Abstract
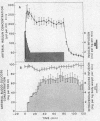
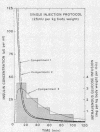
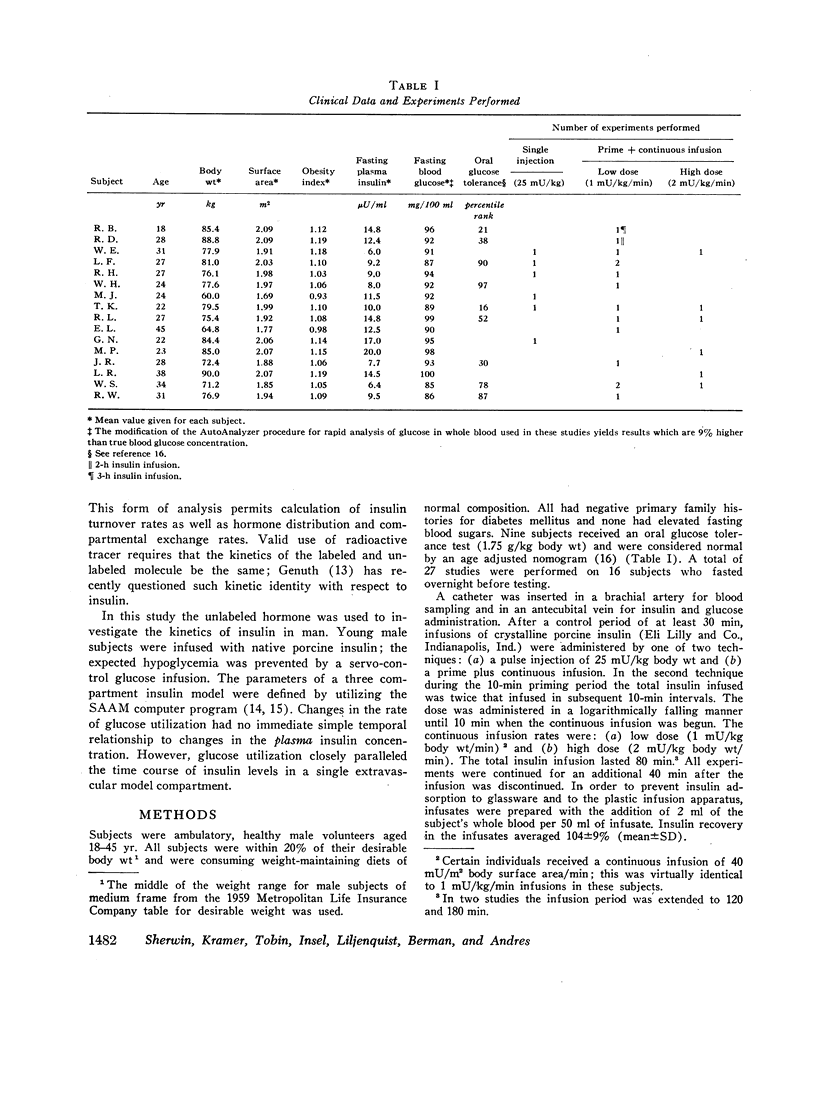
The design of the present study of the kinetics of insulin in man combines experimental features which obviate two of the major problems in previous insulin studies. (a) The use of radioiodinated insulin as a tracer has been shown to be inappropriate since its metabolism differs markedly from that of the native hormone. Therefore porcine insulin was administered by procedures which raised insulin levels in arterial plasma into the upper physiologic range. Hypoglycemia was prevented by adjusting the rate of an intravenous infusion of glucose in order to control the blood glucose concentration (the glucose-clamp technique). (b) Estimation of a single biological half-time of insulin after pulse injection of the hormone has been shown to be inappropriate since plasma insulin disappearance curves are multiexponential. Therefore the SAAM 25 computer program was used in order to define the parameters of a three compartment insulin model.
