Abstract
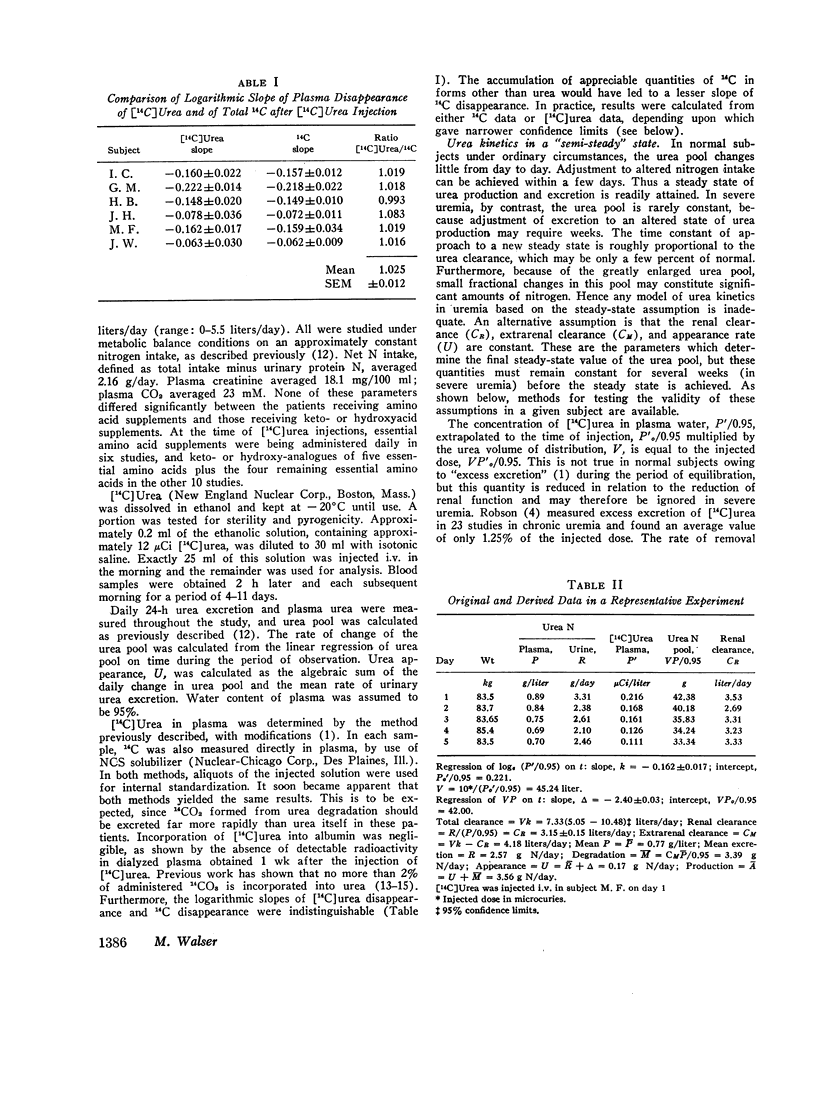
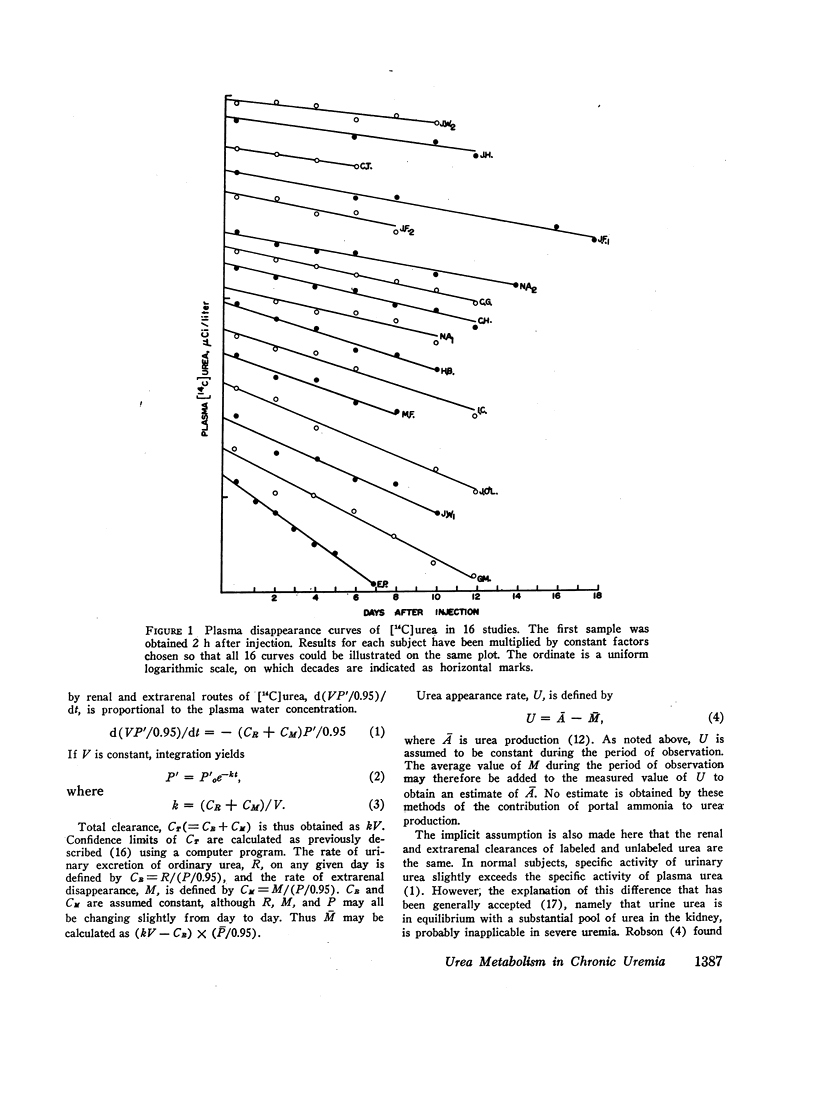
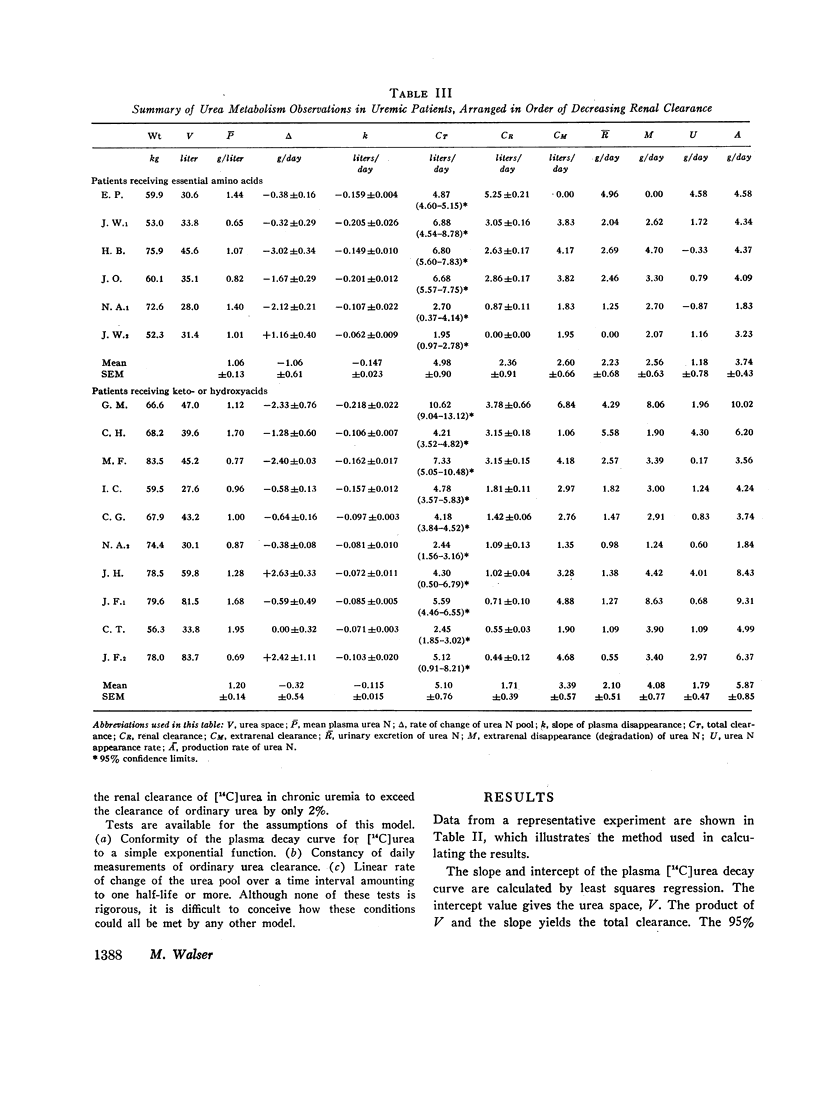
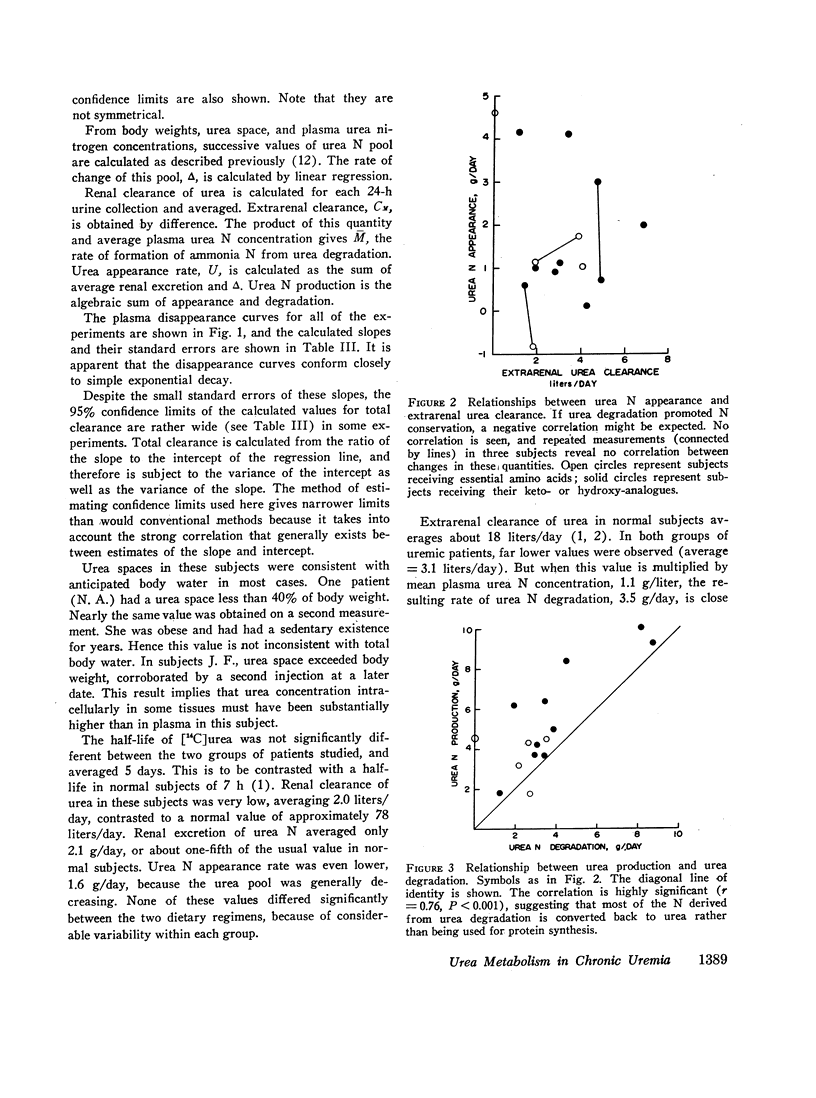
Urea degradation was measured during 16 experiments in 13 chronic uremic patients being treated with essential amino acids or their analogues. [14C]Urea was injected i.v. and the clearance of labeled urea from its volume of distribution was compared with the simultaneous renal clearance of ordinary urea, which averaged 2.0 liters/day. The difference, extrarenal clearance of urea, averaged 3.1 liters/day as compared with a previously reported mean of 18 liters/day in normal subjects. Thus urea-splitting activity in the gut of uremic subjects expressed in these terms is far less than in normal individuals. Nevertheless, the amount of ammonia N formed from urea in these patients, 3.5 g/day, is not significantly different from normal, owing to their elevated plasma urea. In the same subjects, urea appearance rate was measured as the sum of urea excretion and the daily change in the urea pool. No negative correlation was noted between urea appearance and urea degradation, as might be expected if portal ammonia were being utilized for protein synthesis. However, urea production was positively correlated (r = 0.76) with urea degradation, suggesting that most of the resulting portal ammonia is converted back to urea. The results fail to support the view that degradation of urea in the gut promotes N conservation in uremic subjects maintained on low protein diets.