Abstract
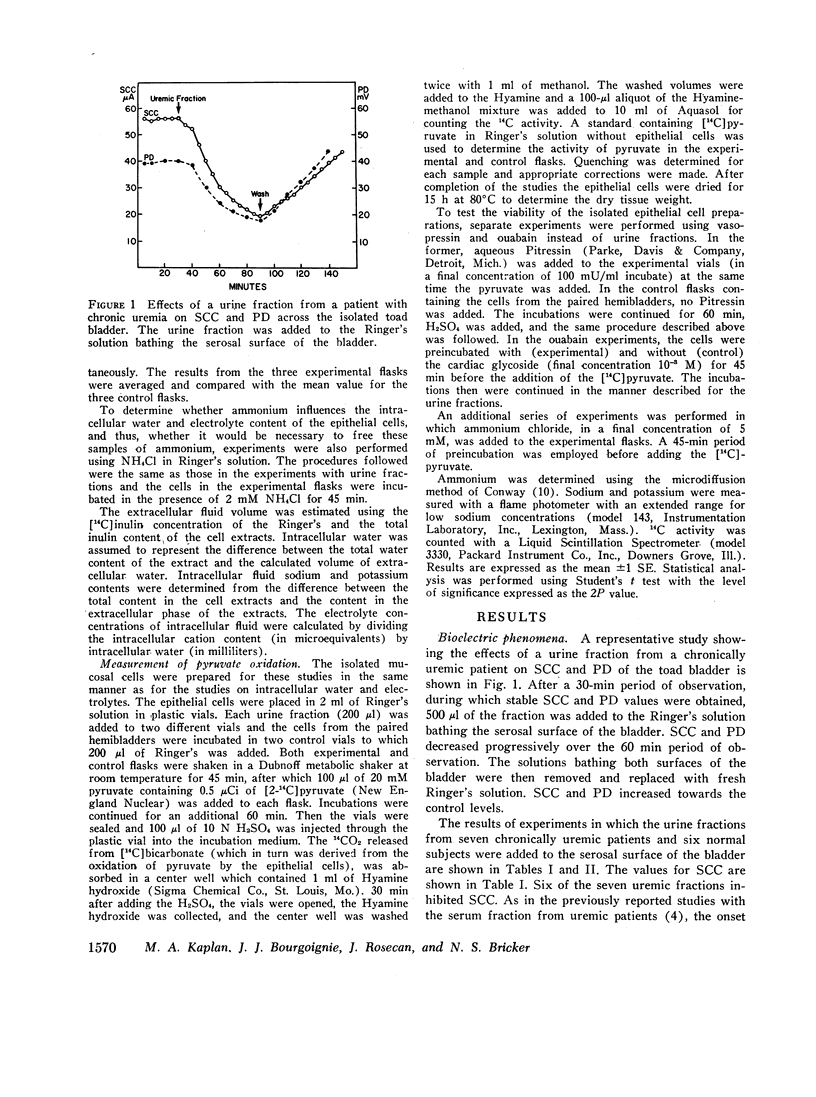
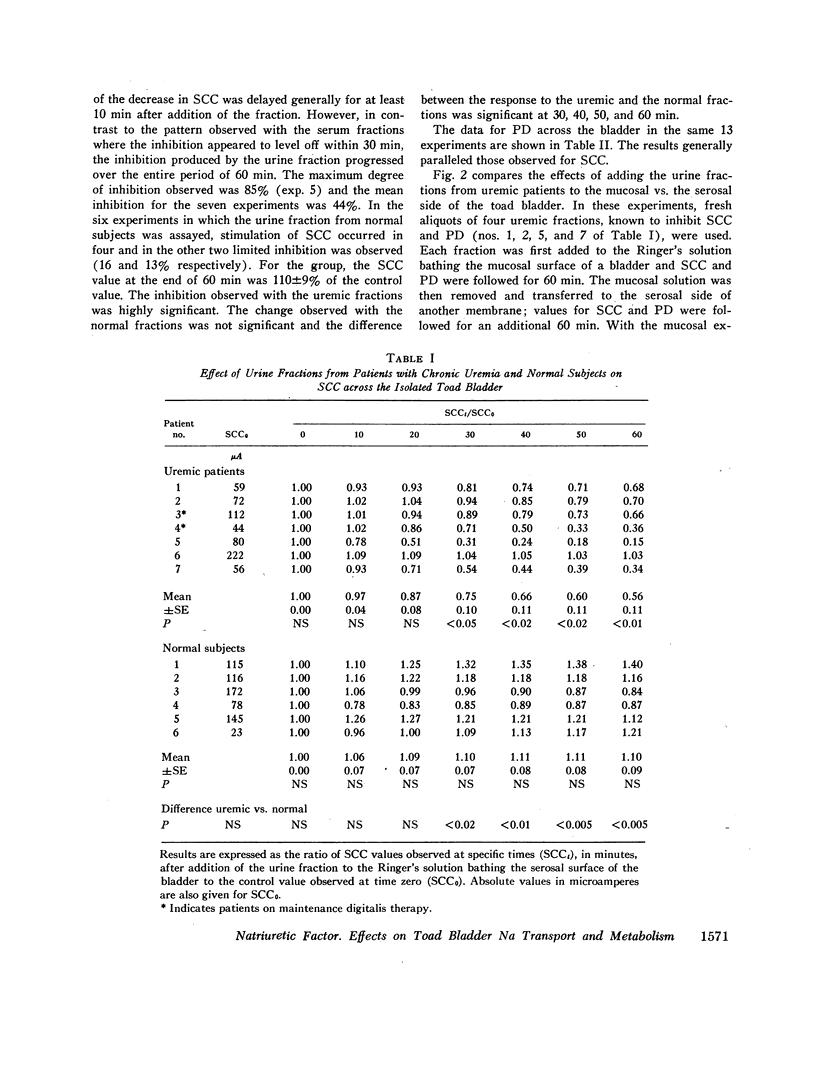
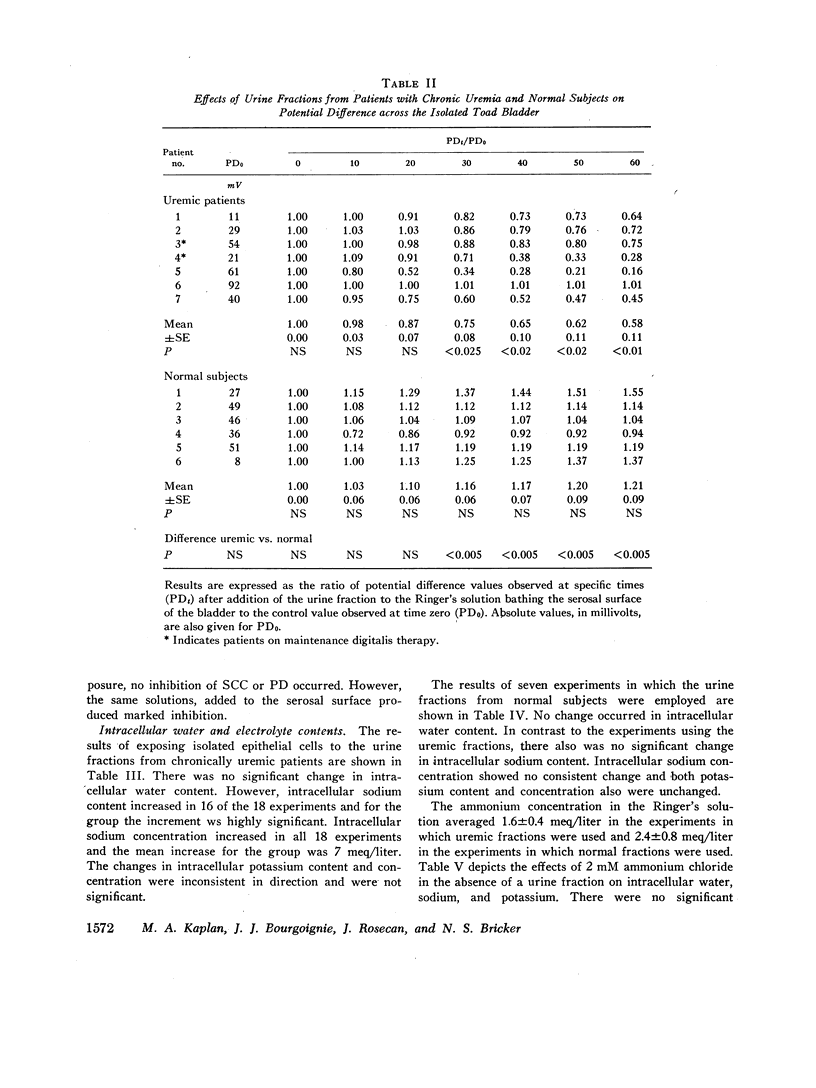
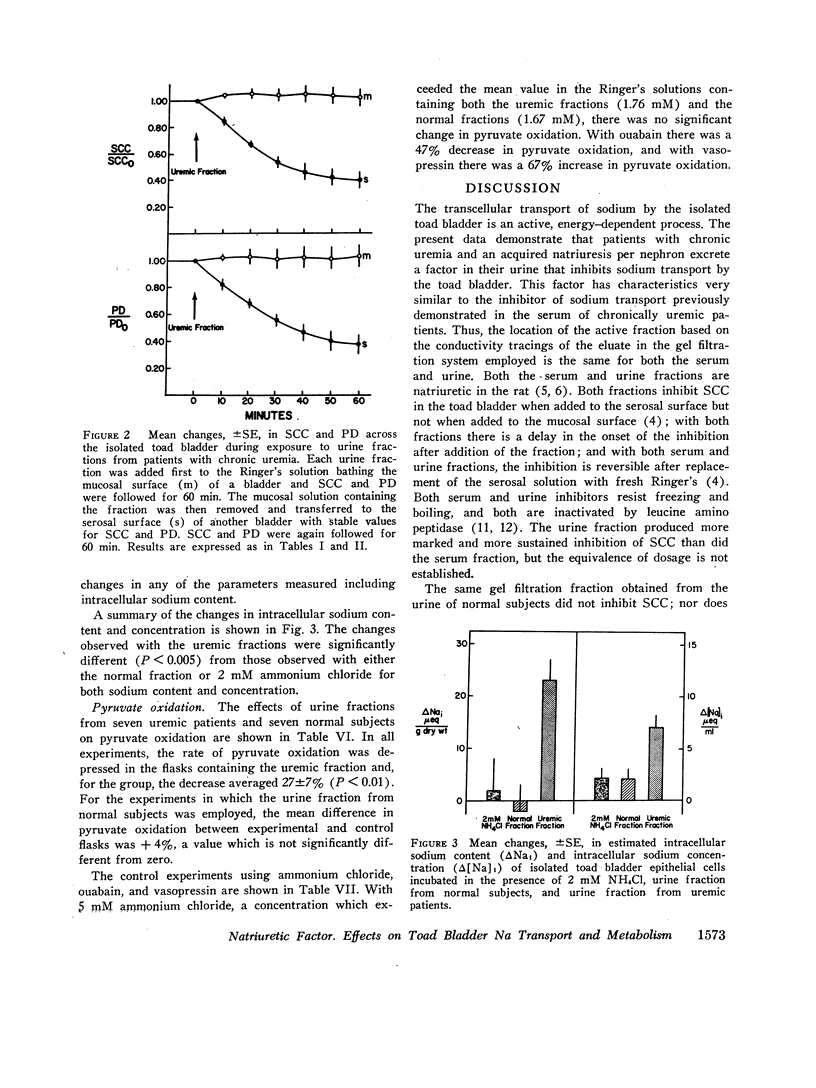
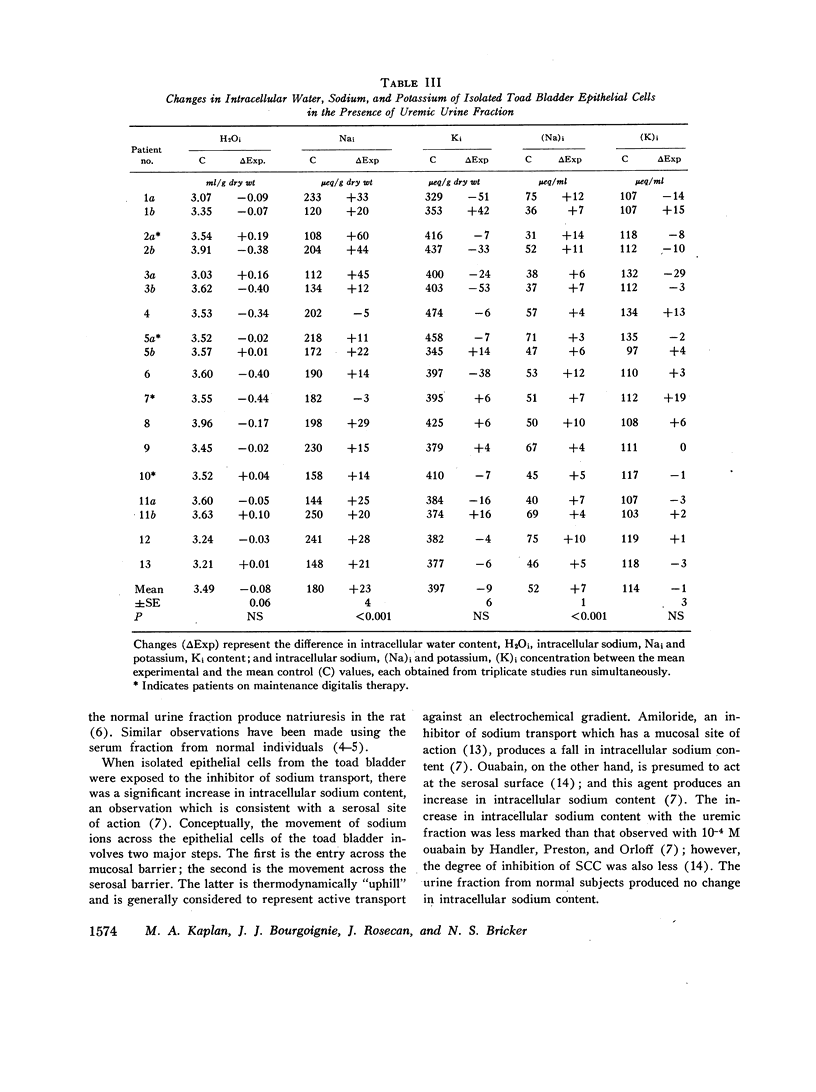
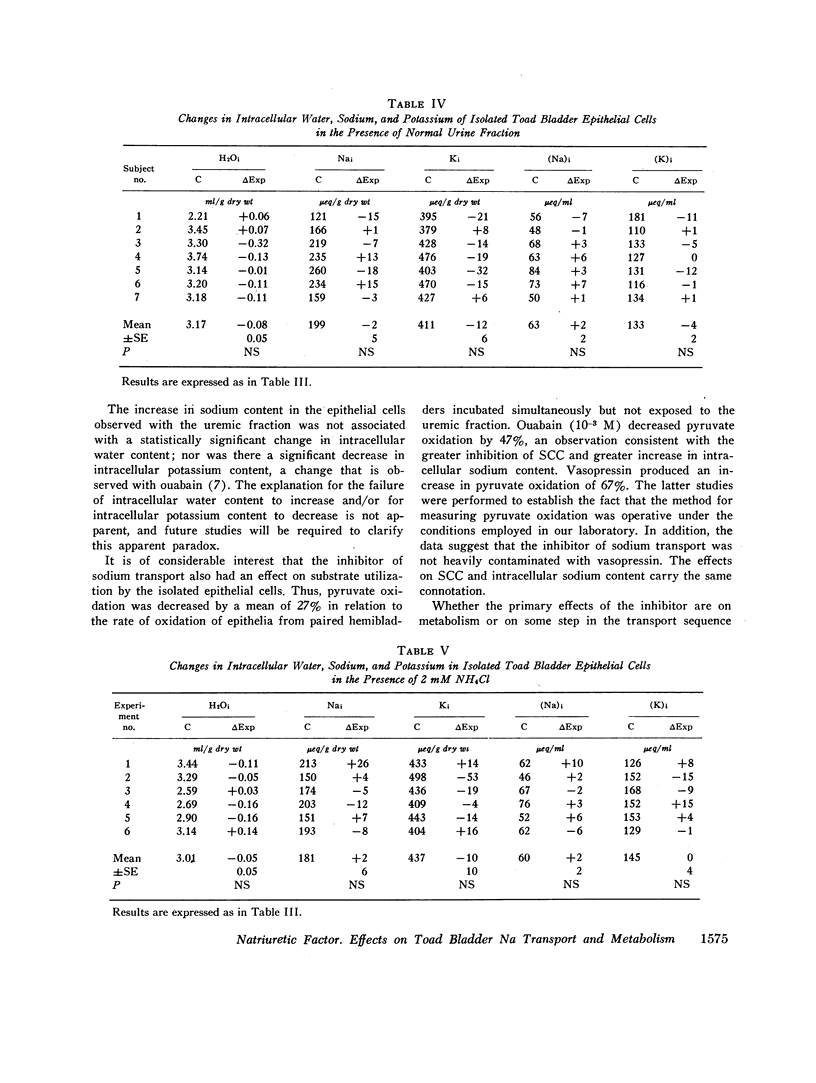
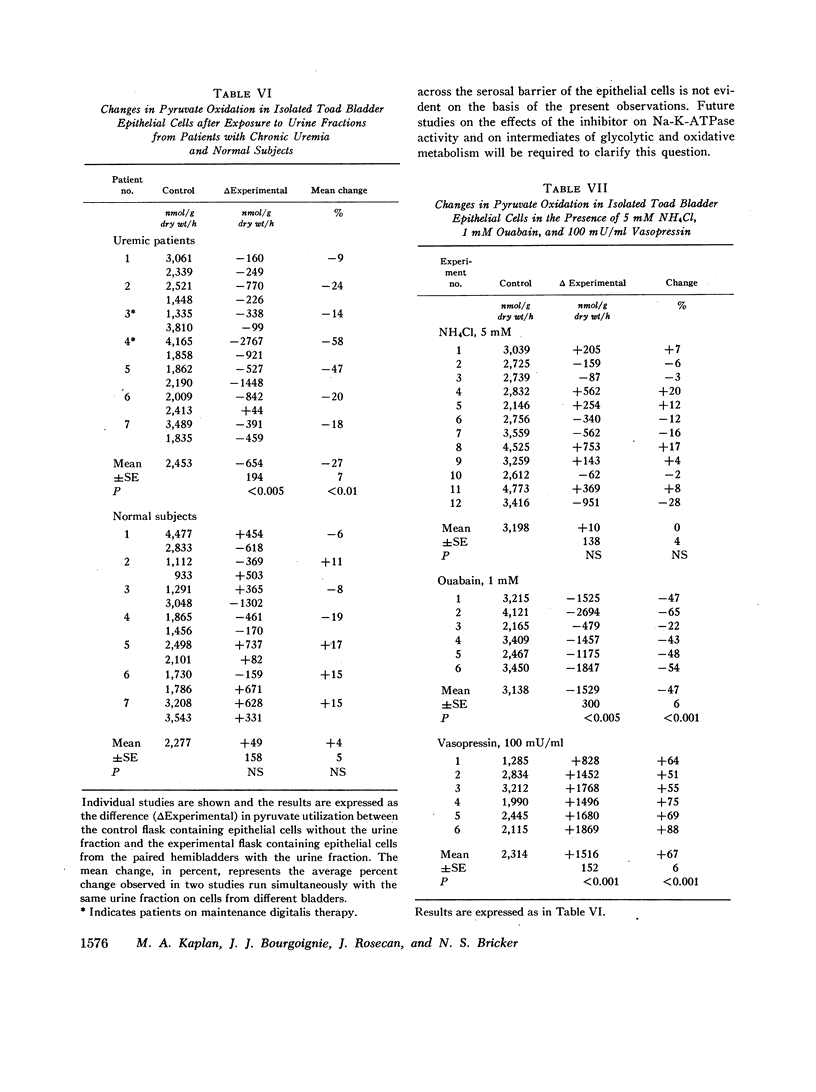
The urine of patients with chronic uremia contains a gel filtration fraction that is natriuretic in the rat. The effects of this fraction on the isolated urinary bladder of the toad were examined in the present studies. When added to the serosal surface of the bladder, a significant and substantial fall in short-circuit current and potential difference was observed. The changes began after a lag period of at least 10 min and continued over a period of 60 min. The decrease in short-circuit current at the end of 1 h averaged 