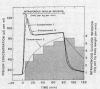
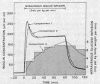
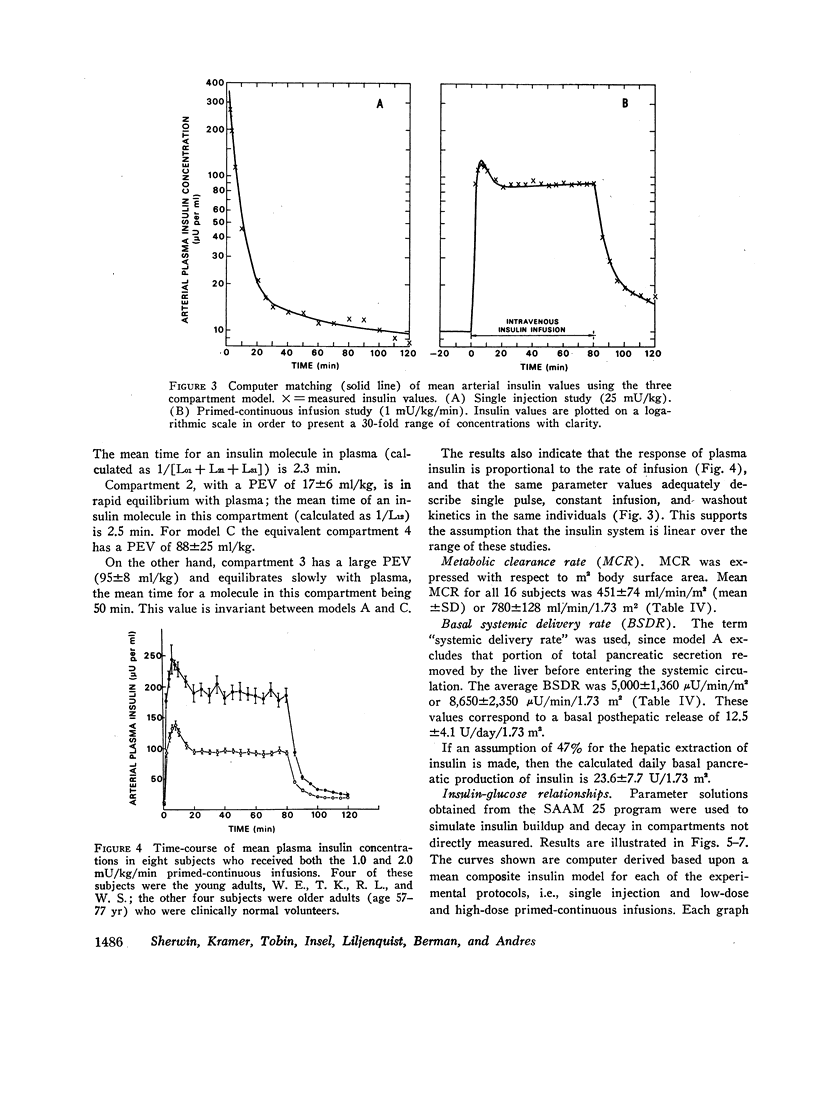
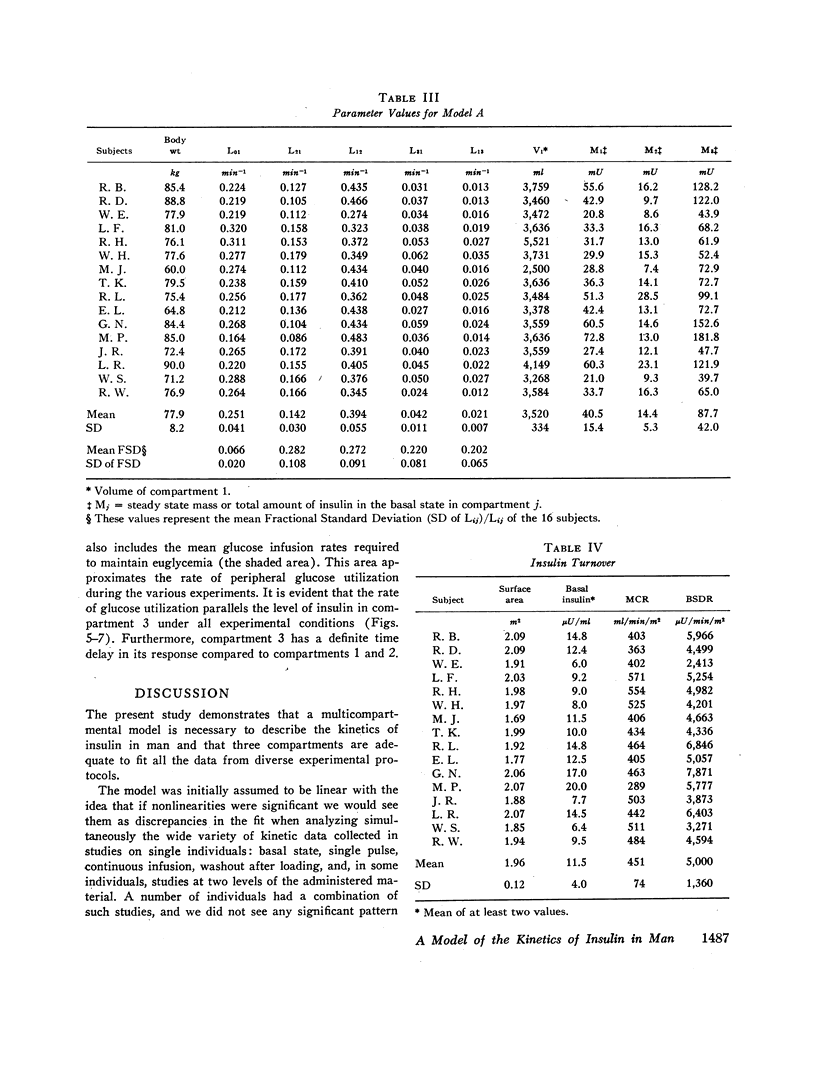
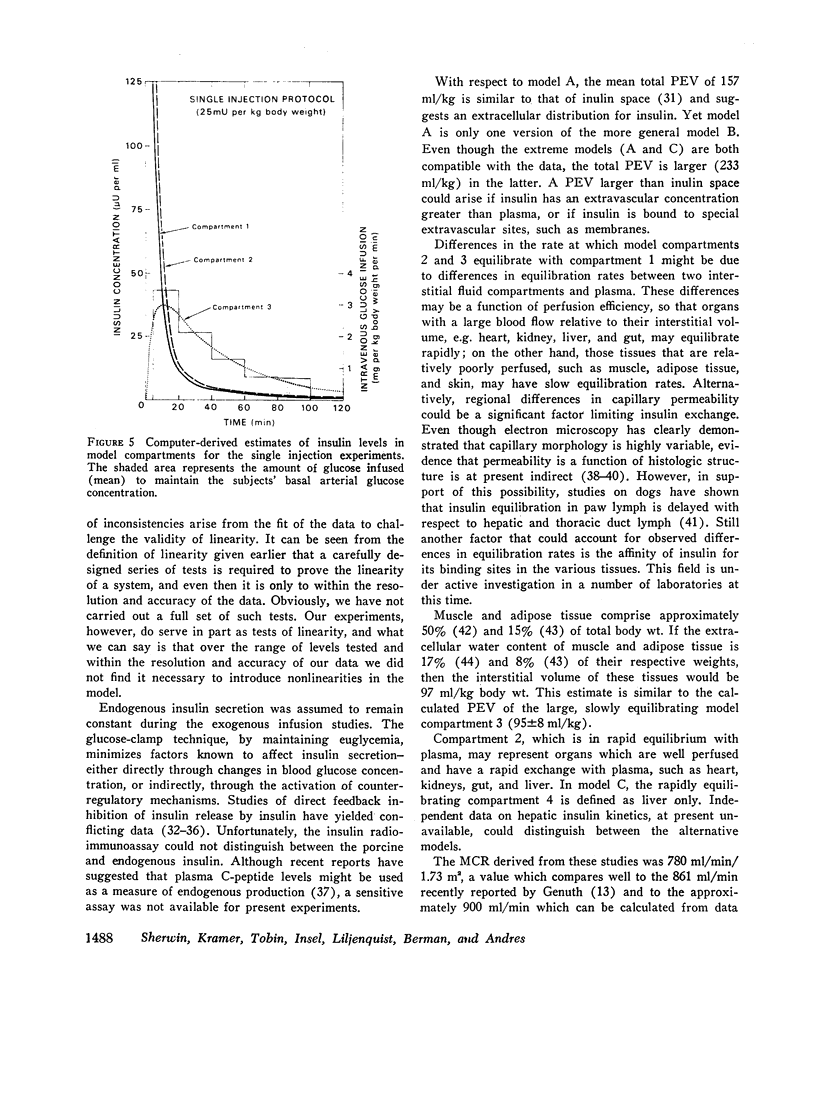
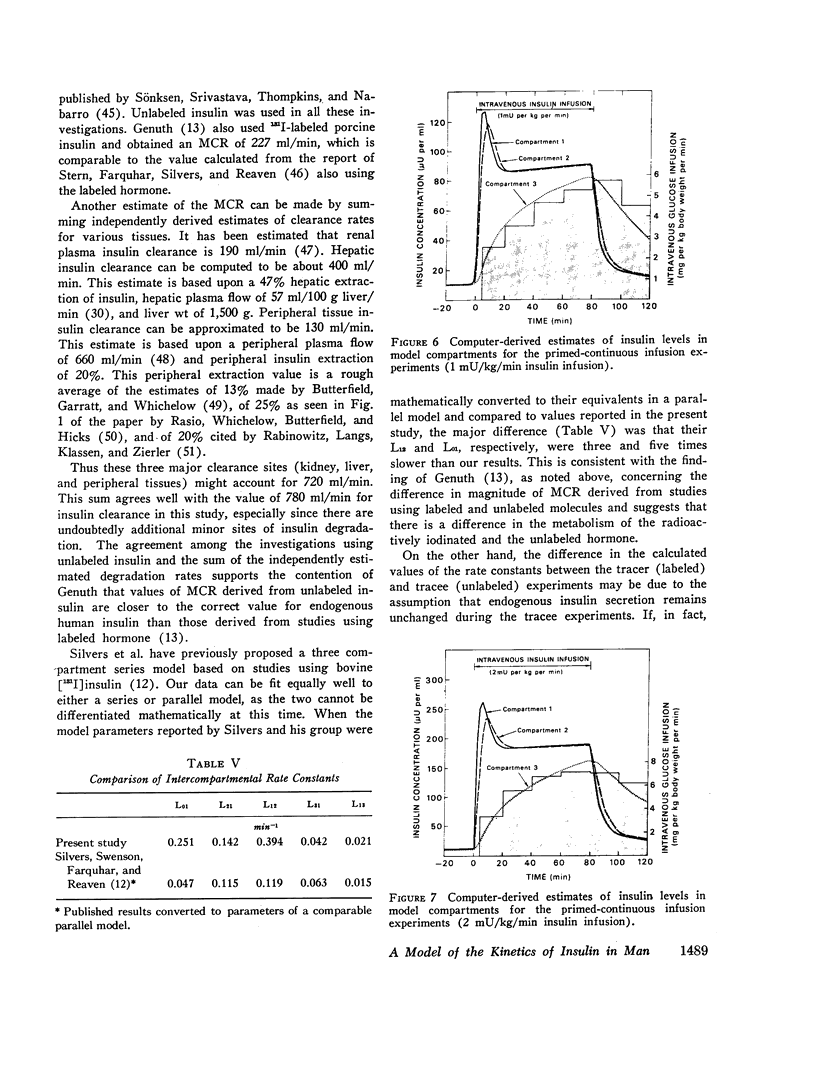
The combined insulin mass of the three compartments (expressed as plasma equivalent volume) is equal to inulin space (15.7% body wt). Compartment 1 is apparently the plasma space (4.5%). The other two compartments are extra-vascular; compartment 2 is small (1.7%) and equilibrates rapidly with plasma, and compartment 3 is large (9.5%) and equilibrates slowly with plasma.
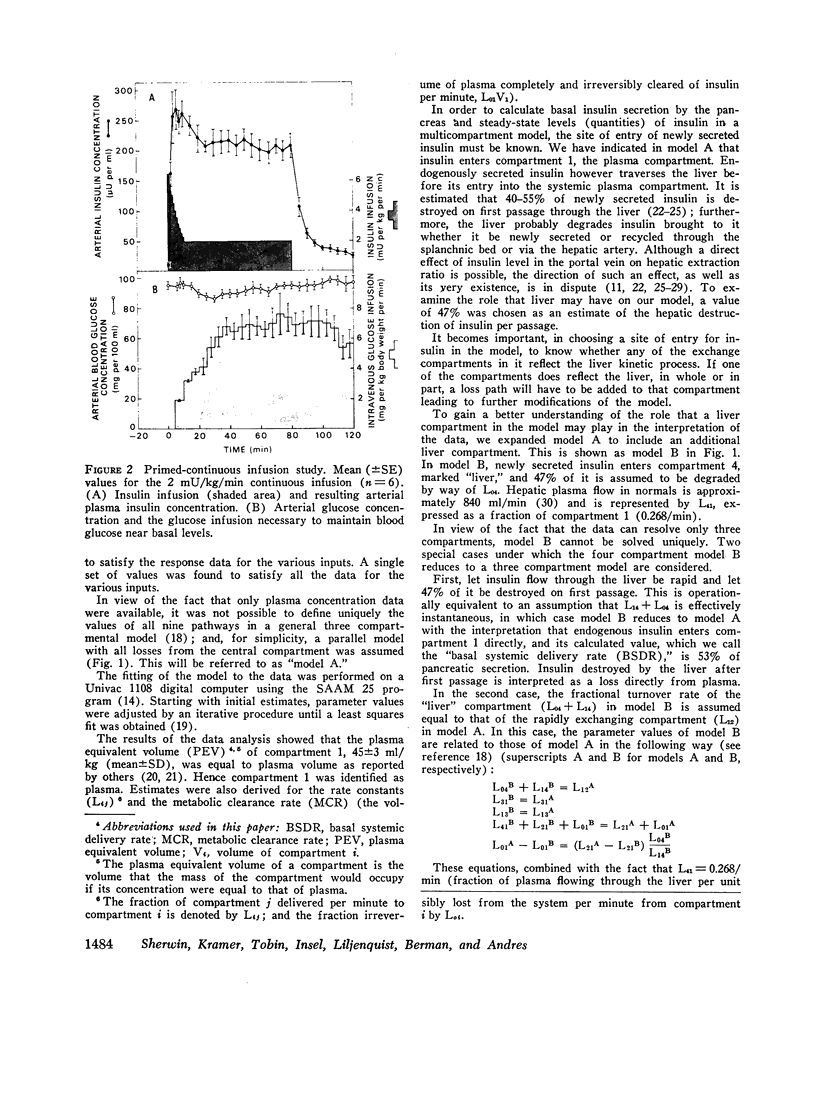
The SAAM 25 program can simulate the buildup and decay of insulin in compartments 2 and 3 which cannot be assayed directly. Insulin in compartment 3 was found to correlate remarkably with the time-course of the servo-controlled glucose infusion. Under conditions of a steady-state arterial glucose level, glucose infusion is a measure of glucose utilization. We conclude that compartment 3 insulin (rather than plasma insulin) is a more direct determinant of glucose utilization.
We suggest that the combined use of glucose-clamp and kinetic-modeling techniques should aid in the delineation of pathophysiologic states affecting glucose and insulin metabolism.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres R. Aging and diabetes. Med Clin North Am. 1971 Jul;55(4):835–846. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32479-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT H. S., LUFT J. H., HAMPTON J. C. Morphological classifications of vertebrate blood capillaries. Am J Physiol. 1959 Feb;196(2):381–390. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.2.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN M., SHAHN E., WEISS M. F. The routine fitting of kinetic data to models: a mathematical formalism for digital computers. Biophys J. 1962 May;2:275–287. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86855-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., BAUMAN A., ROTHSCHILD M. A., NEWERLY K. Insulin-I131 metabolism in human subjects: demonstration of insulin binding globulin in the circulation of insulin treated subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):170–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI103262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROZEK J., GRANDE F., ANDERSON J. T., KEYS A. DENSITOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF BODY COMPOSITION: REVISION OF SOME QUANTITATIVE ASSUMPTIONS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Sep 26;110:113–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Nelson N. C. Portal and peripheral vein immunoreactive insulin concentrations before and after glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1970 May;19(5):302–306. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.5.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell G. L., Berman M., Robertson J. S. Nomenclature for tracer kinetics. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1968 Mar;19(3):249–262. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(68)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain M. J., Stimmler L. The renal handling of insulin. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI105597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGERSEN M. I., NICKERSON J. L. Relation of blood volume and cardiac output to body type. J Appl Physiol. 1950 Dec;3(6):329–341. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1950.3.6.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuth S. M. Metabolic clearance of insulin in man. Diabetes. 1972 Oct;21(10):1003–1012. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.10.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V., Stark R. D. Hepatic vascular bed. Physiol Rev. 1971 Jan;51(1):23–65. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Rodrigo J. J. [Factors influencing different rates of insulin release in vitro]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1968 Oct;5 (Suppl 1):140–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. L., Shenkman L., Weissman P., Andres R. A semiautomated technic for radioimmunoassay. Double antibody assay of insulin. Diabetes. 1970 Feb;19(2):127–131. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. S., Johnson C., Lebovitz H. E. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jan;68(1):63–74. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen J., Miles D. W. Evidence for a feedback inhibition of insulin on insulin secretion in the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. Diabetes. 1971 Jan;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo J. L., Bartlett J. W., Roncone A., Izzo M. J., Bale W. F. Physiological processes and dynamics in the disposition of small and large doses of biologically active and inactive 131-I-insulins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2343–2355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADISON L. L., COMBES B., ADAMS R., STRICKLAND W. The physiological significance of the secretion of endogenous insulin into the portal circulation. III. Evidence for a direct immediate effect of insulin on the balance of glucose across the liver. J Clin Invest. 1960 Mar;39:507–522. doi: 10.1172/JCI104065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADISON L. L., COMBES B., UNGER R. H., KAPLAN N. The relationship between the mechanism of action of the sulfonylureas and the secretion of insulin into the portal circulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 30;74(3):548–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb39579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E., TIETZE F. Studies on the mechanism of capture and degradation of insulin-1131 by the cyclically perfused rat liver. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Lacy P. E., Wright P. H. Insulin secretion by isolated islets in presence of glucose, insulin and anti-insulin serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):497–500. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. I., Stocks A. E., Pearson M. J. Significance of disappearance-rate of injected insulin. Lancet. 1967 Mar 18;1(7490):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov H., Christensen N. J. Plasma disappearance rate of injected human insulin in juvenile diabetic, maturity-onset diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1969 Oct;18(10):653–659. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.10.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport A. M., Ohira S., Coddling J. A., Empey G., Kalnins A., Lin B. J., Haist R. E. Effects on insulin output and on pancreatic blood flow of exogenous insulin infusion into an in situ isolated portion of the pancreas. Endocrinology. 