Abstract
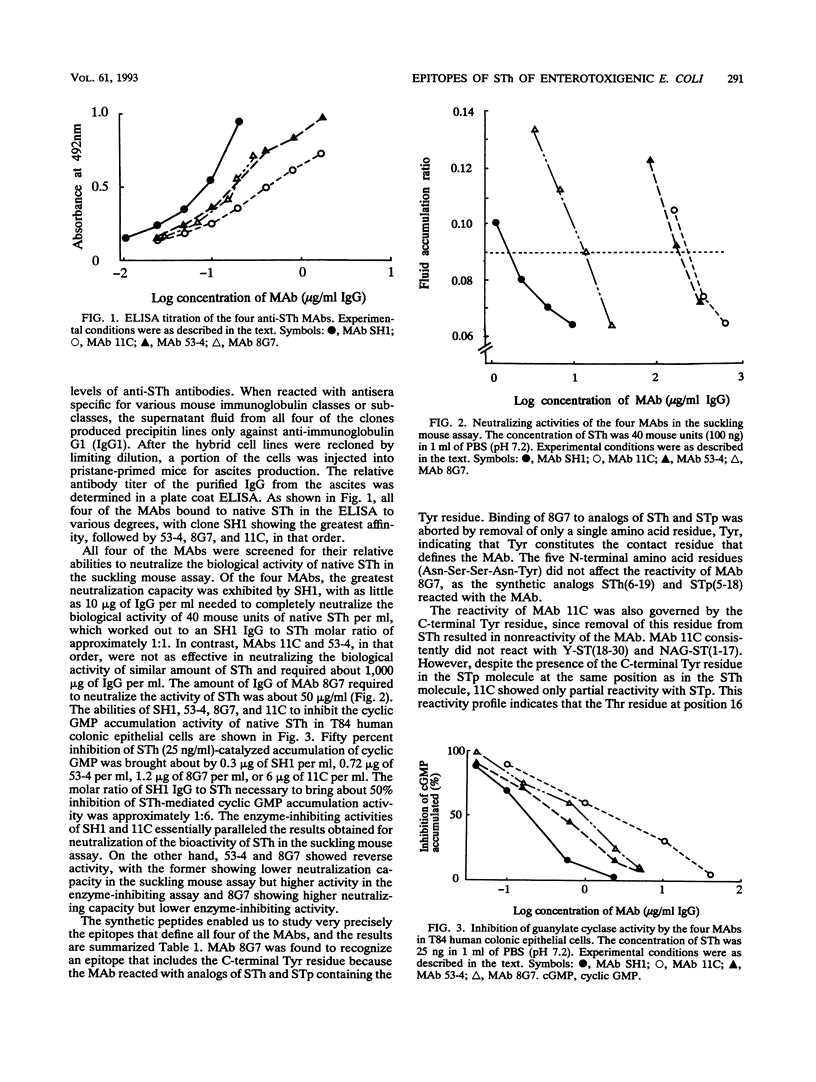
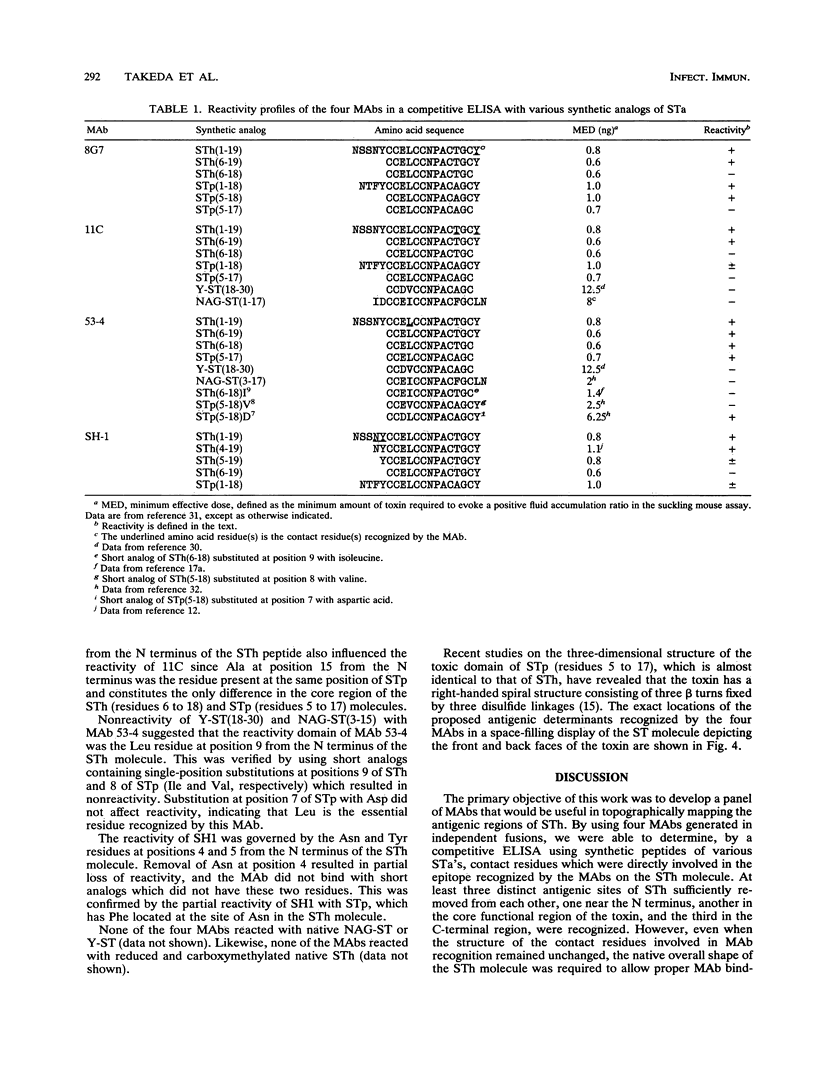
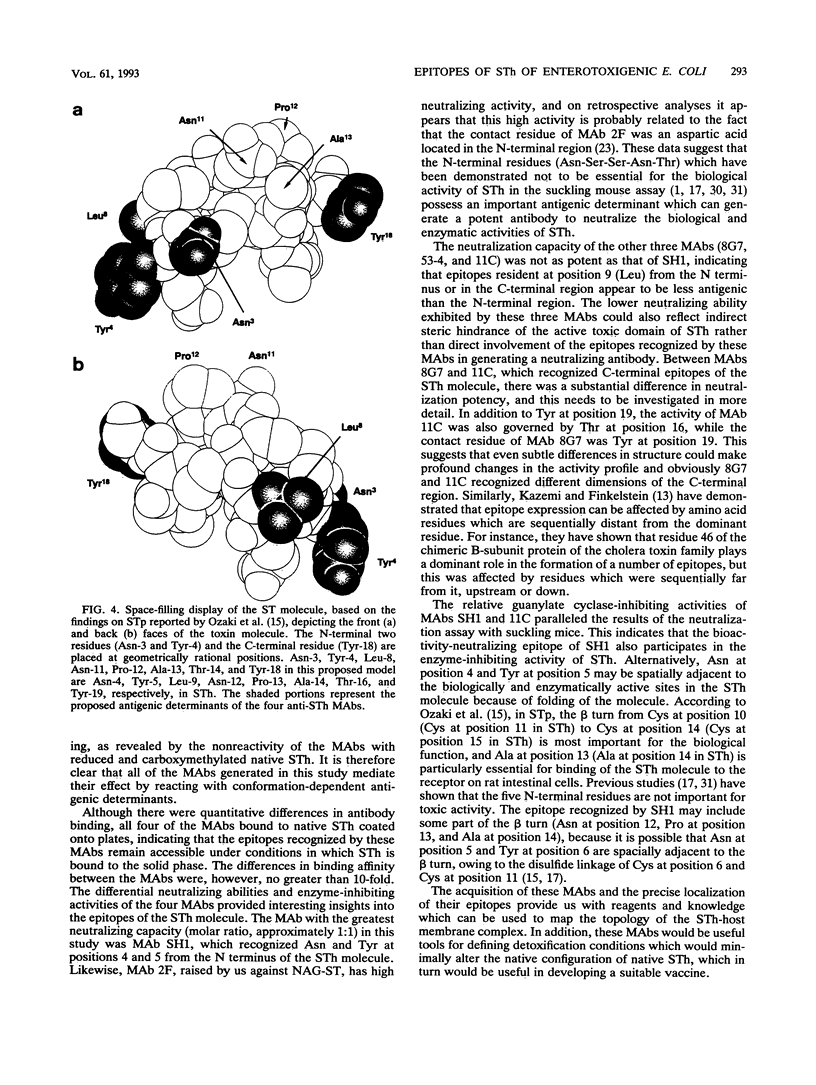
A panel of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) specific for the heat-stable enterotoxin (STh) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli was produced. All four MAbs (8G7, 53-4, 11C, and SH1) bound to native STh in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to various degrees, with clone SH1 showing the best affinity. The MAbs were screened for neutralizing and guanylate cyclase-inhibiting activities by the suckling mouse assay and the cyclic GMP assay using T84 cells, respectively. The contact amino acid residues governing the reactivity of the four MAbs were precisely determined by using several chemically synthesized analogs of the various heat-stable enterotoxins (STa's). Three distinct antigenic sites of STh sufficiently removed from each other, one near the N terminus, another in the core functional region of the toxin, and the third in the C-terminal region, were recognized by the different MAbs. MAb SH1, which recognized Asn at position 4 and Tyr at position 5 from the N terminus was 100 times more potent in neutralizing the bioactivity of STh in the suckling mouse assay than was MAb 11C, which recognized Thr at position 16 and Tyr at position 19 from the N terminus of the STh molecule. The MAbs which recognized Leu at position 9 from the N terminus (MAb 53-4) and Tyr at position 19 from the N terminus (MAb 8G7) showed intermediate activities in the neutralization assay. The guanylate cyclase-inhibiting activities of SH1 and 11C essentially paralleled the results for the neutralization of bioactivity, while MAbs 53-4 and 8G7 exhibited reverse activity. These results indicate that MAbs that recognize the N-terminal residues which have been shown not to be essential for toxic activity have a potent protective capacity. None of the MAbs reacted with reduced and carboxy-methylated native STh. This suggests that all of the MAbs mediate their effect by reacting with conformation-dependent antigenic determinants.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimoto S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino-acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arita M., Honda T., Miwatani T., Ohmori K., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Purification and characterization of a new heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Vibrio cholerae non-O1 serogroup Hakata. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2186–2188. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2186-2188.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arita M., Honda T., Miwatani T., Takeda T., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Purification and characterization of a heat-stable enterotoxin of Vibrio mimicus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Mar 15;63(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90536-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arita M., Takeda T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):45–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.45-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandwein H., Deutsch A., Thompson M., Giannella R. Production of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):242–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.242-246.