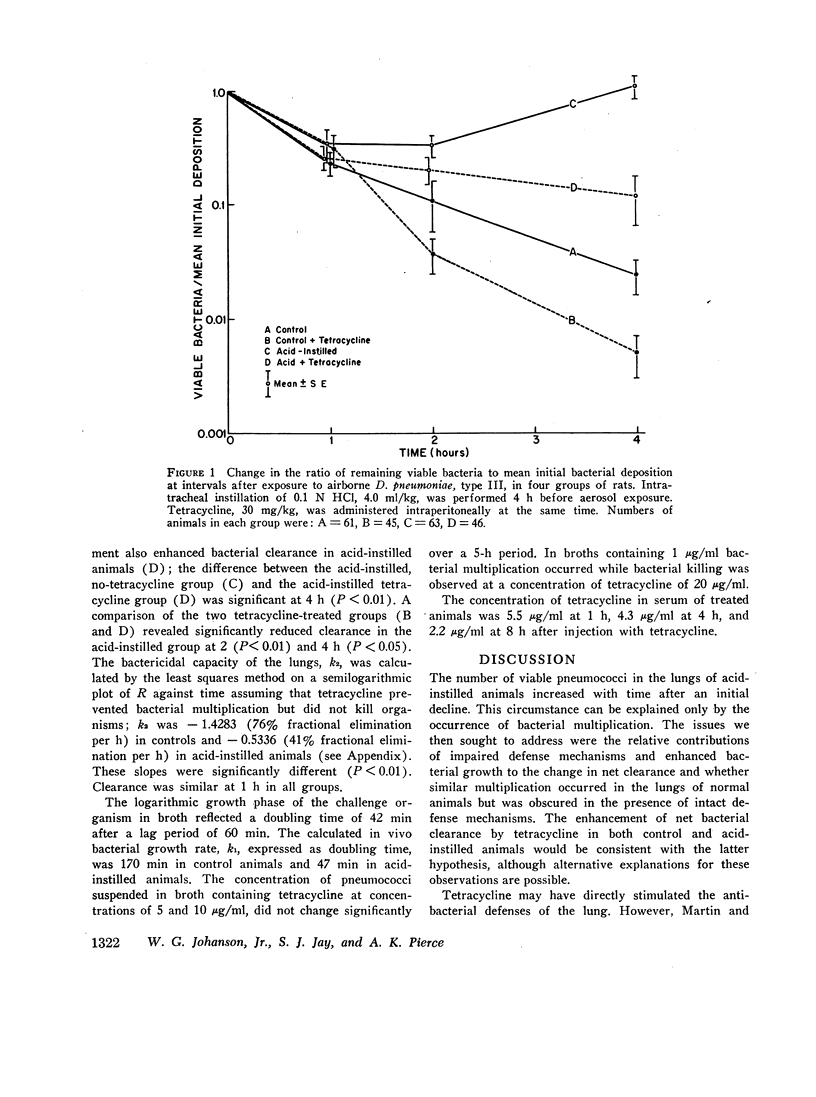
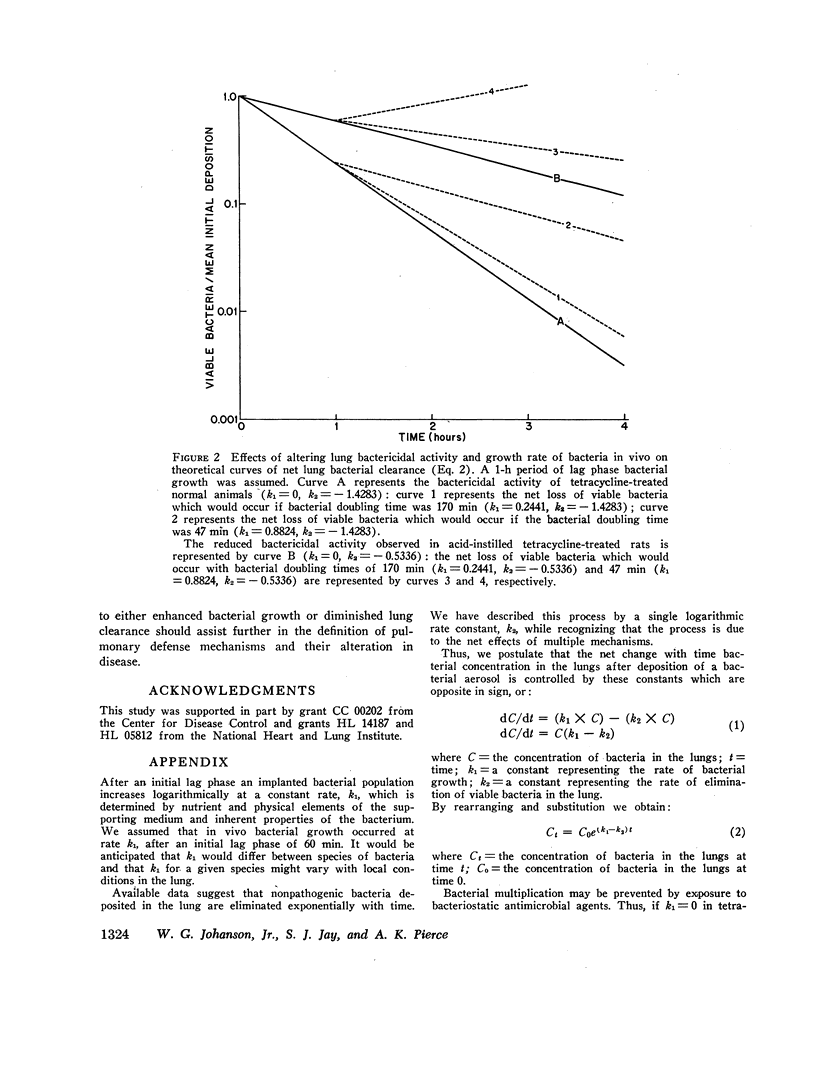
Abstract
Lung clearance of Diplococcus pneumoniae was markedly reduced in rats with acute hemorrhagic pulmonary edema produced by instillation of hydrochloric acid. Bacterial clearance was enhanced in both control and acid-instilled animals by pretreatment with a bacteriostatic antibiotic, tetracycline, 30 mg/kg. From these data the contributions of bacterial multiplication and bacterial elimination to net lung bacterial clearance were estimated. In control animals the constant for exponential bacterial elimination was -1.4283 (fractional clearance = 76% per h), and the doubling time for the pneumococcus was 170 min. In acid-instilled rats the elimination constant was -0.5336 (fractional clearance = 41% per h), and the doubling time of the pneumococcus was 47 min, approximating the doubling time of 42 min observed with pneumococci grown in broth.
These results indicate that, in the case of pneumococci, both bacterial elimination and bacterial growth contribute to lung bacterial clearance in normal animals as well as animals with damaged lungs. In the present study changes in both parameters were required to explain the observed results in acid-instilled animals. The pulmonary pathogenicity of some bacterial species may be determined by their capacity for growth in the lung, since infection of the lung occurs when bacterial multiplication exceeds the rate of elimination of viable organisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GREEN G. M., KASS E. H. FACTORS INFLUENCING THE CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA BY THE LUNG. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:769–776. doi: 10.1172/JCI104961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN G. M., KASS E. H. THE ROLE OF THE ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGE IN THE CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA FROM THE LUNG. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:167–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Green G. M., Seamans C. The effect of silicosis on the antibacterial defense mechanisms of the murine lung. J Infect Dis. 1969 Aug;120(2):210–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.2.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Munson E. S., Eagle C., Martucci R. W., Hoeprich P. D. The effects of anesthetic agents on murine pulmonary bactericidal activity. Anesthesiology. 1971 Apr;34(4):344–352. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197104000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Tyler W. S., Hoeprich P. D., Eagle C. Ozone and the antibacterial defense mechanisms of the murine lung. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Jun;127(6):1099–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Goldstein E. A method for quantitating intrapulmonary bacterial inactivation in individual animals. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Oct;68(4):669–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Kass E. H. The influence of bacterial species on pulmonary resistance to infection in mice subjected to hypoxia, cold stress, and ethanolic intoxication. