Abstract
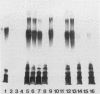
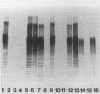
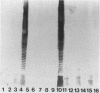
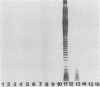
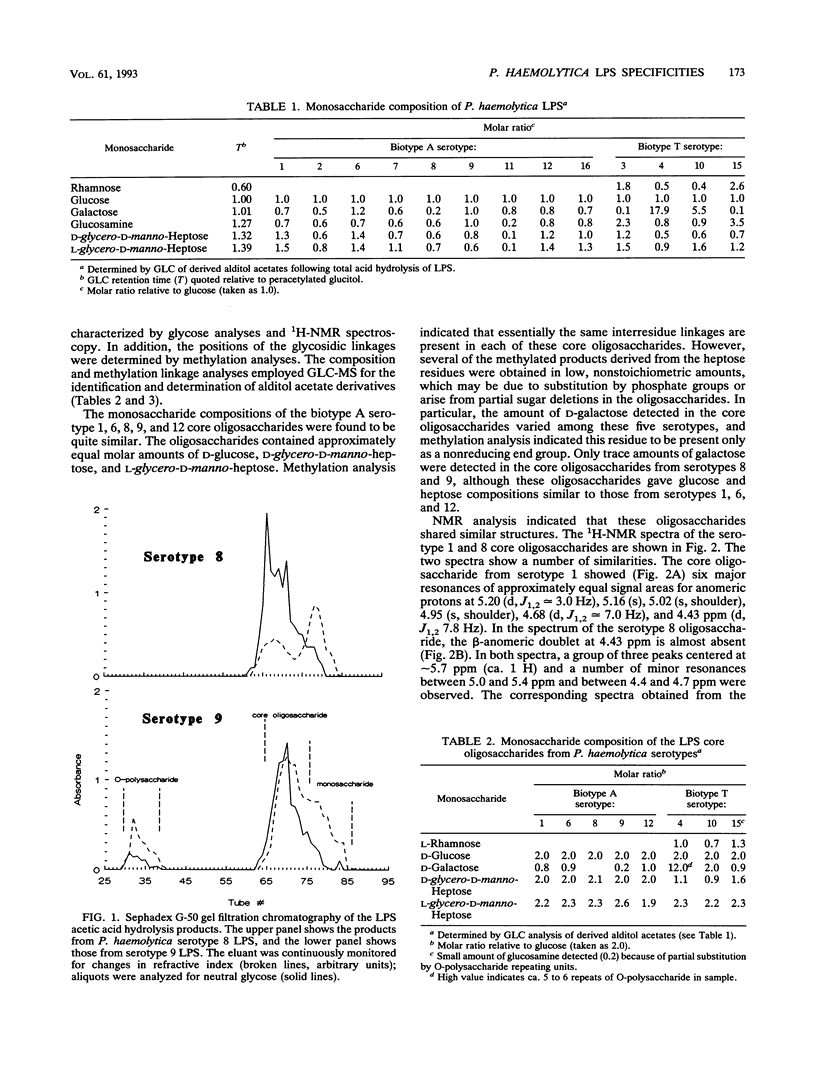
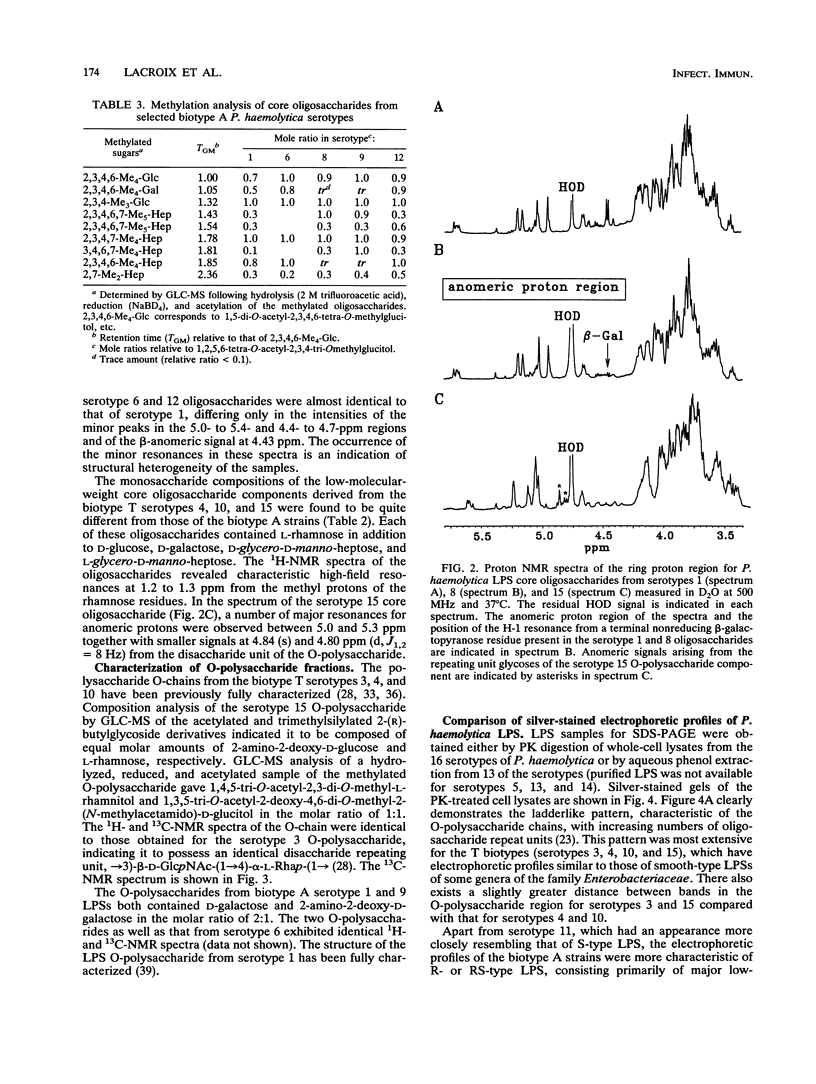
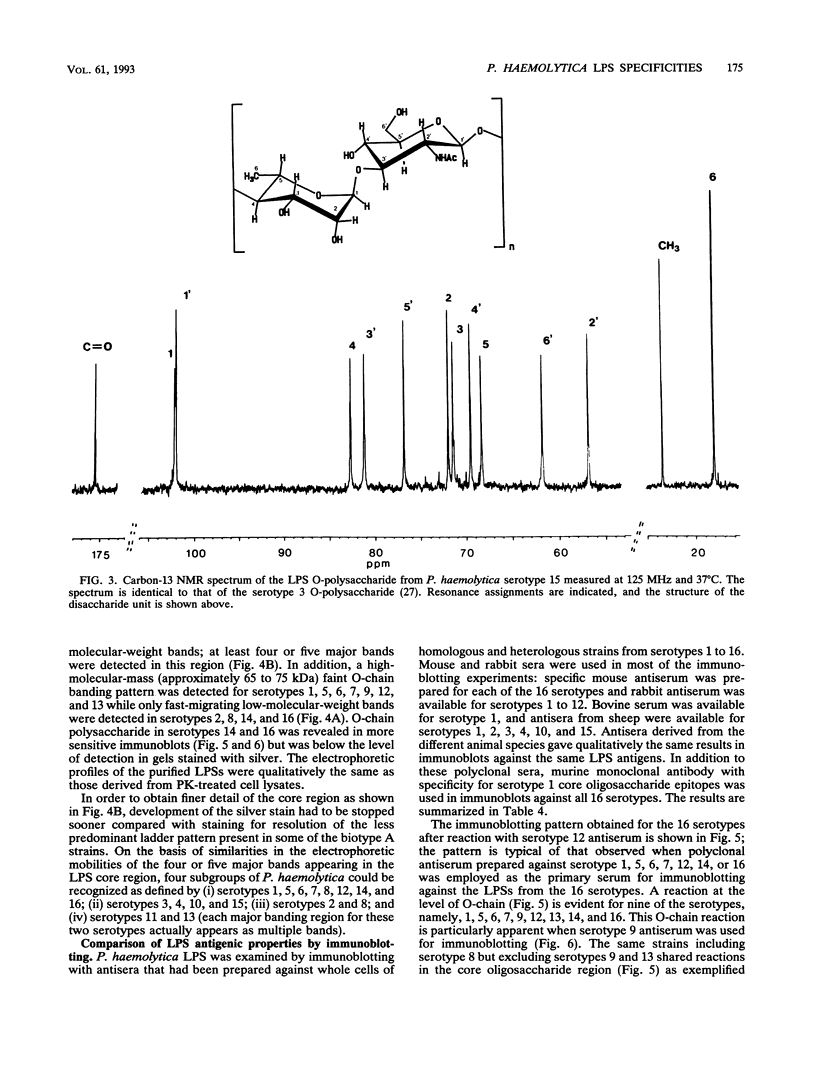
Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) from 16 serotypes of Pasteurella haemolytica were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and examined by silver staining and immunoblotting. Silver staining of proteinase K-digested cell lysates revealed two rough LPS serotypes (serotypes 2 and 8), which lacked demonstrable O-polysaccharide, while 14 others demonstrated a ladder pattern characteristic of smooth-type LPS. Purified LPSs from several serotypes yielded O-polysaccharide in addition to low-molecular-weight core oligosaccharide components when subjected to mild acid hydrolysis. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy revealed the O-chain polysaccharides of serotypes 1, 6, and 9 to be identical. Immunoblots using hyperimmune rabbit, mouse, bovine, and ovine sera from homologous and heterologous serotypes supported this finding and suggested that most of the A biotypes share common O-chain epitopes. Immunoblotting results also supported structural data which demonstrated that the O-polysaccharides of serotypes 3 and 15 and of serotypes 4 and 10 (T biotypes) are identical. Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis indicated that the core oligosaccharides of serotypes 1, 6, 8, 9, and 12 share similar structures, but that they are distinct from those of serotypes 3, 4, 10, and 15. Immunoblots with hyperimmune antisera and monoclonal antibody having specificity for the core region of serotype 1 LPS revealed shared epitopes in the core oligosaccharides of several A biotypes. Characterization of the molecular structure and antigenic specificities of LPS has been an important consideration in the development of purity and potency assays for veterinary vaccines which contain P. haemolytica.
