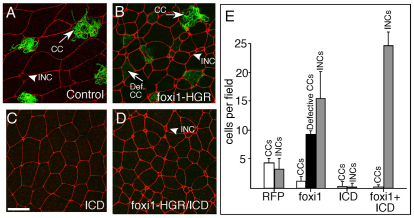
Fig. 3.
foxi1-HGR promotes INC formation. (A-D) Two-cell Xenopus embryos were injected with RNA encoding foxi1-HGR and ICD along with mRFP RNA as a tracer, treated with DEX at stage 12, fixed at stage 26, and stained with anti-acetylated tubulin (green) to identify ciliated cells (CCs). Shown is a confocal image of the skin in embryos injected with just RFP (A), foxi1-HGR (B), ICD (C) or with both foxi1-HGR and ICD RNA (D). (E) Quantification of different cell types in the skin under the indicated experimental conditions. CCs stained with the acetylated tubulin antibody (green) were classified as defective if they failed to form cilia. INCs and outer cells (OCs) were scored based on their characteristic small and large apical domain, respectively. Error bars indicate + s.d. All values are significantly different relative to the control, based on a two-tailed t-test (P≤0.005). Scale bar: 20 μm.