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown C. L., Hill M. J., Richards P. Bacterial ureases in uraemic men. Lancet. 1971 Aug 21;2(7721):406–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIORDANO C. USE OF EXOGENOUS AND ENDOGENOUS UREA FOR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN NORMAL AND UREMIC SUBJECTS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Aug;62:231–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERIN M., WALSER M. The reliability of estimated rates of production in simple turnover experiments. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Jul;70(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. A., Smallwood R. A., Craigie A., Rosenoer V. M. The enterohepatic circulation of urea nitrogen. Clin Sci. 1969 Dec;37(3):825–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLANE A. S. MEASUREMENT OF SYNTHESIS RATES OF LIVER-PRODUCED PLASMA PROTEINS. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:277–290. doi: 10.1042/bj0890277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picou D., Phillips M. Urea metabolism in malnourished and recovered children receiving a high or low protein diet. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Nov;25(11):1261–1266. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.11.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGOECZI E., IRONS L., KOJ A., MCFARLANE A. S. ISOTOPIC STUDIES OF UREA METABOLISM IN RABBITS. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:521–532. doi: 10.1042/bj0950521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards P., Metcalfe-Gibson A., Ward E. E., Wrong O., Houghton B. J. Utilisation of ammonia nitrogen for protein synthesis in man, and the effect of protein restriction and uraemia. Lancet. 1967 Oct 21;2(7521):845–849. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92588-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards P. Nutritional potential of nitrogen recycling in man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Jun;25(6):615–625. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.6.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild M. A., Oratz M., Zimmon D., Schreiber S. S., Weiner I., Van Caneghem A. Albumin synthesis in cirrhotic subjects with ascites studied with carbonate-14C. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):344–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI105990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSER M., BODENLOS L. J. Urea metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1959 Sep;38:1617–1626. doi: 10.1172/JCI103940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walser M., Coulter A. W., Dighe S., Crantz F. R. The effect of keto-analogues of essential amino acids in severe chronic uremia. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):678–690. doi: 10.1172/JCI107229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