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Jun;46(3):360–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M. Patterns of bacterial clearance in murine influenza. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBBY G. L., LENERT T. F., PIKULA D., KISELUK M., HUDDERS M. E. The antimicrobial action of terramycin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1950 Sep;53(2):266–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1950.tb42158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Martin C. H. Effect of tetracycline, polymyxin B, and rifampin on phagocytosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 May-Jun;11(3):418–422. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970113418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. E., Southern P. M., Pierce A. K., Fallis B. D., Sanford J. P. Pulmonary clearance of gram-negative bacilli. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 May;69(5):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENZI G. A., BERMAN L., FIRST M., KASS E. H. A QUANTITATIVE STUDY OF THE DEPOSITION AND CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA IN THE MURINE LUNG. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:759–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI104960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENZI G. A., GUARNERI J. J., ENDRIGA R. B. IMPORTANT DETERMINANTS IN PULMONARY RESISTANCE TO BACTERIAL INFECTION. Med Thorac. 1965;22:48–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy P. S., Green G. M. A stochastic model of the bactericidal activity of the lung. J Theor Biol. 1968 Oct;21(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow P. E., Gibb F. R., Gazioglu K. M. A study of particulate clearance from the human lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Dec;96(6):1209–1221. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.6.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rylander R. Pulmonary defence mechanisms to airborne bacteria. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1968;306:1–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E. Interaction between phagocytes and pathogenic microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Jun;20(2):94–132. doi: 10.1128/br.20.2.94-132.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. J., Yin E. J. Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):573–579. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.573-579.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. M., Jr, Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Comparison of the pulmonary bactericidal capacity of mice and rats against strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Feb;21(2):377–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. M., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Clearance of Serratia marcescens from Lungs of Normal Mice. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):187–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.187-188.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