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mol P., Hemelhof W., Retoré P., Takeda T., Miwatani T., Takeda Y., Butzler J. P. A competitive immunosorbent assay for the detection of heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Aug;20(1):69–74. doi: 10.1099/00222615-20-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino A., Cohen M., Thompson M., Dharmsathaphorn K., Giannella R. T84 cell receptor binding and guanyl cyclase activation by Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):G775–G780. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.6.G775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino A., Giannella R., Thompson M. R. Citrobacter freundii produces an 18-amino-acid heat-stable enterotoxin identical to the 18-amino-acid Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin (ST Ia). Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.649-652.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemelhof W., Retore P., De Mol P., Butzler J. P., Takeda T., Miwatani T., Takeda Y. Production of a monoclonal antibody against heat-stable enterotoxin produced by human strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1984 May 5;1(8384):1011–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi M., Finkelstein R. A. Study of epitopes of cholera enterotoxin-related enterotoxins by checkerboard immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2352–2360. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2352-2360.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy D. J., Greenberg R. N., Dunn J. A., Abernathy R., Ryerse J. S., Guerrant R. L. Effects of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin STb on intestines of mice, rats, rabbits, and piglets. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):639–643. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.639-643.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki H., Sato T., Kubota H., Hata Y., Katsube Y., Shimonishi Y. Molecular structure of the toxin domain of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a pathogenic strain of Escherichia coli. A putative binding site for a binding protein on rat intestinal epithelial cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5934–5941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotland S. M., Willshaw G. A., Said B., Smith H. R., Rowe B. Identification of Escherichia coli that produces heat-stable enterotoxin STA by a commercially available enzyme-linked immunoassay and comparison of the assay with infant mouse and DNA probe tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jul;27(7):1697–1699. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.7.1697-1699.