Abstract
Type III radical hysterectomy reported in 1974 by Piver, Rutledge, and Smith is considered worldwide by many as the standard surgical therapy for invasive cervical carcinoma stage IB and IIA. With the increasing number of robotic surgeries being performed for early stage cervical cancer worldwide, the purpose of the paper is to present our personal perspective of the 21st century role of Piver-Rutledge type III radical hysterectomy for stage IB cervical cancer in the era of robotic surgery using the da Vinci robot.
Keywords: Cervix cancer, Type III radical hysterectomy, Robotic surgey
INTRODUCTION
Since the mid 20th century, radical hysterectomy has become the primary treatment for early stage invasive cervical cancer. Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer in women worldwide and the most common cancer in many developing countries.1 Because cervical cancer affects women at a much younger age than other gynecologic malignancies including ovarian, endometrial, vulvar and vaginal cancers, the best choice of therapy can have an important impact for a significantly longer period of their lives.
HISTORY PRIOR TO THE DA VINCI ROBOTIC ERA
The original staging for cervical cancer was introduced in 1928 and from 1950 to 1994 had seven revisions. In 1994, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) classifications revised stages IA1, IA2, IB1, and IB2. The latest FIGO classification in 2009, approved by the International Union Against Cancer (UICC), American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC), and FIGO, the only change relative to the radical hysterectomy was the subdivision of II into IIA1 and IIA2 (Table 1).2
Table 1.
2009 FIGO stage IB and IIA
From Pecorello S, et al. Int J Gynecol Obstet 2009; 105: 107-8.2
With the FIGO 1974 changes in classification of stage IA1, IA2, IB1, and IB2, we reported in The Twenty-First Century Role of the Piver Type II Hysterectomy in FIGO Stage IA and IB Cervical Cancer.3 We concluded that it is our opinion based on this review that FIGO stage IA1 without lymphovascular space invasion is treated by type I hysterectomy without lymphadenectomy but that type II hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy would be a reasonable choice for stage IA1 with lymphovascular space involvement. Also, all stage IA2 patients with or without lymphovascular space involvement are suitable for type II hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy.
We also concluded in our 2008 paper that until imaging allows for possible detection of early parametrial invasion, that the type III radical hysterectomy plus pelvic lymphadenectomy in medically suitable patients is preferred treatment for stage IB1 cervical cancer but that patients with stage IB2 may be considered for type III hysterectomy with tailored postoperative radiation.
1994 CHANGES IN FIGO STAGE IB1 AND IB2 CERVICAL CANCER
Prior to the 1994 changes in cervical cancer into IB1 (less than 4 cm) and IB2 (greater than 4 cm), FIGO stage IB consisted of macroscopic lesions limited to the cervix. In 1975 we reported on 145 women who underwent type II and type III hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy.4 For those patients with cervical tumors equal to or less than 3 cm in diameter had an incidence of lymph node metastasis of 22% as compared to a much higher 35.1% for patients with tumors greater than 3 cm. Even more striking was the fact that for patients with tumors 1 cm less in diameter, the five year survival was 84.1% and 90.1% for patients with tumors 2-3 cm and this decreased significantly to a five year survival of only 69.9% for tumors measuring 4-5 cm and 60% for tumors equal or greater than 6 cm in greatest diameter (Table 2).4 This was the basis for our 2008 conclusion that "until improved imaging allows for a possible detection of early parametrial invasion, the type III hysterectomy plus pelvic lymphadenectomy in medically suitable patients is preferred treatment for IB1. Patients with IB2 may be considered for a type III hysterectomy with tailored postoperative radiation."
Table 2.