Full text
PDF


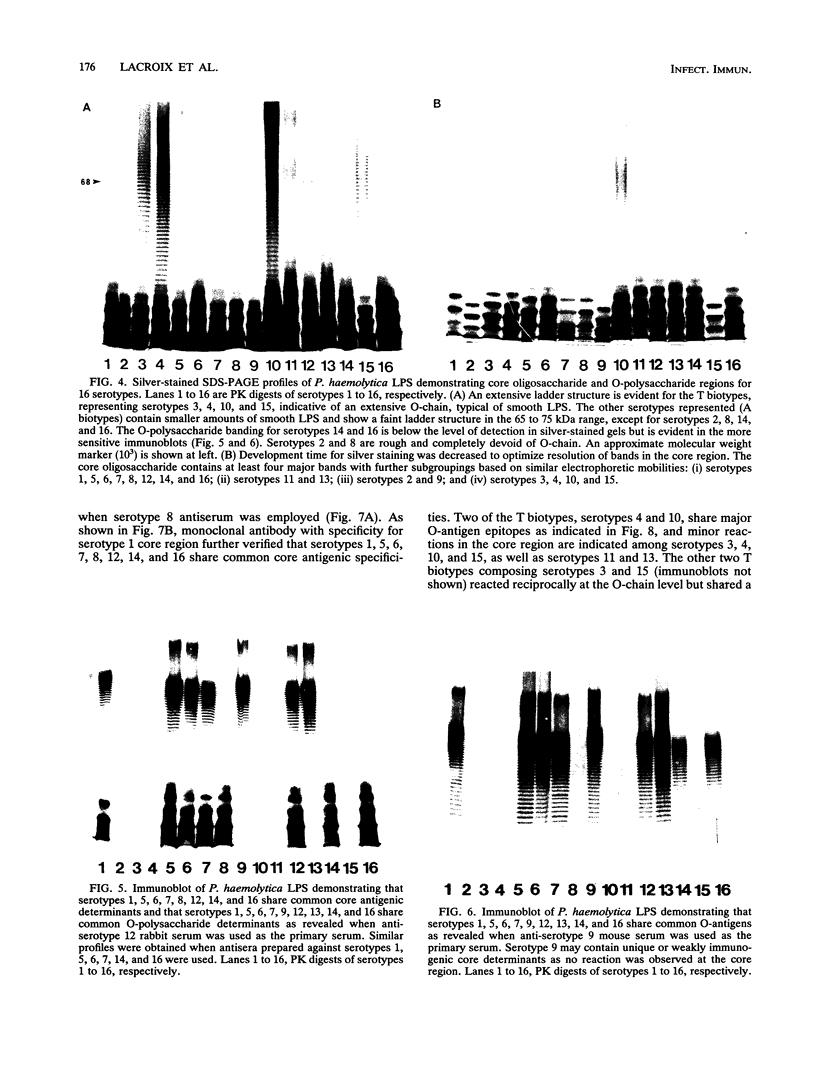
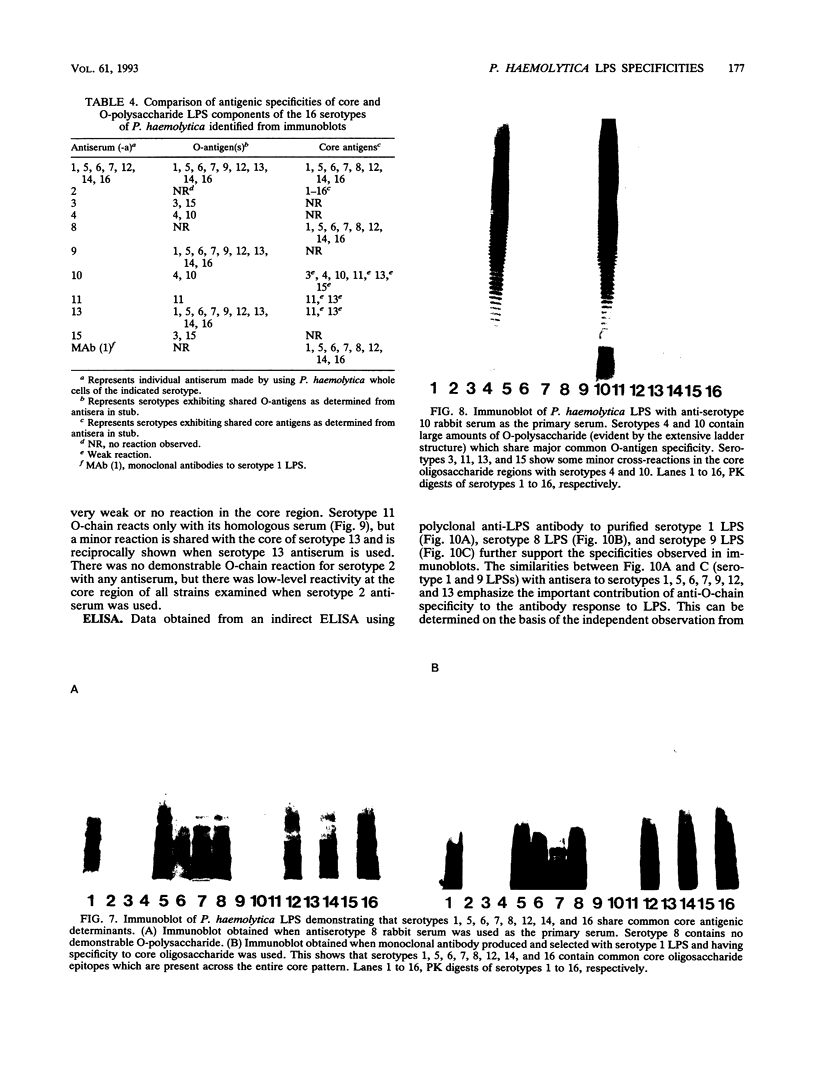

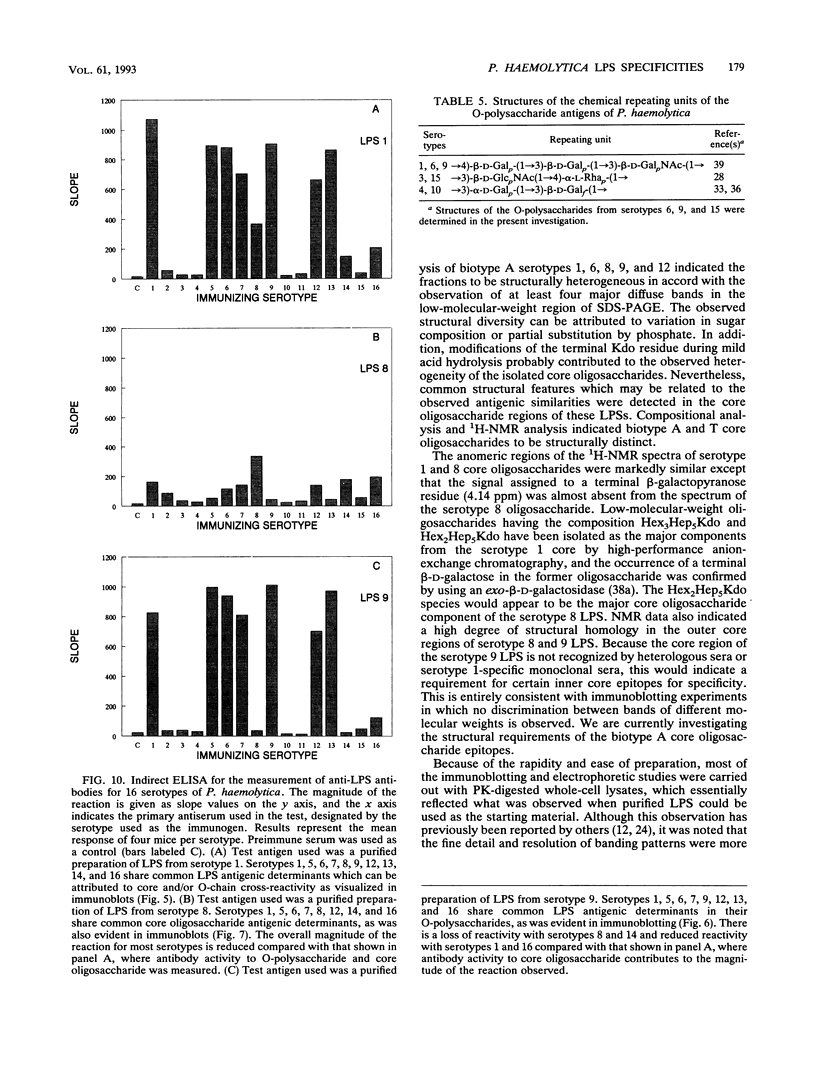


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIBERSTEIN E. L., MEYER M. E., KENNEDY P. C. Colonial variation of Pasteurella haemolytica isolated from sheep. J Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(4):445–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.4.445-452.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breider M. A., Kumar S., Corstvet R. E. Bovine pulmonary endothelial cell damage mediated by Pasteurella haemolytica pathogenic factors. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1671–1677. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1671-1677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breider M. A., Kumar S., Corstvet R. E. Interaction of bovine neutrophils in Pasteurella haemolytica mediated damage to pulmonary endothelial cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Feb;27(4):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(91)90030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrells C., Evans H. B., Dawson A. M. Antigenic relationships between the serotypes of Pasteurella haemolytica demonstrable by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Vet Microbiol. 1983 Apr;8(2):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Meadow P. M., Pitt T. L. The relationship between the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides and serological specificity in strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different O-serotypes. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):305–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Mosier D. A. Serum antibodies to Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide: relationship to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 May;47(5):1134–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Simons K. R. Effects of Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide on selected functions of bovine leukocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):154–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. L., Ali Q., Parton R., Coote J. G., Gibbs A., Freer J. H. Optimal conditions for the analysis of Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Dec 15;69(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90640-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W., Gilmour N. J., Mould D. L., Poxton I. R. Comparison of cell surface antigen extracts from two serotypes of Pasteurella haemolytica. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 May;130(5):1209–1216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-5-1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukes T. W., Glover G. J., Brooks B. W., Duncan J. R., Swendrowski M. Paratuberculosis in saiga antelope (Saiga tatarica) and experimental transmission to domestic sheep. J Wildl Dis. 1992 Apr;28(2):161–170. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-28.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham J. A., Antone S. M., Cunningham M. W., Confer A. W. Monoclonal antibodies to Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1 lipopolysaccharide: demonstration of antigenic similarities among several serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):885–889. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.885-889.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emau P., Giri S. N., Bruss M. L. Effects of smooth and rough Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharides on plasma cyclic-nucleotides and free fatty acids in calves. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Dec;15(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor L., Varga J., Hajtós J., Donachie W., Gilmour N. J. Characterisation of a new serotype of P haemolytica isolated in Hungary. Res Vet Sci. 1988 May;44(3):399–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Wessman G. E. Rapid plate agglutination procedure for serotyping Pasteurella haemolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):142–145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.142-145.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J., Laird S., Gilmour N. J. A new serotype (biotype T) of Pasteurella haemolytica. Res Vet Sci. 1982 Jan;32(1):127–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Freudenberg M. A., Jay F., Nerkar D., Veleva K., Brade H., Strittmatter W. Immunogenic properties of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):546–552. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt R., Berman E. R. A rapid procedure for the estimation of amino sugars on a micro scale. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He W., Fong Y., Marano M. A., Gershenwald J. E., Yurt R. W., Moldawer L. L., Lowry S. F. Tolerance to endotoxin prevents mortality in infected thermal injury: association with attenuated cytokine responses. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):859–864. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Gogolewski R. P., Corbeil L. B. Phenotypic phase variation in Haemophilus somnus lipooligosaccharide during bovine pneumonia and after in vitro passage. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2943–2951. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2943-2951.