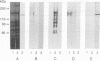
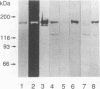
Abstract
Thirty-three murine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against the three glucosyltransferases (GTFs) (GTF-I, -SI, and -S) from Streptococcus mutans were obtained by the fusion of murine myeloma cells (P3X63-Ag8-U1) with spleen cells of BALB/c mice immunized with pure GTF-S or partially purified GTF-I from serotype c S. mutans PS14. The immunoreactivities of these MAbs were tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blotting (immunoblotting) with various GTF preparations. GTF-I and GTF-SI were expressed from two Streptococcus milleri or Escherichia coli transformants harboring gtfB or gtfC, respectively. All of the five MAbs raised against the GTF-S from PS14 reacted only with the homologous enzymes. Of these, 8 MAbs reacted only with the gtfB gene product (GTF-I), 4 MAbs reacted only with the gtfC gene product (GTF-SI), and the remaining 16 MAbs reacted with both gene products. The existence of GTF-SI in the purified GTF-I from PS14 was demonstrated by Western blot analysis using the representative monospecific MAbs. Further, the relative levels of the three GTFs in the extracellular and cellular fractions of S. mutans clinical isolates were examined by immunoblot analysis. The findings indicated that the relative level of GTF-SI, unlike that of GTF-I or GTF-S, differed markedly among isolates although the three GTFs were synthesized extracellularly by all the strains.
Full text
PDF

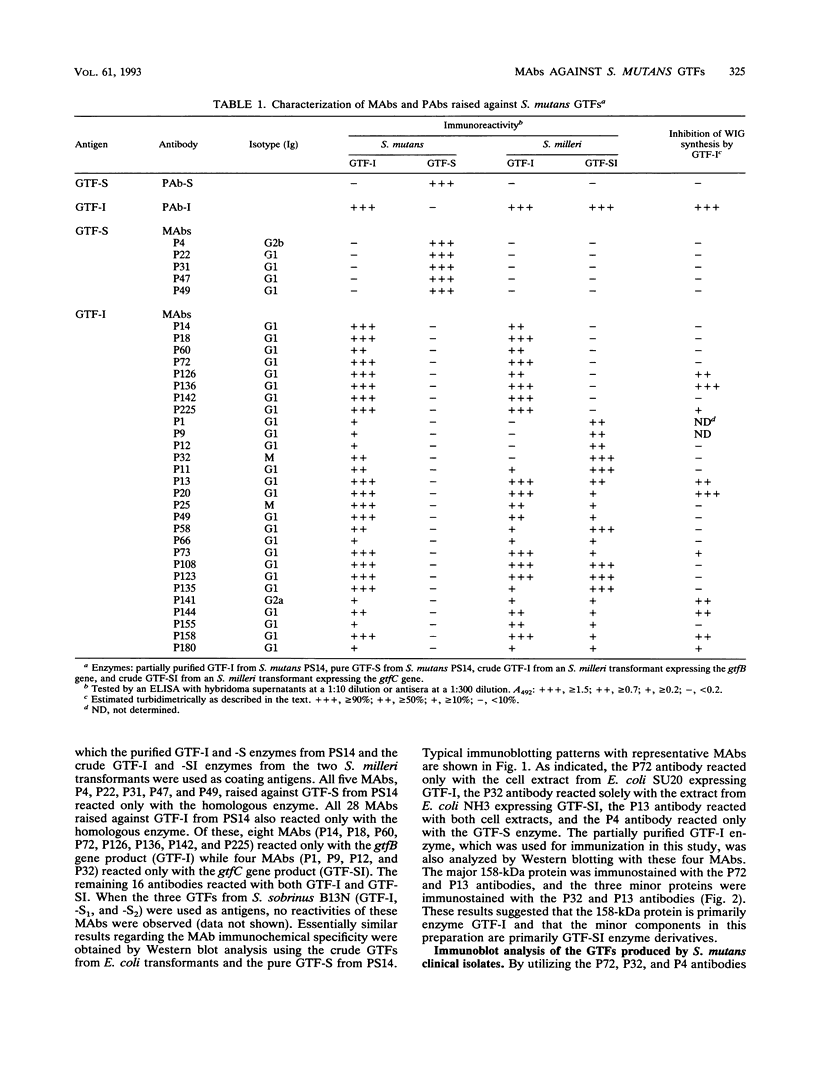
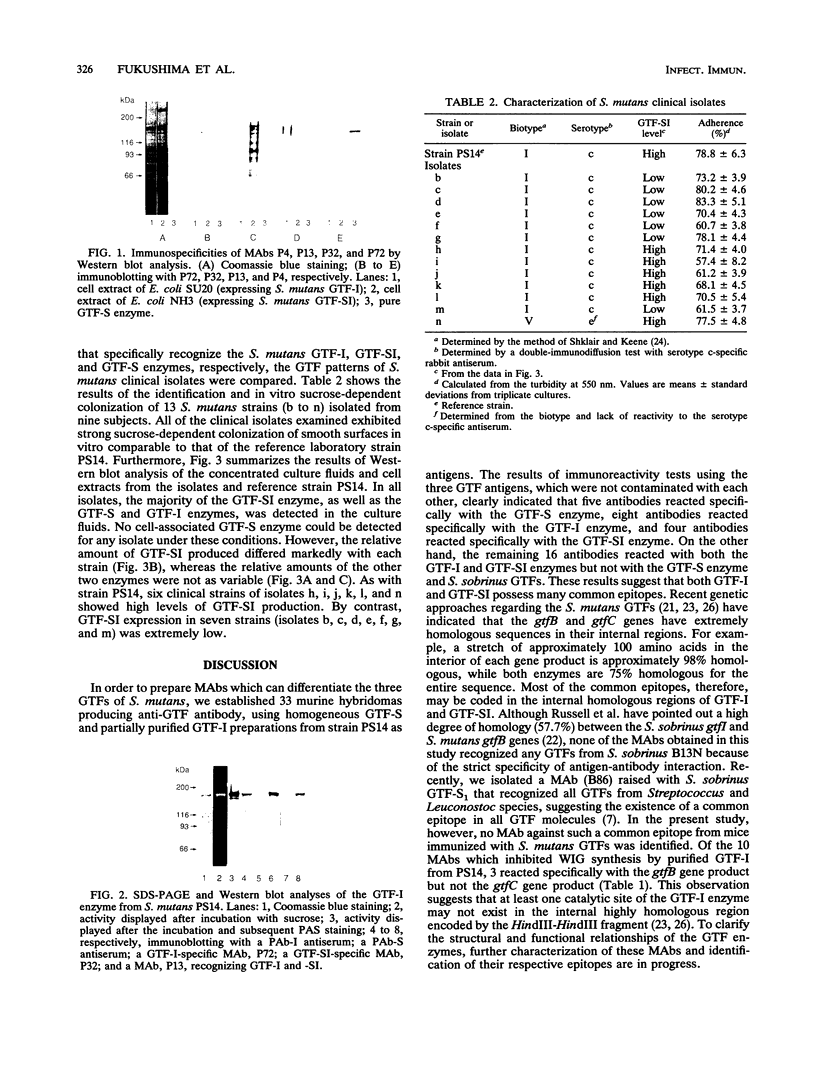


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki H., Shiroza T., Hayakawa M., Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Cloning of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene coding for insoluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.587-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba T., Ogawa T., Okahashi N., Yakushiji T., Koga T., Morimoto M., Hamada S. Purification and characterisation of the extracellular D-glucosyltransferase from serotype c Streptococcus mutans. Carbohydr Res. 1986 Dec 15;158:147–155. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(86)84013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Ikeda T., Kuramitsu H. K. Expression of Streptococcus mutans gtf genes in Streptococcus milleri. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2815–2822. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2815-2822.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Motoda R., Takada K., Ikeda T. Resolution of Streptococcus mutans glycosyltransferases into two components essential to water-insoluble glucan synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Horikoshi T., Minami T., Okahashi N., Koga T. Purification and characterization of cell-associated glucosyltransferase synthesizing water-insoluble glucan from serotype c Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Feb;135(Pt 2):335–344. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Masuda N., Ooshima T., Sobue S., Kotani S. Epidemiological survey of Streptococcus mutans among Japanese children. Identification and serological typing of the isolated strains. Jpn J Microbiol. 1976 Feb;20(1):33–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1976.tb00905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the Streptococcus mutans gtfC gene, coding for synthesis of both soluble and insoluble glucans. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1999–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1999-2005.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the Streptococcus mutans gtfD gene, coding for primer-dependent soluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2079–2085. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2079-2085.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K., Wondrack L. Insoluble glucan synthesis by Streptococcus mutans serotype c strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.763-770.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Shimamura A., Tsumori H. Purification and characterization of cell-associated glucosyltransferase synthesizing insoluble glucan from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):2055–2063. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-2055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Tsumori H., Shimamura A. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular glucosyltransferase synthesizing insoluble glucan from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):790–796. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.790-796.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pucci M. J., Jones K. R., Kuramitsu H. K., Macrina F. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the glucosyltransferase C gene (gtfC) from Streptococcus mutans LM7. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2176–2182. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2176-2182.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Shiroza T., Kuramitsu H. K., Ferretti J. J. Homology of glucosyltransferase gene and protein sequences from Streptococcus sobrinus and Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1988 Mar;67(3):543–547. doi: 10.1177/00220345880670030401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroza T., Ueda S., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the gtfB gene from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4263–4270. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4263-4270.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shklair I. L., Keene H. J. A biochemical scheme for the separation of the five varieties of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 Nov;19(11):1079–1081. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Fukushima K. Effects of certain salts on glucosyltransferase synthesis by Streptococcus mutans strain PS-14. J Dent Res. 1986 Mar;65(3):452–455. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650031601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S., Shiroza T., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the gtfC gene from Streptococcus mutans GS-5. Gene. 1988 Sep 15;69(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90382-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita Y., Bowen W. H., Kuramitsu H. K. Molecular analysis of a Streptococcus mutans strain exhibiting polymorphism in the tandem gtfB and gtfC genes. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1618–1624. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1618-1624.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Soet J. J., van Loveren C., Lammens A. J., Pavicić M. J., Homburg C. H., ten Cate J. M., de Graaff J. Differences in cariogenicity between fresh isolates of Streptococcus sobrinus and Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res. 1991;25(2):116–122. doi: 10.1159/000261353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]