Size of cervical cancer and 5 year survival stage IB radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy
From Piver MS and Chung MS. Obstet Gynecol 1975; 46: 507-10, with permission from Obstetrics & Gynecology.4
TYPE II AND TYPE III PIVER-RUTLEDGE RADICAL HYSTERECTOMY
1. Type II radical hysterectomy
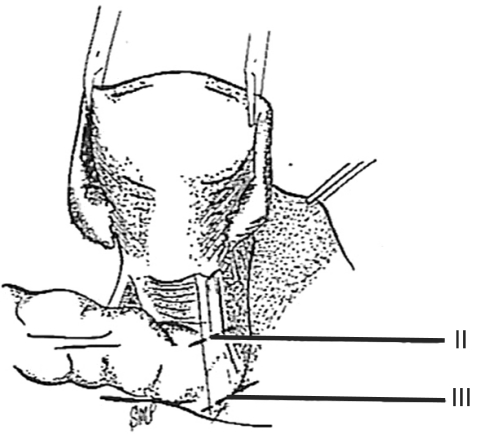
In 1974 we described five types (classes) of hysterectomies used for treating cervical cancer.5 In the type II hysterectomy the uterine artery is divided medial to the ureters thus limiting the dissection of the ureters from the cardinal ligament thus preserving the blood supply to the ureter with a decreased chance of devascularizing the ureter. The purpose of the type II hysterectomy is to remove more paracervical tissue, while still preserving the blood supply to the ureters and bladder. The ureters are freed from the paracervical tissue but are not dissected out of the pubovesical ligament. Ligation of the uterine artery just medial to the ureters insures preservation of the distal ureteral blood supply (Fig. 1).5 The uterosacral ligaments are resected midway between the uterus and the sacral attachments (Fig. 2).5 The medial half of the cardinal ligament is removed as is the upper one-third of the vagina (Figs. 3 and 4).5
Fig. 1.
In a class II hysterectomy the uterine artery is ligated medical to the ureter, whereas in a class III it is ligated as it originates from the internal iliac artery. From Piver MS, et al. Obstet Gynecol 1974; 44: 265-72, with permission from Obstetrics & Gynecology.5
Fig. 2.
In a class II hysterectomy the uterosacral ligaments are divided midway between the uterus and their sacral attachments. In a class III operation the uterosacral ligaments are excised at their sacral attachments. From Piver MS, et al. Obstet Gynecol 1974; 44: 265-72, with permission from Obstetrics & Gynecology.5
Fig. 3.
The medial one-half of the cardinal ligament is removed in a class II hysterectomy. In a class III operation the cardinal ligament is removed at the pelvic wall. From Piver MS, et al. Obstet Gynecol 1974; 44: 265-72, with permission from Obstetrics & Gynecology.5
Fig. 4.
The upper one-third of the vagina is removed in a class II hysterectomy and one-half in a class III procedure. Not illustrated is removal of three-fourths of the vagina in class IV hysterectomy. From Piver MS, et al. Obstet Gynecol 1974; 44: 265-72, with permission from Obstetrics & Gynecology.5
2. Type III radical hysterectomy
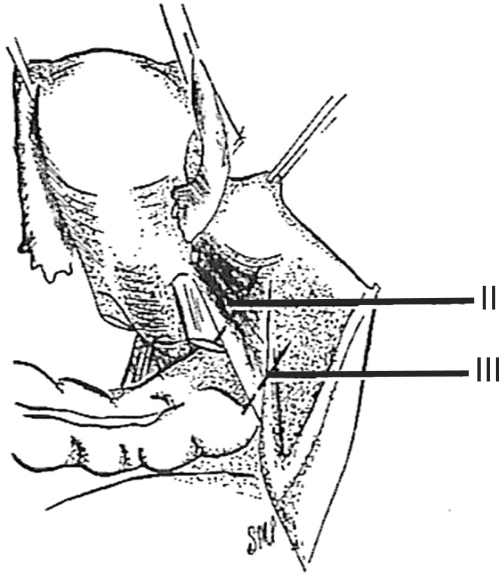
In 2007, Pikaart et al.6 in their paper on radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer stated that "the Piver type III radical hysterectomy is considered worldwide as the standard surgical therapy for invasive carcinoma stage IB and IIA." The aim of the type III hysterectomy is wide radical excision of the parametrial and paravaginal tissues. The uterine artery is ligated as it originates from the internal iliac artery (Fig. 1).5 Dissection of the ureter from the pubovesical ligament is completed to entry into the bladder except that a small lateral portion of the pubovesical ligament between the lower end of the ureter and the superior vesical artery is preserved, thus maintaining some blood supply to the distal ureter (Fig. 5).5 The uterosacral ligaments are excised at their sacral attachment (Fig. 2)5 and the cartilage is resected at the pelvic wall (Fig. 3).5 One-half of the vagina is removed (Fig. 4).5
Fig. 5.