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J., Work E. A colorimetric estimation of lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch R. A., Richards J. C. Structure of the O-chain of the lipopolysaccharide of Pasteurella haemolytica serotype T3. Biochem Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;66(10):1055–1065. doi: 10.1139/o88-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxley D., Wilkinson S. G. Structures of neutral glycans isolated from the lipopolysaccharides of reference strains for Serratia marcescens serogroups O16 and O20. Carbohydr Res. 1989 Oct 31;193:241–248. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(89)85122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick D., Betts J., Frey E. A., Prameya R., Dorovini-Zis K., Finlay B. B. Haemophilus influenzae lipopolysaccharide disrupts confluent monolayers of bovine brain endothelial cells via a serum-dependent cytotoxic pathway. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):865–872. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen D. B., Mosier D. A., Clinkenbeard K. D., Confer A. W. Direct effects of Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide on bovine pulmonary endothelial cells in vitro. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Sep;50(9):1633–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Mosseri R., Kaplan E., Johns M. A., Shibolet S. Distribution of polysaccharide side chains of lipopolysaccharide determine resistance of Escherichia coli to the bactericidal activity of serum. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):953–956. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. C., Leitch R. A. Elucidation of the structure of the Pasteurella haemolytica serotype T10 lipopolysaccharide O-antigen by n.m.r. spectroscopy. Carbohydr Res. 1989 Mar 15;186(2):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(89)84041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsay R. L., Coyle-Dennis