Abstract
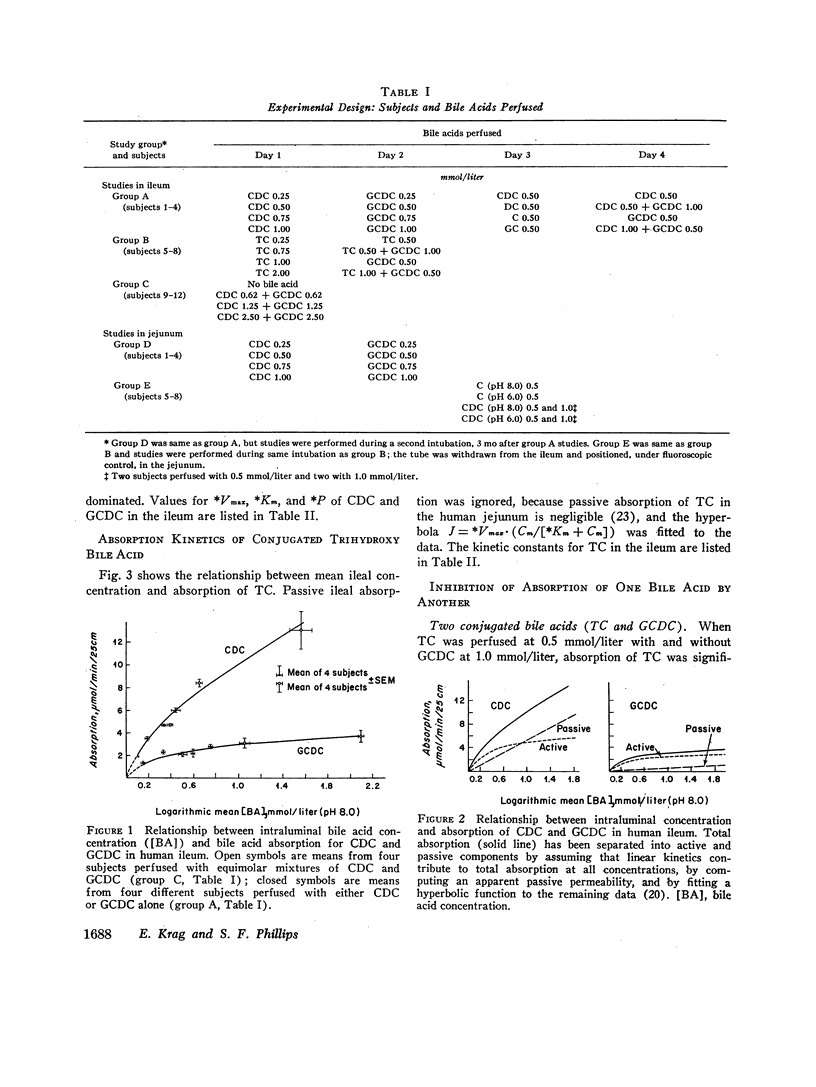
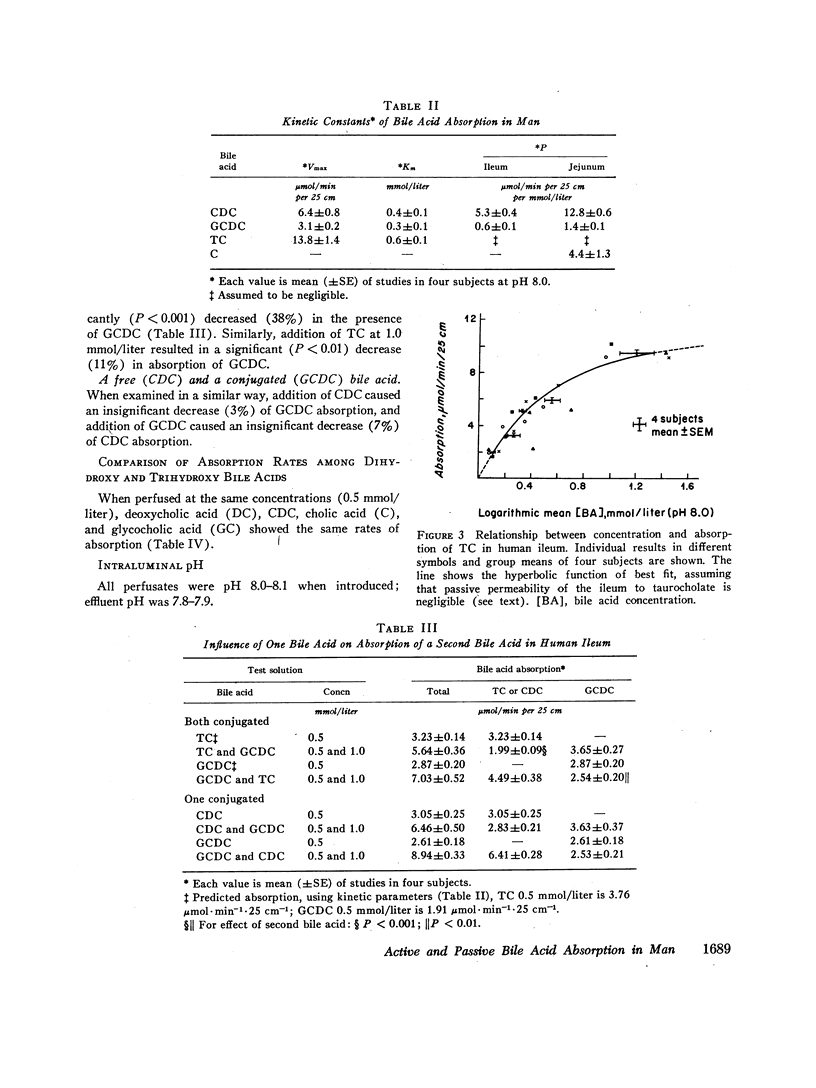
Absorption of the major human bile acids was studied in 12 healthy volunteers by steady state perfusion of the ileum in 112 experiments and of the jejunum in 48 experiments. Use of a randomized order of four perfusions on 1 day of study and use of up to 4 consecutive days of study in a subject allowed important comparisons of data from the same individuals. That there is active ileal absorption of chenodeoxycholic, glycochenodeoxycholic, and taurocholic acids in man was supported by the finding of saturation kinetics and of competition for absorption among conjugated bile acids. Values for apparent kinetic constants (apparent maximal transport velocity [*Vmax] and apparent Michaelis constant) in man are similar to those in other species. The ileum absorbed chenodeoxycholic acid more rapidly than its glycine conjugate, due mainly to a ninefold greater permeability for the free acid. Taurocholate had the highest *Vmax and was absorbed more rapidly than glycochenodeoxycholate. Passive permeability of the jejunum to bile acids was twice that of the ileum, and the permeabilities to free and glycine-conjugated chenodeoxycholate were in the same ratio as in the ileum (9: 1). Jejunal permeability to chenodeoxycholic acid was three times that to cholic acid. Variation of intraluminal pH by up to 1.4 units did not influence jejunal uptake of free bile acids. These results, which are comparable with those from animal experiments, provide a basis for estimation of intestinal reabsorption of bile acids in intact man.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER R. D., SEARLE G. W. Bile salt absorption at various levels of rat small intenstine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Dec;105:521–523. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROEM B., LUNDH G., HOFMANN A. THE SITE OF ABSORPTION OF CONJUGATED BILE SALTS IN MAN. Gastroenterology. 1963 Aug;45:229–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B., DAHLQVIST A., LUNDH G., SJOVALL J. Studies of intestinal digestion and absorption in the human. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1521–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI103549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzinger R. G., Hofmann A. F., Schoenfield L. J., Thistle J. L. Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by chenodeoxycholic acid. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 6;286(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201062860101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Sallee V. L., Wilson F. A. Unstirred water layers and absorption across the intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1971 Dec;61(6):932–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Salomon H. S., Siperstein M. D. Bile acid metabolism. I. Studies on the mechanisms of intestinal transport. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):832–846. doi: 10.1172/JCI105399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Locklear T. W. Ionic constituents and osmolality of gastric and small-intestinal fluids after eating. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Jul;11(7):503–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02233563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASSER J. E., WEINER I. M., LACK L. COMPARATIVE PHYSIOLOGY OF INTESTINAL TAUROCHOLATE TRANSPORT. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:359–362. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. F. Method for simultaneous direct estimation of glucose and xylose in serum. Clin Chem. 1970 Feb;16(2):85–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. M. Carbohydrate digestion and absorption. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jan;58(1):96–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGBEN C. A., TOCCO D. J., BRODIE B. B., SCHANKER L. S. On the mechanism of intestinal absorption of drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Apr;125(4):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT P. R. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF BILE SALTS IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:1–7. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton K. W., Lack L. Ileal bile salt transport: mutual inhibition in an in vivo system. Am J Physiol. 1968 Mar;214(3):585–590. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. II. Glycine-conjugated dihydroxy bile acids. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1898–1905. doi: 10.1172/JCI106992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Sturman J. A., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. 3. Cholyltaurine (taurocholic acid). J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):433–440. doi: 10.1172/JCI107200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. Bile acid malabsorption caused by ileal resection. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Small D. M. Detergent properties of bile salts: correlation with physiological function. Annu Rev Med. 1967;18:333–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.18.020167.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK L., WEINER I. M. In vitro absorption of bile salts by small intestine of rats and guinea pigs. Am J Physiol. 1961 Feb;200:313–317. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSTEDT S. The turnover of cholic acid in man: bile acids and steroids. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957 Sep 17;40(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1957.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lack L., Weiner I. M. Intestinal bile salt transport: structure-activity relationships and other properties. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):1142–1152. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic secretion of water and electrolytes induced by bile acids: perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1569–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI106644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., McColl I. Postprandial concentrations of free and conjugated bile acids down the length of the normal human small intestine. Gut. 1973 Jul;14(7):513–518. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.7.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLAYOUST M. R., ISSELBACHER K. J. STUDIES ON THE TRANSPORT AND METABOLISM OF CONJUGATED BILE SALTS BY INTESTINAL MUCOSA. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:467–476. doi: 10.1172/JCI104932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F., Summerskill W. H. Occlusion of the jejunum for intestinal perfusion in man. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966 Apr;41(4):224–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff E. R., Small N. C., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of the kinetics of the passive and active transport mechanisms for bile acid absorption in the small intestine and colon of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1351–1362. doi: 10.1172/JCI106931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singletary W. V., Jr, Walker J. T., Lack L. Ileal transport of bile acids conjugated with norleucine and lysine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 14;266(1):238–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Dowling R. H., Redinger R. N. The enterohepatic circulation of bile salts. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):552–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Hatzioannou J., Booth C. C. Bile-salt deconjugation and steatorrhoea in patients with the stagnant-loop syndrome. Lancet. 1968 Jul 6;2(7558):12–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92888-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER I. M., LACK L. Absorption of bile salts from the small intestine in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1962 Jan;202:155–157. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of bile acid absorption across the unstirred water layer and brush border of the rat jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3015–3025. doi: 10.1172/JCI107129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Effect of glycine-conjugated bile acids with and without lecithin on water and glucose absorption in perfused human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1230–1236. doi: 10.1172/JCI107290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Sandberg R. J., Phillips S. F. A comparison of stable and 14 C-labelled polyethylene glycol as volume indicators in the human jejunum. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):812–815. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.10.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winne D. Unstirred layer, source of biased Michaelis constant in membrane transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 27;298(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