44%. The same fraction from the urine of normal subjects produced no significant change in either short-circuit current or potential difference. When the isolated epithelial cells from the toad bladder were incubated in the presence of the inhibitor, intracellular sodium content increased significantly. There was no change in intracellular water content; hence the intracellular concentration of sodium increased by a mean of 7 meq/liter. The changes in intracellular potassium content and concentration were not satistically significant. When the isolated epithelia were incubated with the uremic factor, there was also a significant decrease in pyruvate utilization in relation to cells from paired hemibladders incubated in the absence of the fraction. The fraction from normal subjects produced no change in either intracellular sodium content or pyruvate oxidation.
The results suggest that the inhibitor acts from the serosal surface, inhibits sodium transport across the serosal barrier, and produces a decrease in substrate utilization in association with the change in transepithelial sodium transport.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley P. J. Amiloride: a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoignie J. J., Hwang K. H., Espinel C., Klahr S., Bricker N. S. A natriuretic factor in the serum of patients with chronic uremia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1514–1527. doi: 10.1172/JCI106948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoignie J. J., Hwang K. H., Ipakchi E., Bricker N. S. The presence of a natriuretic factor in urine of patients with chronic uremia. The absence of the factor in nephrotic uremic patients. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1559–1567. doi: 10.1172/JCI107706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoignie J., Klahr S., Bricker N. S. Inhibition of transepithelial sodium transport in the frog skin by a low molecular weight fraction of uremic serum. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):303–311. doi: 10.1172/JCI106495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricker N. S. The control of sodium excretion with normal and reduced nephron populations. The pre-eminence of third factor. Am J Med. 1967 Sep;43(3):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley L. E., Daugharty T. M. Sodium metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 10;281(2):72–86. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907102810205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatzy J. T., Berndt W. O. Isolated epithelial cells of the toad bladder. Their preparation, oxygen consumption, and electrolyte content. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jun;51(6):770–784. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.6.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim S. J., Bourgoignie J., Klahr S. Inhibition by ammonium of sodium transport across isolated toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):1651–1659. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. S., Preston A. S., Orloff J. Effect of ADH, aldosterone, ouabain, and amiloride on toad bladder epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1972 May;222(5):1071–1074. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.5.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera F. C. Action of ouabain on bioelectric properties and ion content in toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):183–189. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. W., De Wardener H. E. Tubular reabsorption of sodium ion: influence of factors other than aldosterone and glomerular filtration rate. 1. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov;285(22):1231–1243. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111252852205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H., Bourgoignie J. J., Bricker N. S. Effects of the natriuretic serum fraction on proximal tubular sodium reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1974 Feb;226(2):419–425. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