J. E., Lauerman L. H., Squire P. G. Purification and biological characterizationof endotoxin fractions from Pasteruella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Dec;42(12):2134–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Chu C., Schneerson R. Hypothesis for vaccine development: protective immunity to enteric diseases caused by nontyphoidal salmonellae and shigellae may be conferred by serum IgG antibodies to the O-specific polysaccharide of their lipopolysaccharides. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;15(2):346–361. doi: 10.1093/clinids/15.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slocombe R. F., Mulks M., Killingsworth C. R., Derksen F. J., Robinson N. E. Effect of Pasteurella haemolytica-derived endotoxin on pulmonary structure and function in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Mar;51(3):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacheron F., Mandine E., Lenaour R., Smets P., Zalisz R., Guenounou M. Inhibition of production of tumor necrosis factor by monoclonal antibodies to lipopolysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):873–878. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield C., Richards J. C., Perry M. B., Clarke B. R., MacLean L. L. Expression of two structurally distinct D-galactan O antigens in the lipopolysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype O1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1420–1431. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1420-1431.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. F., Sutherland A. D., Inglis L., Donachie W. Characterisation and biological activity of monoclonal antibodies specific for Pasteurella haemolytica A1 capsule and lipopolysaccharide. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Jun 1;31(2-3):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]