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonishi Y., Hidaka Y., Koizumi M., Hane M., Aimoto S., Takeda T., Miwatani T., Takeda Y. Mode of disulfide bond formation of a heat-stable enterotoxin (STh) produced by a human strain of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 4;215(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Wikström M., Lindblad M., Holmgren J. Monoclonal antibodies against Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin (STa) and their use in a diagnostic ST ganglioside GM1-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):585–590. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.585-590.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Hitouji T., Aimoto S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin isolated from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain 18D. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 7;152(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Tominaga N., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Inoue T., Miyama A. Primary structure of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):845–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Tominaga N., Yoshimura S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Inoue T., Miyama A. Isolation, primary structure and synthesis of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., Nair G. B., Suzuki K., Shimonishi Y. Production of a monoclonal antibody to Vibrio cholerae non-O1 heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) which is cross-reactive with Yersinia enterocolitica ST. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2755–2759. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2755-2759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., Peina Y., Ogawa A., Dohi S., Abe H., Nair G. B., Pal S. C. Detection of heat-stable enterotoxin in a cholera toxin gene-positive strain of Vibrio cholerae O1. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 May 1;64(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90203-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Brandwein H., LaBine-Racke M., Giannella R. A. Simple and reliable enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies for detection of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxins. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):59–64. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.59-64.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weikel C. S., Guerrant R. L. STb enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: cyclic nucleotide-independent secretion. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;112:94–115. doi: 10.1002/9780470720936.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura S., Ikemura H., Watanabe H., Aimoto S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Miwatani T., Takeda Y. Essential structure for full enterotoxigenic activity of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 11;181(1):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnendaele F., Dobrescu L., Boon B. Induction of immunity against E. coli ST-enterotoxin. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1982 Jul;29(6):441–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1982.tb01246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


