. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.8.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Production of highly purified choleragen and choleragenoid. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(Suppl):63+–63+. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.supplement.s63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Ionic conductances of extracellular shunt pathway in rabbit ileum. Influence of shunt on transmural sodium transport and electrical potential differences. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Mar;59(3):318–346. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.3.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Chen L. C., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in canine cholera: correlation with fluid accumulation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):377–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim A. A., Lifson N. Effects of pressure on water and solute transport by dog intestinal mucosa in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1969 Feb;216(2):276–284. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.2.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. T., Jr, Blair N. P. Intestinal transport of water and electrolytes during extracellular volume expansion in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2569–2579. doi: 10.1172/JCI106757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys M. H., Earley L. E. The mechanism of decreased intestinal sodium and water absorption after acute volume expansion in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2355–2367. doi: 10.1172/JCI106734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. I., Davis J. O. Evidence from cross circulation studies for a humoral mechanism in the natriuresis of saline loading. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Apr;121(4):1058–1063. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeschke K., Bentzel C. J., Csáky T. Z. Asymmetry of osmotic flow in frog intestine: functional and structural correlation. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jun;218(6):1723–1731. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.6.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Carpenter C. C., Jr Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin and its mode of action. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Mar;35(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/br.35.1.1-13.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richet G., Hornych A. The effect of an expansion of extracellular fluids on net Na flux in the jejunum of rats. An experimental model for the study of the third factor. Nephron. 1969;6(3):365–378. doi: 10.1159/000179739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormey J. M., Diamond J. M. The ultrastructural route of fluid transport in rabbit gall bladder. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Sep;50(8):2031–2060. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.8.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]