In a class III hysterectomy the ureter is dissected from the pubovesicle ligament superiorly, medially, and inferiorly. A small lateral portion of the pubovesicle artery is preserved, thus maintaining some blood supply to the distal ureter. From Piver MS, et al. Obstet Gynecol 1974; 44: 265-72, with permission from Obstetrics & Gynecology.5
3. da Vinci robotic surgery era
Since Wertheim7 of Vienna described radical hysterectomy in 1990 and Meigs8 in 1951 began to perform pelvic lymphadenectomy with radical hysterectomy and our 1974 report of five classes of radical hysterectomy there were no major changes in surgical technique for early cervical cancer until Querleu et al.9 reported the first laparoscopic pelvic lymphadenectomy in cervical cancer in 1989. This was followed in 1992 by Nezhat et al.10 reporting the first case of cervical cancer treated by laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy.
The da Vinci Surgical System (Intuitive Surgical Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) was approved by the FDA for gynecologic surgery in 2005. With the increasing number of robotic surgeries being performed for early stage cervical cancer worldwide, the purpose of this paper is to present our personal perspective of the 21st century role of the Piver-Rutledge Type III radical hysterectomy for stage IB cervical cancer in the era of robotic surgery using the da Vinci robot.
Minimally invasive surgery via laparoscopy has been pursued by gynecologic oncologic surgeons since the early 1990s. The objective of using a minimally invasive approach for the treatment of early cervical cancer has been to decrease surgical morbidity while maintaining surgical and oncologic outcomes. Laparoscopic radical hysterectomy has been clearly shown to be safe and feasible for the treatment of early cervical cancer. Despite having comparable complication rates and long-term outcomes to open radical hysterectomy, laparoscopic radical hysterectomy has not received widespread adoption in gynecologic oncology. This is in large part due to obvious disadvantages of conventional laparoscopy including an unstable camera platform, two-dimensional visualization, lack of depth of perception, limited range of motion of the instruments, counterintuitive and poor surgical ergonomics, prolonged operating time, and steep learning curve.11-19
Robotic technology provided by da Vinci Surgical System is an advanced innovation aimed to overcome the shortcomings of conventional laparoscopy. The da Vinci surgical system offers the surgeon a stable, three-dimensional, magnified, high-resolution vision. The robotic instruments and camera are tele-controlled by the surgeon, while comfortably seated at the surgical console. Robotic instruments articulate with seven degrees of freedom and controlled with a wrist-like mechanism (Endowrist®, Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) that allows full replication of the range of motion of the surgeon's hand. Surgical dexterity and precision are by far superior compared to human hands as tremors are eliminated.11
Having the promise of addressing the disadvantages of laparoscopy, the application of robotic technology in gynecologic oncology has been growing rapidly worldwide since it was first introduced in the operating room. What follows is a summary of descriptive and comparative publications in the medical literature outlining the safety and feasibility of robotic radical hysterectomy for the treatment of early cervical cancer.
The first robotic-assisted radical hysterectomy was reported by Sert and Abeler20 in 2006 for the treatment of FIGO stage IB1 squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix in a 43-year-old patient. The operation lasted 445 minutes with an estimated blood loss was 200 mL. The authors concluded that performing robotic-assisted Piver type III hysterectomy was feasible and offered higher degree of precision compared to conventional laparoscopy.
In 2007, the same authors conducted a pilot case-control study that was designed to evaluate the feasibility and safety of robotic-assisted radical hysterectomy compared to total laparoscopic radical hysterectomy. Type II and type III hysterectomies were performed on 15 patients with diagnoses of early cervical carcinoma. Seven patients were treated with robotic-assisted radical hysterectomy compared to 8 patients who underwent conventional laparoscopic radical hysterectomy. No conversions to laparotomy were performed in either group. Median operative time was 241 and 300 minutes in the robotic and laparoscopic group respectively, (p=0.165). Lymph node retrieval, the size of the excised parametrial and vaginal tissue were similar in both groups. Duration of hospital stay (4 vs. 8 days) and estimated blood loss (71 vs. 160 mL) were significantly less in the robotic arm.21
The third series reporting on robotic radical hysterectomy was published by the group from South Korea in 2008. Kim et al.22 described 10 patients with FIGO stage IA2-IB1 cervical carcinoma who underwent robotic radical hysterectomies. All operations were completed successfully. Mean operative time was 207 minutes (range, 120 to 240 minutes). Mean estimated blood loss was 355 mL. No cases of ureteral injury or fistula formation were encountered.
