Abstract
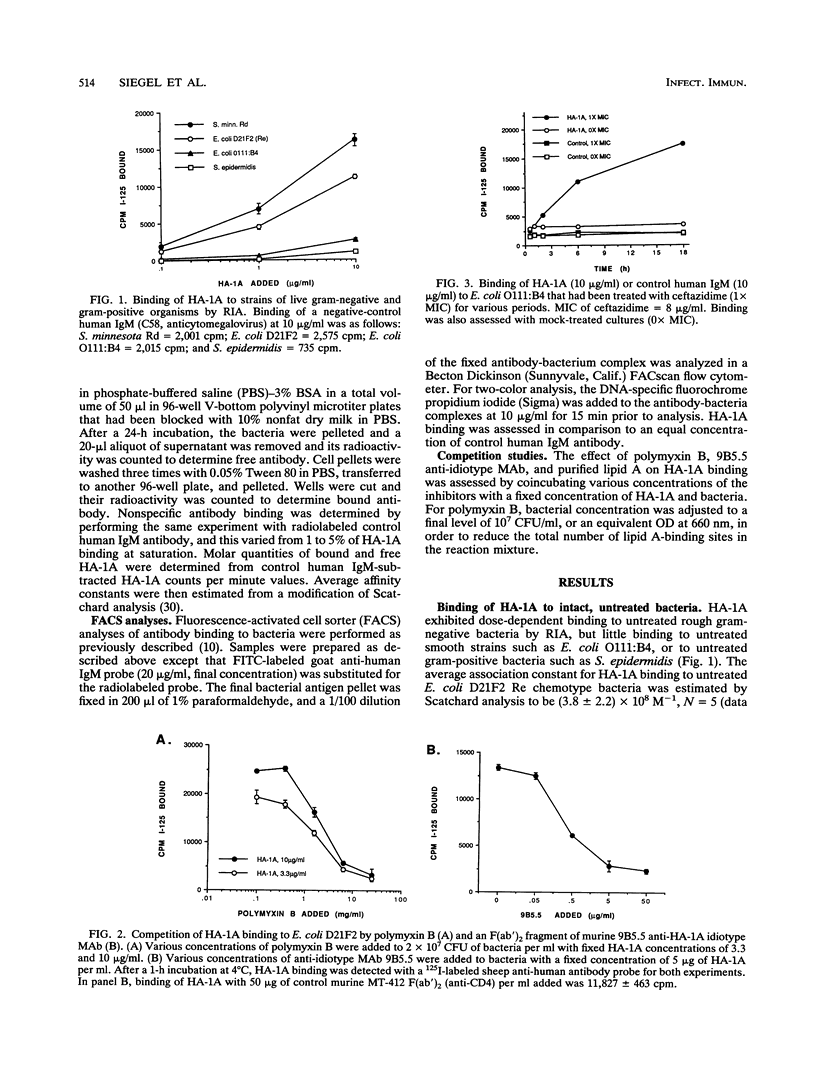
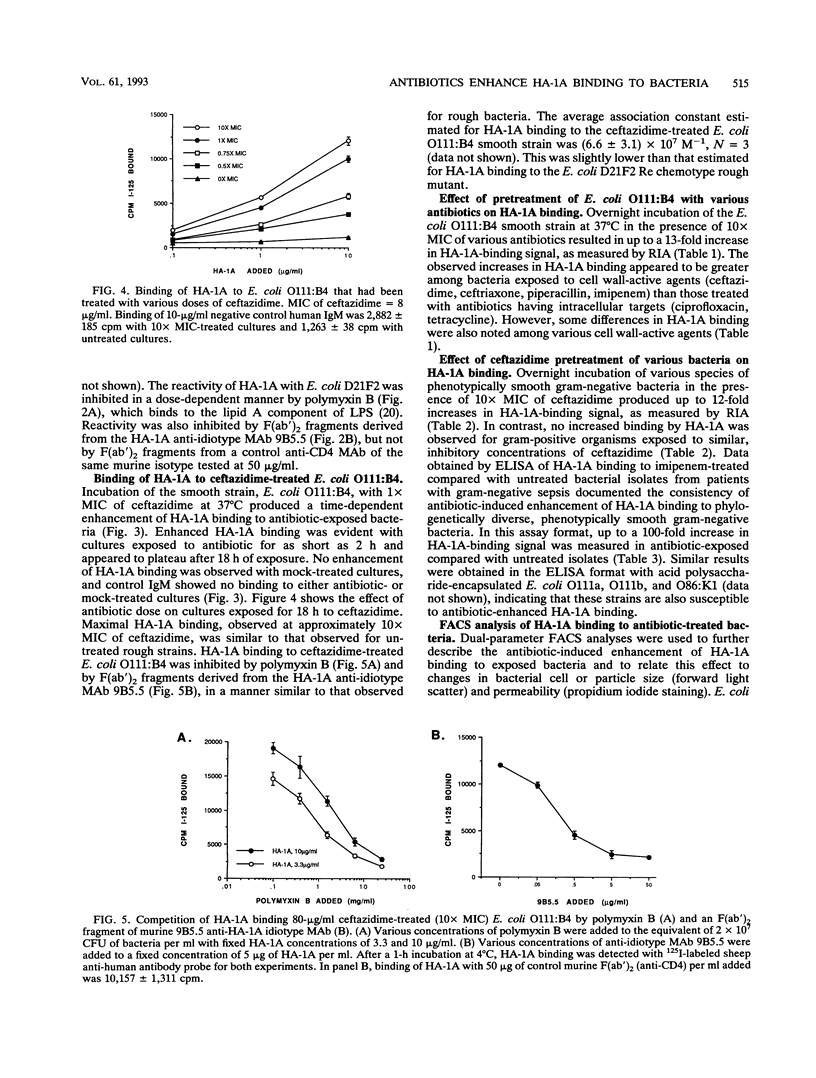
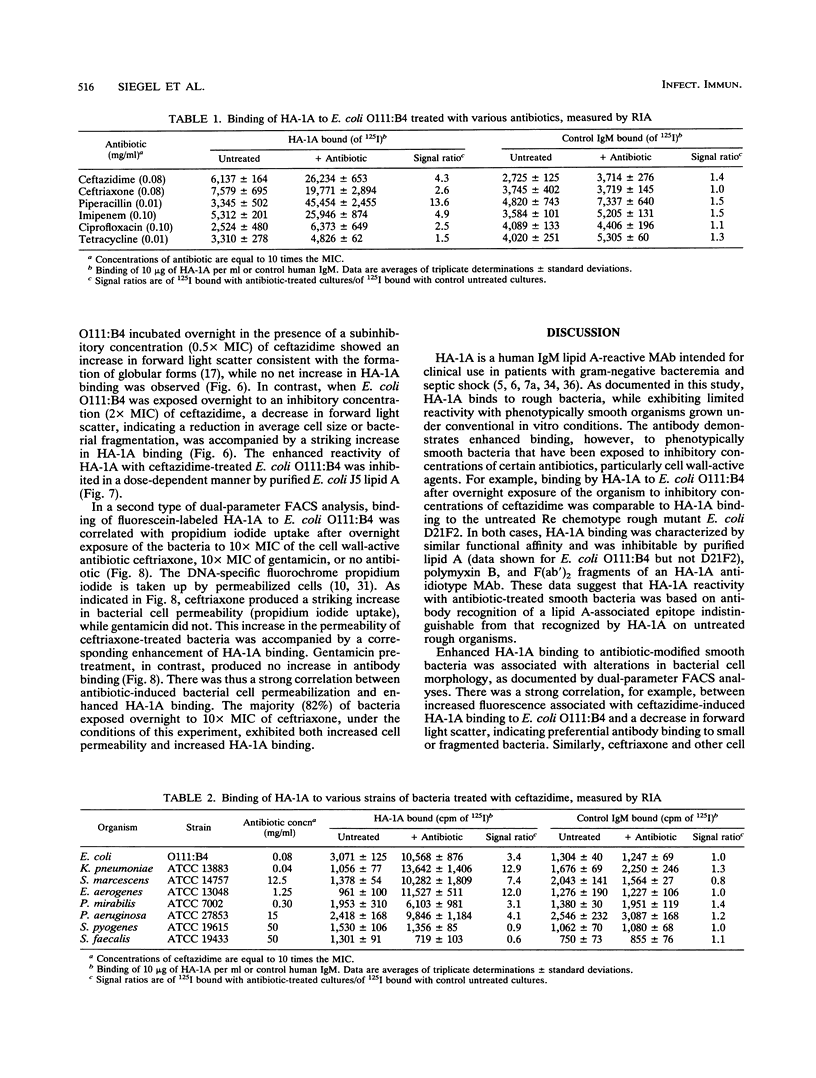
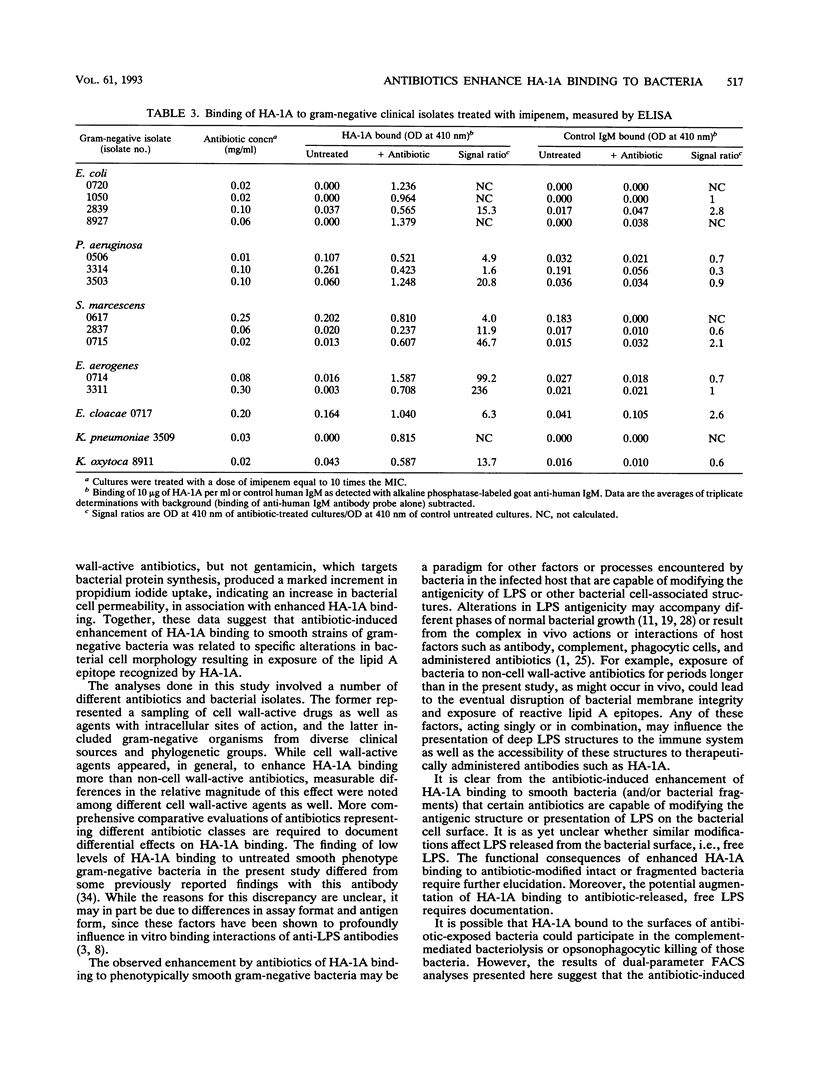
The effect of antibiotic exposure of phenotypically smooth gram-negative bacteria on binding by the human lipid A-reactive monoclonal antibody HA-1A (trademark of Centocor, Inc.) was examined by liquid-phase immunoassay and by dual-parameter flow cytometry (fluorescence-activated cell sorter [FACS]) analysis. HA-1A exhibited dose-dependent binding to untreated rough gram-negative bacteria such as the Escherichia coli D21F2 Re chemotype strain but little binding to untreated smooth strains such as E. coli O111:B4, or to gram-positive bacteria. However, overnight incubation of E. coli O111:B4 with inhibitory concentrations of ceftazidime produced dose-dependent enhancement of HA-1A binding. Similar augmentation of HA-1A binding was observed when other smooth strains were exposed to cell wall-active agents. Dual-parameter FACS analysis of E. coli O111:B4 exposed overnight to two times the MIC of ceftazidime revealed a decrease in forward light scatter, indicating a reduction in average cell size or bacterial fragmentation, accompanied by a striking increase in lipid A-inhibitable HA-1A binding. Moreover, ceftriaxone, but not gentamicin, produced a marked increase in propidium iodide uptake, indicating an increase in bacterial cell permeability, and a corresponding enhancement of HA-1A binding. Antibiotic-induced enhancement of HA-1A binding to smooth strains of gram-negative bacteria thus appears related to specific alterations in bacterial cell morphology resulting in exposure of the epitope recognized by HA-1A.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi L. E., Bonventre P. F. Enhanced phagocytosis, killing, and serum sensitivity of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus treated with sub-MICs of imipenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1012–1018. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aydintug M. K., Inzana T. J., Letonja T., Davis W. C., Corbeil L. B. Cross-reactivity of monoclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli J5 with heterologous gram-negative bacteria and extracted lipopolysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):846–857. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayston K. F., Cohen J. Bacterial endotoxin and current concepts in the diagnosis and treatment of endotoxaemia. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Feb;31(2):73–83. doi: 10.1099/00222615-31-2-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogard W. C., Jr, Dunn D. L., Abernethy K., Kilgarriff C., Kung P. C. Isolation and characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies specific for gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide: association of cross-genus reactivity with lipid A specificity. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):899–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.899-908.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade L., Brandenburg K., Kuhn H. M., Kusumoto S., Macher I., Rietschel E. T., Brade H. The immunogenicity and antigenicity of lipid A are influenced by its physicochemical state and environment. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2636–2644. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2636-2644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel D., Peppard J., Chehimi J., Hammerling U., O'Reilly R. The diagnostic, prophylactic, and therapeutic uses of monoclonal antibodies to human cytomegalovirus. Transplant Proc. 1987 Dec;19(6 Suppl 7):132–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. E., Pollack M., Hardegen N. J., Koles N. L., Guelde G., Chia J. K. Fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis of binding by lipopolysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies to gram-negative bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):148–155. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. E., Pollack M., Koles N. L., Hardegen N. J., Panopoulos D. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Escherichia coli J5 variants: analysis by flow cytometry. J Infect Dis. 1992 Oct;166(4):803–811. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.4.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn P. M., Shenep J. L., Gigliotti F., Davis D. S., Hildner W. K. Immunolabeling of lipopolysaccharide liberated from antibiotic-treated Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2760–2762. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2760-2762.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Shenep J. L. Failure of monoclonal antibodies to core glycolipid to bind intact smooth strains of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1005–1011. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazaeli M. B., Rogers K. J., LoBuglio A. F. Quantitative assay of a human monoclonal IgM antibody (HA-1A) in human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Feb 24;117(2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmo T., Boven E., Cuttitta F., Fedorko J., Bunn P. A., Jr Determination of the immunoreactive fraction of radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies by linear extrapolation to binding at infinite antigen excess. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):77–89. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90435-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorain V., Sabath L. D. Penicillins and cephalosporins: differences in morphologic effects on Proteus mirabilis. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):560–564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Kaijser B. Lipid A and anti-lipid A. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):758–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.758-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallus D. E., Norcross N. L. Antibody specific for Escherichia coli J5 cross-reacts to various degrees with an Escherichia coli clinical isolate grown for different lengths of time. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1042–1046. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1042-1046.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Crockford G., Bogard W. C., Jr, Hancock R. E. Monoclonal antibodies specific for Escherichia coli J5 lipopolysaccharide: cross-reaction with other gram-negative bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):631–636. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.631-636.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek B. P., Schellekens J. F., Lippe W., Dekker B. A., Verhoef J. Carumonam enhances reactivity of Escherichia coli with mono- and polyclonal antisera to rough Escherichia coli J5. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1009–1013. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1009-1013.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek B. P., Veringa E. M. Role of antibodies and antibiotics in aerobic gram-negative septicemia: possible synergism between antimicrobial treatment and immunotherapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;13(4):751–760. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Chia J. K., Koles N. L., Miller M., Guelde G. Specificity and cross-reactivity of monoclonal antibodies reactive with the core and lipid A regions of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):168–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Raubitschek A. A., Larrick J. W. Human monoclonal antibodies that recognize conserved epitopes in the core-lipid A region of lipopolysaccharides. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1421–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI112970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Barton R. P., Mogan K. A. Role of antibiotic class in the rate of liberation of endotoxin during therapy for experimental gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1012–1018. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Mogan K. A. Kinetics of endotoxin release during antibiotic therapy for experimental gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):380–388. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng N. N., Kaplan H. S., Hebert J. M., Moore C., Douglas H., Wunderlich A., Braude A. I. Protection against gram-negative bacteremia and endotoxemia with human monoclonal IgM antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Fisher C. J., Jr, Sprung C. L., Straube R. C., Sadoff J. C., Foulke G. E., Wortel C. H., Fink M. P., Dellinger R. P., Teng N. N. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and septic shock with HA-1A human monoclonal antibody against endotoxin. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The HA-1A Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 14;324(7):429–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102143240701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