1972 Jul;91(1):168–176. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-1-168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasio E. A., Hampers C. L., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Diffusion of glucose, insulin, inulin, and Evans blue protein into thoracic duct lymph of man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):903–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI105596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasio E. A., Mack E., Egdahl R. H., Herrera M. G. Passage of insulin and inulin across vascular membranes in the dog. Diabetes. 1968 Nov;17(11):668–672. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.11.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasio E., Whichelow M. J., Butterfield W. J., Hicks B. H. Insulin fixation and glucose uptake by forearm tissues in response to infusions of physiological amounts of insulin in non-diabetic subjects. Diabetologia. 1972 Aug;8(4):244–249. doi: 10.1007/BF01225567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Farquhar J. W. Steady state plasma insulin response to continuous glucose infusion in normal and diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1969 May;18(5):273–279. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.5.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Block M. B., Starr J., Melani F., Steiner D. F. Proinsulin and C-peptide in blood. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):661–672. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMOLS E., RYDER J. A. Studies on tissue uptake of insulin in man using a differential immunoassay for endogenous and exogenous insulin. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:2092–2102. doi: 10.1172/JCI104435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., BISHOP J. S., DUNN A., ALTSZULER N., RATHBEB I., DEBODO R. C. INHIBITION BY INSULIN OF HEPATIC GLUCOSE PRODUCTION IN THE NORMAL DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:301–306. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvers A., Swenson R. S., Farquhar J. W., Reaven G. M. Derivation of a three compartment model describing disappearance of plasma insulin-131-I in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1461–1469. doi: 10.1172/JCI106112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodoyez J. C., Sodoyez-Goffaux F., Foà P. P. Evidence for an insulin-induced inhibition of insulin release by isolated islets of Langerhans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Feb;130(2):568–571. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. P., Farquhar J. W., Silvers A., Reaven G. M. Insulin delivery rate into plasma in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):1947–1957. doi: 10.1172/JCI105884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimmler L. Disappearance of immunoreactive insulin in normal and adult-onset diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1967 Sep;16(9):652–655. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.9.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimmler L., Mashiter K., Snodgrass G. J., Boucher B., Abrams M. Insulin disappearance after intravenous injection and its effect on blood glucose in diabetic and non-diabetic children and adults. Clin Sci. 1972 Mar;42(3):337–344. doi: 10.1042/cs0420337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönksen P. H., Srivastava M. C., Tompkins C. V., Nabarro J. D. Growth-hormone and cortisol responses to insulin infusion in patients with diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1972 Jul 22;2(7769):155–159. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. C., Grayburn J. A., Newman G. B., Nabarro J. D. Measurement of the insulin delivery rate in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):279–286. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell W. R., Sussman K. E. Plasma insulin after diversion of portal and pancreatic venous blood to vena cava. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Apr;22(4):808–812. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.4.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. F., Gleason R. E., Soeldner J. S. The half-life of endogenous serum immunoreactive insulin in man. Metabolism. 1968 Nov;17(11):1025–1029. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]