The group from Mayo Clinic in Arizona published a comparative study of patients receiving robotic radical hysterectomy for the treatment of stage IA2-IB cervical cancer versus open or laparoscopic approaches. 27 patients undergoing robotic radical hysterectomy were included in this study and followed up for an average of 31.1 months. The investigators found that there was significantly less blood loss associated with the robotic group. The estimated blood loss was 133.1, 208.4, and 443.6 mL for robotic, laparoscopic and laparotomy groups respectively. The patients undergoing robotic surgery had shorter hospital stay when compared to the other two groups, 1.7, 2.4, 3.6 days respectively. Operative times were similar between the robotic and laparotomy groups (189 vs. 168 minutes), and significantly shorter than the laparoscopic group (220 minutes). There were no significant differences in the perioperative complications among the three groups. There were no cases of fistula formation or conversion to laparotomy in either robotic or laparoscopic groups.23
Fanning and colleagues reported their experience of performing robotic radical hysterectomy in 2008. Twenty patients were successfully treated with robotic radical hysterectomy for stage IA2-IIA cervical carcinoma. Mean operative time was 6.5 hours, median estimate of blood loss was 300 mL. All patients were discharged on the first postoperative day. Fistula formation was noted in one case and one patient developed intraoperative cystotomy.24
Nezhat et al.25 compared 30 patients who had laparoscopic radical hysterectomy versus 13 patients who underwent robotic radical hysterectomy from 2006 to 2008. The cases were those of newly diagnosed early cervical cancer, stage IAI to IIA. The authors did not find any significant differences with regard to patient characteristics and perioperative variables between the robotic and laparoscopic cohorts: operative time (323 vs. 318 minutes), estimated blood loss (157 vs. 200 mm), hospital stay (2.7 vs. 3.8 days). No conversion to laparotomy was required in the series. The only significant intraoperative complication encountered in either group was incidental cystotomy. No recurrence of the disease was noted after a mean follow-up of 12 months in the robotic group and 29 months in the laparoscopic group. The authors concluded that although there were no significant differences identified between the robotic and laparoscopic groups, the advantages associated with robotic technology such as endowrist action; precision, and superior visualization might allow an easier adoption of robotic approach to radical hysterectomy for gynecologic oncologic surgeons.
One of the largest case control studies of robotic assisted type III hysterectomy was conducted by the group from University of North Carolina. The investigators compared the operative outcomes of 51 consecutive patients who underwent robotic radical hysterectomy with 49 cases of open radical hysterectomy. Stage of the disease was FIGO IA1 to IIA with stage IBI cervical carcinoma being the predominant subgroup. Surprisingly, the operative time in the robotic group was significantly shorter than the laparotomy group (210.9 vs. 247 minutes, p=0.0002). The average estimated blood loss for patients who underwent robotic surgery was 96.5 mL compared with 416.8 mL for the laparotomy group (p<0.0001). Eight percent of the patients in the laparotomy group received blood transfusions versus no patients in the robotic cohort. Pelvic node retrieval was higher in the robotic group than the open cohort (33.8 vs. 23.3 lymph nodes, p=0.0003). All robotic cases were discharged on postoperative day one compared with a 3.2-day average hospitalization for the laparotomy cohort. Complications rate were similar between the groups (7.8% vs. 16.3%).26
Recently, Geisler et al.27 from University of Toledo Medical Center compared the first consecutive 30 cases of robotic type III hysterectomy with 30 cases of open radical hysterectomy performed at the same institution. Notably, the mean operative time was found to be similar between the robotic and laparotomy groups, 154 vs. 166 minutes respectively (p=0.36). The authors partly attributed their relatively fast climb through the learning curve to having two experienced robotic surgeons in many of the cases who had already performed 50 cases of robotic hysterectomy and pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy for endometrial cancer. There were no other differences identified between the groups with regard to estimated blood loss, pelvic nodal yield, and length of stay; the findings were similar to previously published reports on robotic type III hysterectomy.
