Abstract
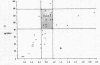
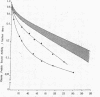
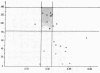
Metabolic studies using radioiodine-labeled third component of complement (C3) and the glycine-rich β glycoprotein (GBG), a major component of the C3b-feedback pathway, were undertaken in normal subjects, in 22 patients with evidence of complement activation, and in 11 patients with various renal diseases without evidence of complement activation. In seven normal subjects GBG was found to be a rapidly metabolized protein with catabolic rates ranging from 1.7% to 2.2% of the plasma pool/h, synthesis rates from 0.14 to 0.21 mg/kg per h. and extravascular/intravascular distribution ratios from 0.81 to 1.31. In patients with reduced plasma C3, both increased C3 fractional catabolic rates and reduced C3 synthesis rates were observed, and in some patients there was evidence of increased extravascular distribution of the protein. GBG catabolism was usually increased when there was evidence of C3 activation, presumably reflecting activation of the C3b-feedback; but GBG turnover was normal or only slightly accelerated in some patients with accelerated C3 catabolism and profound hypocomplementemia, suggesting that reduced C3 synthesis had limited activation of the C3b-feedback.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Abramson N., Johnston R. B., Jr, Jandl J. H., Rosen F. S. Studies in vivo and in vitro on an abnormality in the metabolism of C3 in a patient with increased susceptibility to infection. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):1975–1985. doi: 10.1172/JCI106417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Bloch K. J., Rosen F. S. Increased susceptibility to infection in a patient with type II essential hypercatabolism of C3. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 22;288(12):601–606. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303222881204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Goodkofsky I., Lepow I. H. The relationship of glycine-rich -glycoprotein to factor B in the properdin system and to the cobra factor-binding protein of huan serum. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):424–437. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Alper CA, Rosen FS: Studies of the in vivo behavior of human C'3 in normal subjects and patients. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):2021–2034. doi: 10.1172/JCI105691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Rosen F. S., Lachmann P. J. Inactivator of the third component of complement as an inhibitor in the properdin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2910–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S. Distribution and metabolism of I131 labeled proteins in man. Fed Proc. 1957 Jul;16(2):suppl–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boenisch T., Alper C. A. Isolation and properties of a glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein of human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):529–535. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Naish P., Lachmann P. J., Peters D. K. Metabolism of radio-labelled C3: effects of in vivo activation in rabbits. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Mar;16(3):445–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth J. A., Williams D. G., Sherington E., Peters D. K. Metabolism of the third component of complement (C3) in normal human subjects. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Feb;46(2):223–229. doi: 10.1042/cs0460223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H., Merrill J. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Austen K. F. Metabolism of third complement component (C3) in nephritis. Involvement of the classic and alternate (properdin) pathways for complement activation. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 26;287(17):835–840. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210262871701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J. The purification of specific antibody as F(ab')2 by the pepsin digestion of antigen-antibody precipitates, and its application to immunoglobulin and complement antigens. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jan;8(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90423-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDuffie F. C., Sams W. M., Jr, Maldonado J. E., Andreini P. H., Conn D. L., Samayoa E. A. Hypocomplementemia with cutaneous vasculitis and arthritis. Possible immune complex syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1973 May;48(5):340–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. H., Michael A. F. Properdin anc C3 proactivator: alternate pathway components in human glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):634–644. doi: 10.1172/JCI107225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Götze O. C3 proactivator convertase and its mode of action. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicol P. A., Lachmann P. J. The alternate pathway of complement activation. The role of C3 and its inactivator (KAF). Immunology. 1973 Feb;24(2):259–275. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosslin B. Analysis of disappearance time-curves after single injection of labelled proteins. Ciba Found Symp. 1972;9:113–130. doi: 10.1002/9780470719923.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters D. K., Charlesworth J. A., Sissons J. G., Williams D. G., Boulton-Jones J. M., Evans D. J., Kourilsky O., Morel-Maroger L. Mesangiocapillary nephritis, partial lipodystrophy, and hypocomplementaemia. Lancet. 1973 Sep 8;2(7828):535–538. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92351-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters D. K., Martin A., Weinstein A., Cameron J. S., Barratt T. M., Ogg C. S., Lachmann P. J. Complement studies in membrano-proliferative glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Jul;11(3):311–320. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering R. J., Herdman R. C., Michael A. F., Vernier R. L., Gewurz H., Fish A. J., Good R. A. Chronic glomerulonephritis associated with low serum complement activity (chronic hypocomplementemic glomerulonephritis). Medicine (Baltimore) 1970 May;49(3):207–226. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197005000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwinski A. J., Zvaifler N. J. Decreased synthesis of the third component of complement (C3) in hypocomplementemic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):21–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer R. E., Vallota E. H., Forristal J., Sudora E., Stitzel A., Davis N. C., West C. D. Serum C'3 lytic system in patients with glomerulonephritis. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):436–437. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A. C3 inactivating factor in the serum of a patient with chronic hypocomplementaemic proliferative glomerulo-nephritis. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):147–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westberg N. G., Naff G. B., Boyer J. T., Michael A. F. Glomerular deposition of properdin in acute and chronic glomerulonephritis with hypocomplementemia. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):642–649. doi: 10.1172/JCI106534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. G., Lachmann P. J., Charlesworth J. A., Peters D. K. Role of C3b in the breakdown of C3 in hypocomplementaemic mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Lancet. 1973 Mar 3;1(7801):447–449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91877-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]