Abstract
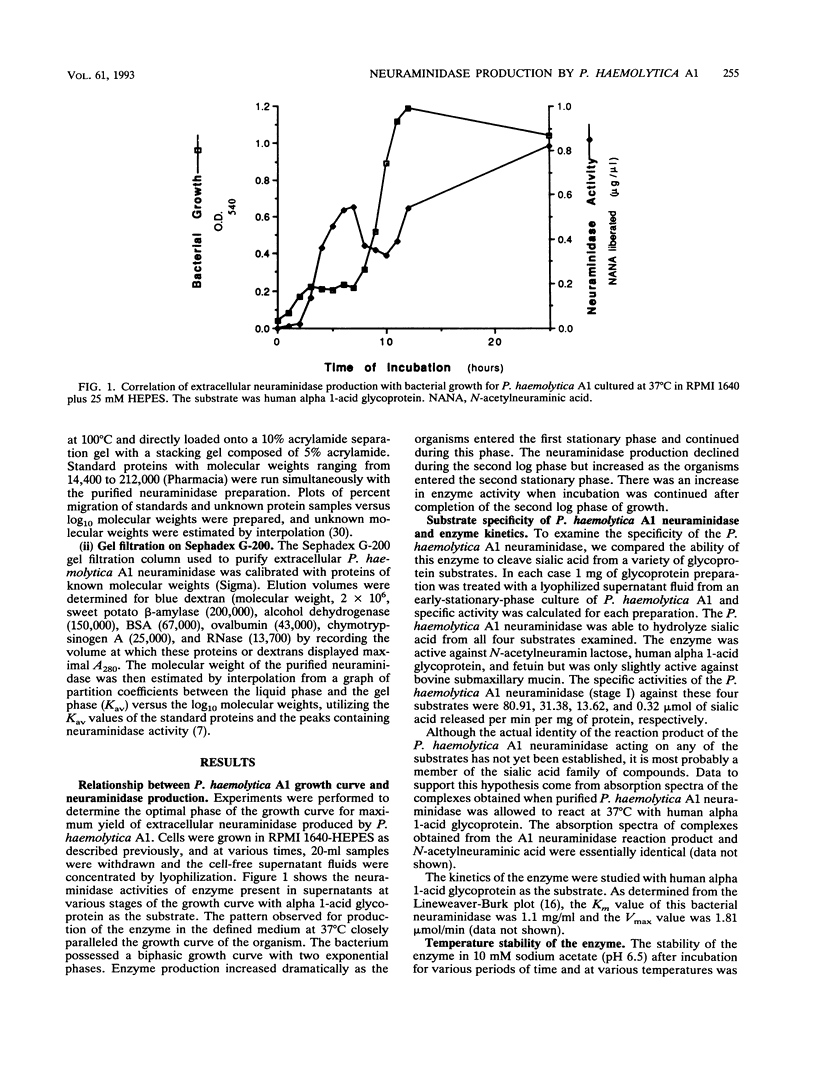
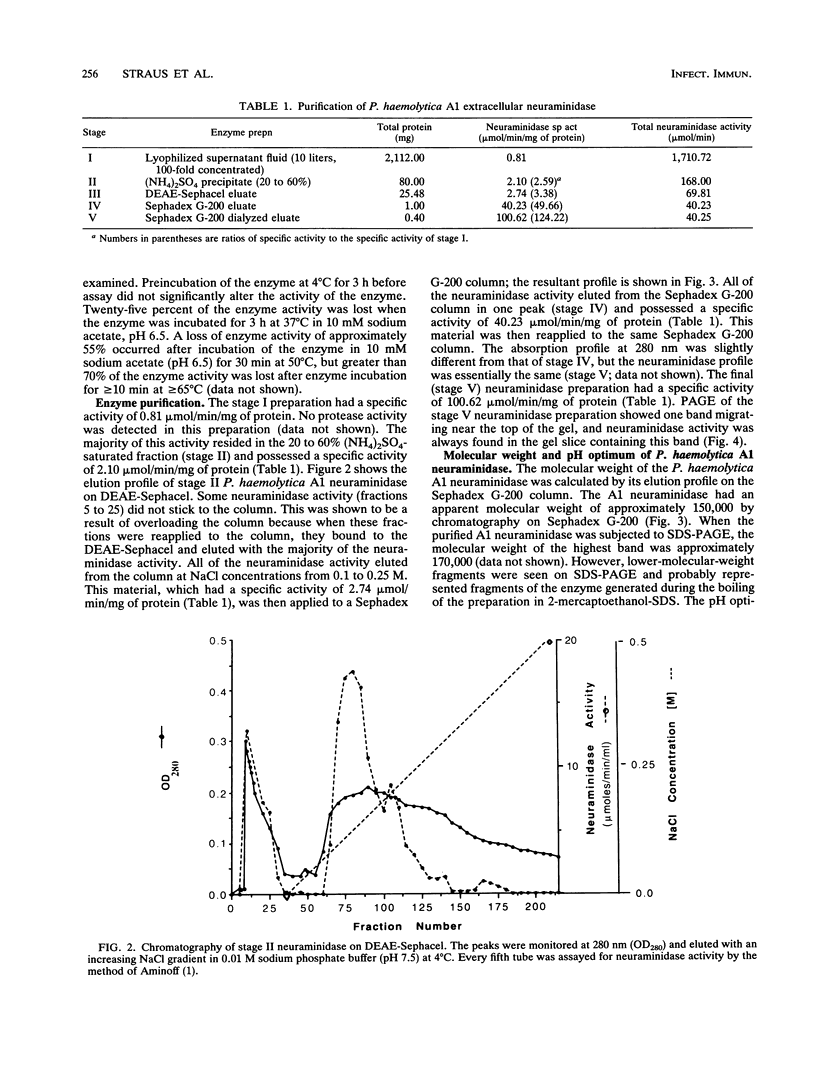
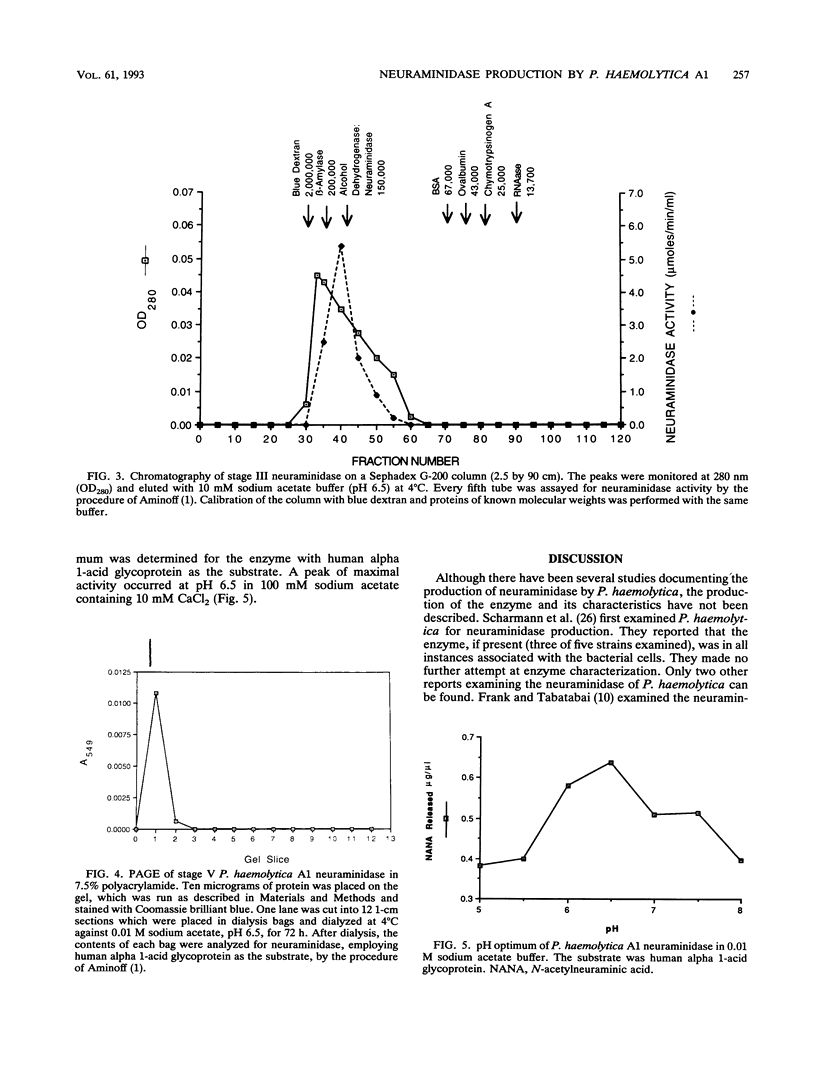
The properties of an extracellular neuroaminidase produced by a Pasteurella haemolytica A1 strain (isolated from a case of bovine pneumonia) during growth in a defined medium were examined in this investigation. This enzyme, isolated from concentrated culture supernatants of P. haemolytica A1, was active against N-acetylneuramin lactose, human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, fetuin, and bovine submaxillary mucin. Neuraminidase production paralleled bacterial growth in a defined medium and was maximal in the stationary phase of growth. The enzyme was purified to homogeneity by a combination of salt fractionation, ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-Sephacel, and gel filtration on Sephadex G-200. These procedures yielded an enzyme preparation that possessed a specific activity of 100.62 mumol of sialic acid released per min per mg of protein against human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. The Km value for this enzyme with human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein as the substrate was 1.1 mg/ml, and the enzyme possessed a pH optimum of 6.5. The P. haemolytica A1 neuraminidase had a molecular weight of approximately 150,000 as estimated by gel filtration and approximately 170,000 when analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The enzyme was stable at 4 degrees C for 3 h. At 37 degrees C for 3 h, 25% of enzymatic activity was lost. Approximately 55% of the enzyme activity was lost within 30 min at 50 degrees C, with greater than 70% of the enzyme activity being destroyed within 10 min at temperatures of > or = 65 degrees C.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy J. T., Jourdian G. W., Roseman S. The sialic acids. VI. Purification and properties of sialidase from Clostridium perfringens. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3501–3506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L., Baig M. M., Ayoub E. M. Properties of extracellular neuraminidase produced by group A streptococcus. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):780–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.780-786.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R. Viral and bacterial neuraminidases. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;59:35–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65444-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flashner M., Wang P., Hurley J. B., Tanenbaum S. W. Properties of an inducible extracellular neuraminidase from an Arthrobacter isolate. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1457-1465.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H. Pasteurella haemolytica and respiratory disease in cattle. Proc Annu Meet U S Anim Health Assoc. 1979;(83):153–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Tabatabai L. B. Neuraminidase activity of Pasteurella haemolytica isolates. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1119–1122. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1119-1122.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. R., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Systematic purification of five glycosidases from Streptococcus (Diplococcus) pneumoniae. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8615–8623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacson P. Myxoviruses and autoimmunity. Prog Allergy. 1967;10:256–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie L. E. The bovine respiratory disease complex. Can Vet J. 1974 Sep;15(9):233–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Baker C. J., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Association of elevated levels of extracellular neuraminidase with clinical isolates of type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):738–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.738-746.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Mattingly S. J., Straus D. C. Purification and partial characterization of neuraminidase from type III group B streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.164-171.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan T. W., Straus D. C., Mattingly S. J. Extracellular neuraminidase production by group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):189–195. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.189-195.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama T., Barksdale L. Neuraminidase of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1565–1581. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1565-1581.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy C. W., Straus D. C., Livingston C. W., Jr, Foster G. S. Immune response to pulmonary injection of Pasteurella haemolytica-impregnated agar beads followed by transthoracic challenge exposure in goats. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Oct;51(10):1629–1634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. K. Bacterial neuraminidase and altered immunological behavior of treated mammalian cells. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1977;21:227–267. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C., Silverman P., Haverback B. J. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharmann W., Drzeniek R., Blobel H. Neuraminidase of Pasteurella multocida. Infect Immun. 1970 Mar;1(3):319–320. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.3.319-320.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. C., Portnoy-Duran C. Neuraminidase production by a Streptococcus sanguis strain associated with subacute bacterial endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):507–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.507-515.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]