Piver type III hysterectomy when performed robotically is therefore safe and feasible. The operative time seems to be equivalent to that of the open approach once the learning curve is reached. Estimated blood loss seems to be less and hospital stay is shorter. Clearly, the patients would benefit from the advantages that are associated with minimally invasive surgery such as less pain, faster recovery, and shorter convalescence. Intraoperative outcomes including lymph node retrieval, excised parametrial and vaginal tissue are comparable to those of open approach.
There is, however, paucity of data regarding the long-term oncologic outcomes of patients with early-stage cervical cancer who are treated by robotic type III hysterectomy. The main objective of surgical management of early-stage cervical cancer is to obtain long-term survival and disease free interval in a relatively young patient population in whom the disease would prove fatal if untreated. Piver and colleagues showed a five-year disease-free interval of 92.3% in 55 women with FIGO stage IB (less than or equal to 3 cm) cervical cancers treated by type III hysterectomy.28 Since that report, other publications have shown similar five-year survival and disease free interval after type III hysterectomy.29,30
Recently, Cantrell et al.31 from University of North Carolina published their data regarding three-year survival after type III robotic hysterectomy for early cervical cancer. The primary investigator performed the majority of cases. Seventy-one patients with early-stage cervical cancer were included in the study. Eight subjects did not meet the inclusion criteria. The remaining 63 patients in the robotic arm were matched with 64 patients who received type III hysterectomy via laparotomy. The subjects were followed up for a median of 12.2 months (range, 0.2 to 36.3 months). Of the robotic group, 20 (32%) received postoperative whole pelvis radiation with chemotherapy sensitization due to positive pelvic lymph nodes. Pelvic lymph node metastasis occurred in five of 63 patients in the robotic group. One subject had a microscopically positive margin at the vaginal cuff. One subject in the robotic group deceased from recurrent disease. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis estimated 94% progression free survival and overall survival at 36 months. Of the patients who received open radical hysterectomy, 38% received pelvic radiation. The median follow-up was 28 months. Two subjects died of recurrent disease in the open cohort. According to the study, there was no difference between robotic and laparotomy groups in progression free and overall survival.
Although five-year data regarding the overall survival after type III robotic hysterectomy are yet available, the initial data seem to be promising. Well-designed studies regarding long-term outcomes after robotic type III hysterectomy are urgently needed as the procedure is increasingly being performed based on the presumption that the long-term outcomes are at least equivalent to those of open and laparoscopic approaches. Although this is a logical assumption, it is prudent to exercise cautious optimism regarding the longterm outcomes after robotic type III hysterectomy for the treatment of early cervical cancer. The senior author remains excited and optimistic about the prospect of robot-assisted Piver type III hysterectomy evolving to a new standard of care for the treatment of early stage cervical cancer in the 21st century.
CONCLUSION
Undoubtedly, robotic approach to type III Piver hysterectomy is feasible and safe. The robotic approach offers the patients the advantages of minimally invasive surgery. In addition, the benefits to the surgeon such as superior visualization, dexterity, precision along with natural endowrist movements and correct surgical ergonomics cannot be overemphasized. Although 3-year data as it pertain to overall outcomes and survival after robotic radical hysterectomy seem to be promising, longer trials are warranted to confirm similar 5-year oncologic outcomes.
