Abstract
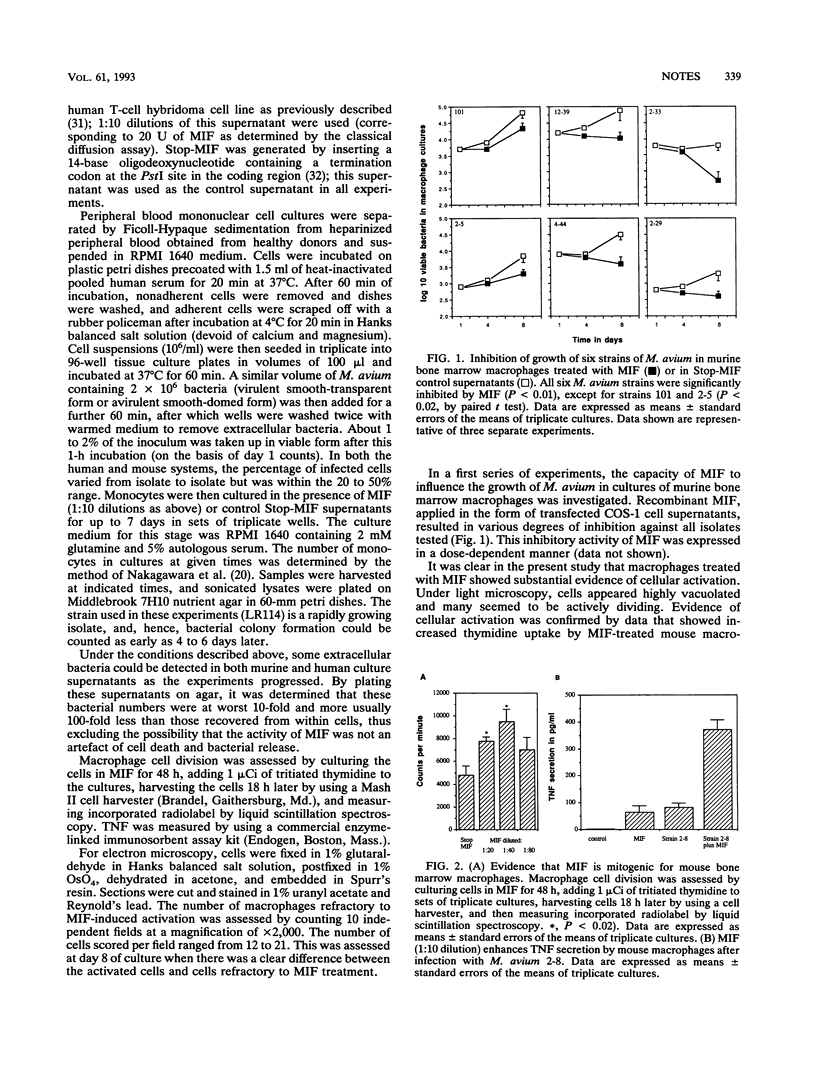
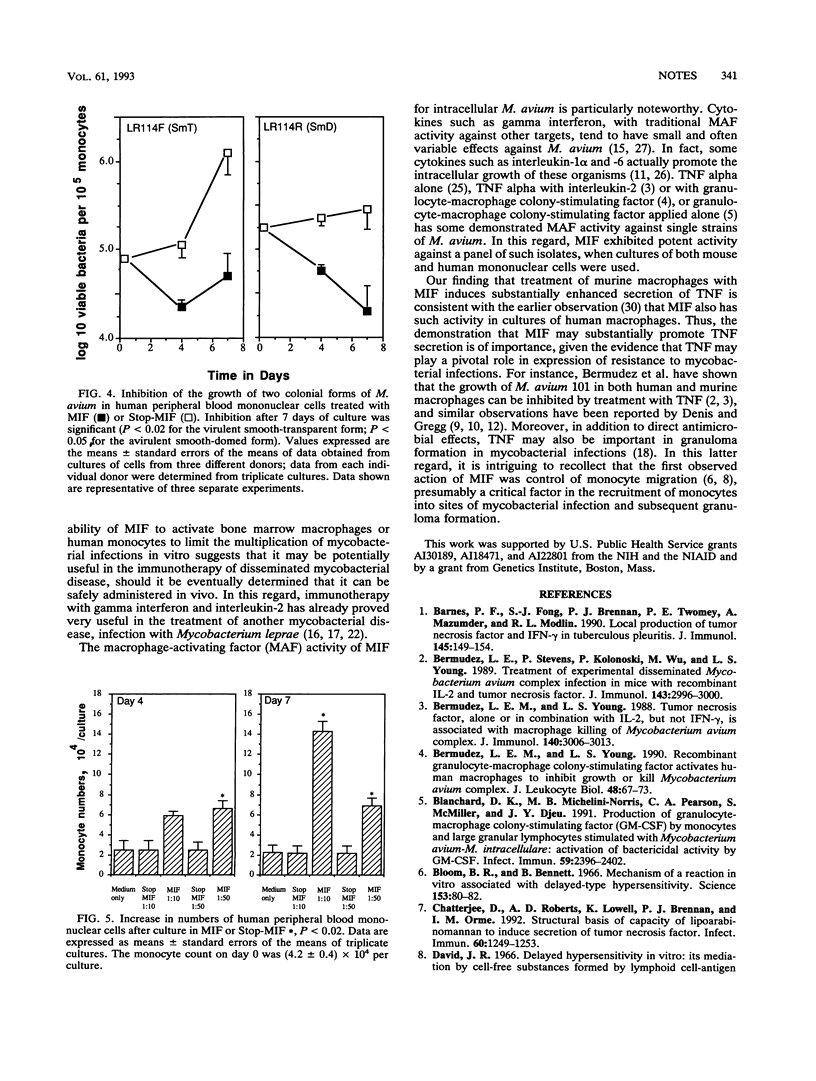
Infections caused by Mycobacterium avium, the most common form of diseminated bacterial disease in AIDS patients, are difficult to treat because of their resistance to many antimycobacterial drugs. The results of the present study show that recombinant migration inhibitory factor, a 12-kDa molecule recently isolated by COS-1 cell expression screening of cDNA from a human T-cell hybridoma, has potent inhibitory activity on the growth of a panel of clinical isolates of M. avium within both bone-marrow-derived murine macrophages and cultured human blood monocytes. These cells cultured in recombinant migration inhibitory factor exhibit various signs of activation, including cell division, morphological changes such as evidence of substantial phagolysosomal fusion, and enhanced secretion of tumor necrosis factor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. F., Fong S. J., Brennan P. J., Twomey P. E., Mazumder A., Modlin R. L. Local production of tumor necrosis factor and IFN-gamma in tuberculous pleuritis. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Stevens P., Kolonoski P., Wu M., Young L. S. Treatment of experimental disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection in mice with recombinant IL-2 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2996–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor activates human macrophages to inhibit growth or kill Mycobacterium avium complex. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Jul;48(1):67–73. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez L. E., Young L. S. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3006–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Michelini-Norris M. B., Pearson C. A., McMillen S., Djeu J. Y. Production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) by monocytes and large granular lymphocytes stimulated with Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare: activation of bactericidal activity by GM-CSF. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2396–2402. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2396-2402.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Bennett B. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Roberts A. D., Lowell K., Brennan P. J., Orme I. M. Structural basis of capacity of lipoarabinomannan to induce secretion of tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1249-1253.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro: its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid cell-antigen interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):72–77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Gregg E. O. Recombinant tumour necrosis factor-alpha decreases whereas recombinant interleukin-6 increases growth of a virulent strain of Mycobacterium avium in human macrophages. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):139–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Growth of Mycobacterium avium in human monocytes: identification of cytokines which reduce and enhance intracellular microbial growth. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):391–395. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Modulation of Mycobacterium avium growth in vivo by cytokines: involvement of tumour necrosis factor in resistance to atypical mycobacteria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Mar;83(3):466–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor stimulate human macrophages to restrict growth of virulent Mycobacterium avium and to kill avirulent M. avium: killing effector mechanism depends on the generation of reactive nitrogen intermediates. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Apr;49(4):380–387. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J., Goldberger M. J., Parenti D. M. Mycobacterium avium infection and AIDS: a therapeutic dilemma in rapid evolution. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1326–1335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Havlik J. A., Ellis D. A., Kennedy E., Fann S. A., Dubois R. E., Thompson S. E. Survival of patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome and disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection with and without antimycobacterial chemotherapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Sep;144(3 Pt 1):557–559. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.3_Pt_1.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Shiratsuchi H., Toba H., Ellner J. J. Preservation of monocyte effector functions against Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare in patients with AIDS. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3639–3645. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3639-3645.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Kiessling R., Teklemariam S., Hancock G., Sheftel G., Job C. K., Converse P., Ottenhoff T. H., Becx-Bleumink M., Dietz M. The reconstitution of cell-mediated immunity in the cutaneous lesions of lepromatous leprosy by recombinant interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):893–907. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Nusrat A., Sarno E. N., Job C. K., McElrath J., Porto J. A., Nathan C. F., Cohn Z. A. Cellular responses to the intradermal injection of recombinant human gamma-interferon in lepromatous leprosy patients. Am J Pathol. 1987 Aug;128(2):345–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnes A., Rennick D. M. Interleukin 4 induces cultured monocytes/macrophages to form giant multinucleated cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):598–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawara A., Nathan C. F. A simple method for counting adherent cells: application to cultured human monocytes, macrophages and multinucleated giant cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jan 28;56(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane A., Minagawa T., Kato K. Endogenous tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is essential to host resistance against Listeria monocytogenes infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2563–2569. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2563-2569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Kaplan G., Levis W. R., Nusrat A., Witmer M. D., Sherwin S. A., Job C. K., Horowitz C. R., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Local and systemic effects of intradermal recombinant interferon-gamma in patients with lepromatous leprosy. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jul 3;315(1):6–15. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607033150102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. W., Gan H. X., McCarthy P. L., Jr, Remold H. G. Survival of human macrophages infected with Mycobacterium avium intracellulare correlates with increased production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-6. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3942–3948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S., Lane H. C., Witebsky F. G., Gosey L. L., Hoggan M. D., Fauci A. S. Host defense against Mycobacterium-avium complex. J Clin Immunol. 1988 Jul;8(4):234–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00916551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratsuchi H., Johnson J. L., Ellner J. J. Bidirectional effects of cytokines on the growth of Mycobacterium avium within human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3165–3170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratsuchi H., Johnson J. L., Toba H., Ellner J. J. Strain- and donor-related differences in the interaction of Mycobacterium avium with human monocytes and its modulation by interferon-gamma. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):932–938. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurman G. B., Braude I. A., Gray P. W., Oldham R. K., Stevenson H. C. MIF-like activity of natural and recombinant human interferon-gamma and their neutralization by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):305–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Sherry B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis factor plays a protective role in experimental murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2097–2104. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser W. Y., Pozzi L. M., David J. R. Human recombinant migration inhibitory factor activates human macrophages to kill Leishmania donovani. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):2006–2011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser W. Y., Remold H. G., David J. R. Generation of human hybridomas producing migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and of murine hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies to human MIF. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jan;90(1):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser W. Y., Temple P. A., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Remold H. G., Clark S. C., David J. R. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a human macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7522–7526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. Mycobacterium avium complex infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):863–867. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