Footnotes
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
- 1.Moore DH. Cervical cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107:1152–1161. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000215986.48590.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pecorelli S, Zigliani L, Odicino F. Revised FIGO staging for carcinoma of the cervix. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2009;105:107–108. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2009.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Piver MS, Lee JY. The 21st century role of Piver type II hysterectomy in FIGO stage IA, IB cervical cancer: a personal perspective. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2008;29:109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Piver MS, Chung WS. Prognostic significance of cervical lesion size and pelvic node metastases in cervical carcinoma. Obstet Gynecol. 1975;46:507–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Piver MS, Rutledge F, Smith JP. Five classes of extended hysterectomy for women with cervical cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 1974;44:265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pikaart DP, Holloway RW, Ahmad S, Finkler NJ, Bigsby GE, 4th, Ortiz BH, et al. Clinical-pathologic and morbidity analyses of Types 2 and 3 abdominal radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;107:205–210. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wertheim E. Zur frage der radicaloperation beim uteruskrebs. Arch Gynecol. 1900;61:627–668. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Meigs JV. Radical hysterectomy with bilateral pelvic lymph node dissections: a report of 100 patients operated on five or more years ago. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1951;62:854–870. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(51)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Querleu D, Leblanc E, Castelain B. Pelvic lymphadenectomy under celioscopic guidance. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris) 1990;19:576–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nezhat CR, Burrell MO, Nezhat FR, Benigno BB, Welander CE. Laparoscopic radical hysterectomy with paraaortic and pelvic node dissection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:864–865. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(92)91351-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Magrina JF. Robotic surgery in gynecology. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2007;28:77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zakashansky K, Bradley WH, Nezhat FR. New techniques in radical hysterectomy. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2008;20:14–19. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0b013e3282f2288a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zakashansky K, Bradley WH, Chuang L, Rahaman J, Dottino P. Recent advances in the surgical management of cervical cancer. Mt Sinai J Med. 2009;76:567–576. doi: 10.1002/msj.20149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ercoli A, Iannone V, Legge F, Fagotti A, Fanfani F, Carone V, et al. Advances in surgical management of cervical cancer. Minerva Ginecol. 2009;61:227–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ramirez PT. Robotic radical hysterectomy: a new standard of care? Future Oncol. 2009;5:23–25. doi: 10.2217/14796694.5.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fanning J, Hojat R, Johnson J, Fenton B. Robotic radical hysterectomy. Minerva Ginecol. 2009;61:53–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Magrina JF, Kho R, Magtibay PM. Robotic radical hysterectomy: technical aspects. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;113:28–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.12.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bandera CA, Magrina JF. Robotic surgery in gynecologic oncology. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2009;21:25–30. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0b013e32831ffe8e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Magrina JF, Zanagnolo VL. Robotic surgery for cervical cancer. Yonsei Med J. 2008;49:879–885. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sert BM, Abeler VM. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (Piver type III) with pelvic node dissection: case report. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2006;27:531–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sert B, Abeler V. Robotic radical hysterectomy in early-stage cervical carcinoma patients, comparing results with total laparoscopic radical hysterectomy cases. The future is now? Int J Med Robot. 2007;3:224–228. doi: 10.1002/rcs.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim YT, Kim SW, Hyung WJ, Lee SJ, Nam EJ, Lee WJ. Robotic radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy for cervical carcinoma: a pilot study. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;108:312–316. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Magrina JF, Kho RM, Weaver AL, Montero RP, Magtibay PM. Robotic radical hysterectomy: comparison with laparoscopy and laparotomy. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;109:86–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fanning J, Fenton B, Purohit M. Robotic radical hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198:649.e1–649.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nezhat FR, Datta MS, Liu C, Chuang L, Zakashansky K. Robotic radical hysterectomy versus total laparoscopic radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy for treatment of early cervical cancer. JSLS. 2008;12:227–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Boggess JF, Gehrig PA, Cantrell L, Shafer A, Ridgway M, Skinner EN, et al. A case-control study of robot-assisted type III radical hysterectomy with pelvic lymph node dissection compared with open radical hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;199:357.e1–357.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2008.06.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Geisler JP, Orr CJ, Khurshid N, Phibbs G, Manahan KJ. Robotically assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy compared with open radical hysterectomy. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010;20:438–442. doi: 10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181cf5c2c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Piver MS, Marchetti DL, Patton T, Halpern J, Blumenson L, Driscoll DL. Radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy versus radiation therapy for small (less than or equal to 3 cm) stage IB cervical carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 1988;11:21–24. doi: 10.1097/00000421-198802000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hopkins MP, Morley GW. Radical hysterectomy versus radiation therapy for stage IB squamous cell cancer of the cervix. Cancer. 1991;68:272–277. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910715)68:2<272::aid-cncr2820680210>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Landoni F, Maneo A, Colombo A, Placa F, Milani R, Perego P, et al. Randomised study of radical surgery versus radiotherapy for stage Ib-IIa cervical cancer. Lancet. 1997;350:535–540. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)02250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cantrell LA, Mendivil A, Gehrig PA, Boggess JF. Survival outcomes for women undergoing type III robotic radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer: a 3-year experience. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;117:260–265. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]