Abstract
Infection of cultured HEp-2 cells with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli causes substantial actin accretion at points of bacterial contact and cell death. Loss of viability was delayed by chelating intracellular free calcium. Actin accretion was partially inhibited by preventing elevation of free cytosolic calcium and prevented by treatment with a calmodulin inhibitor.
Full text
PDF
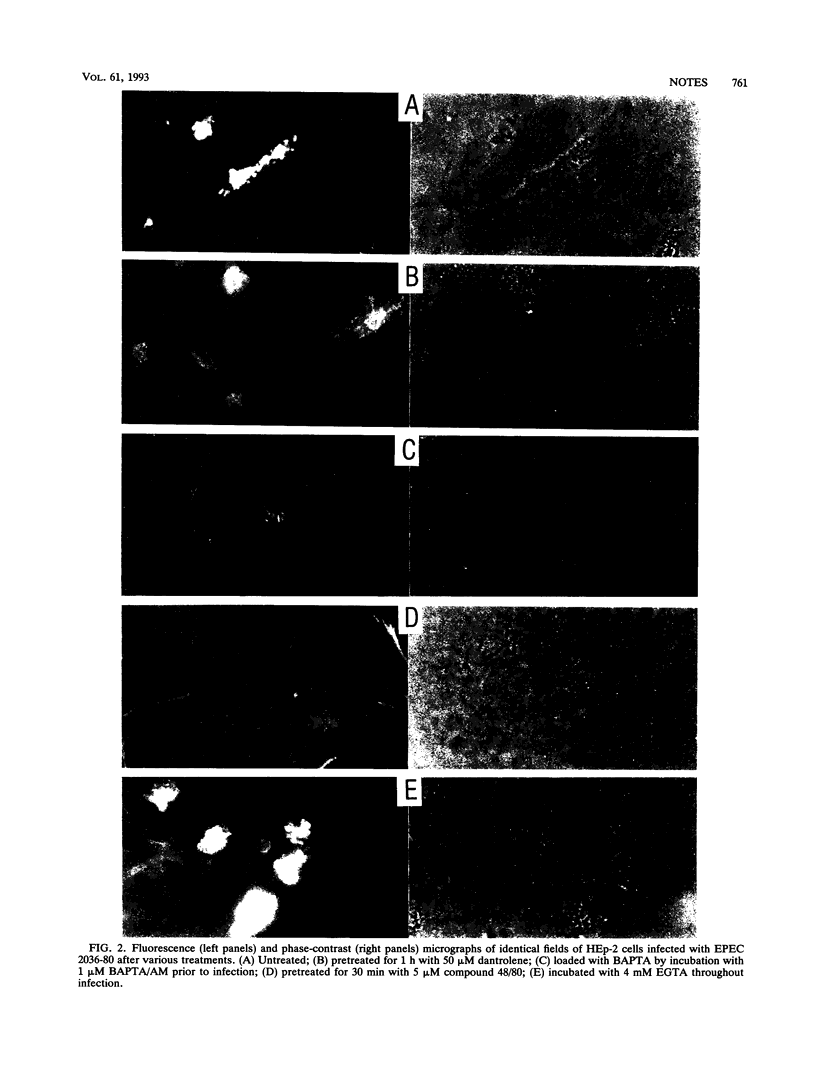


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S. Calmodulin and the regulation of the actin-myosin interaction in smooth muscle and nonmuscle cells. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldini M. M., Nataro J. P., Kaper J. B. Localization of a determinant for HEp-2 adherence by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.334-336.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Brooks S. F., Knutton S., Manjarrez Hernandez H. A., Aitken A., Williams P. H. Protein phosphorylation by protein kinase C in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.761-765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Knutton S., Sellers L., Hernandez H. A., Aitken A., Williams P. H. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli strains secrete a heat-labile toxin antigenically related to E. coli hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):2092–2095. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.2092-2095.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin T. J., Ward W., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Elevation of intracellular free calcium levels in HEp-2 cells infected with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1599–1604. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1599-1604.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. X., Bouquin N., Norris V., Casarégola S., Séror S. J., Holland I. B. A single base change in the acceptor stem of tRNA(3Leu) confers resistance upon Escherichia coli to the calmodulin inhibitor, 48/80. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3113–3122. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danko S., Kim D. H., Sreter F. A., Ikemoto N. Inhibitors of Ca2+ release from the isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. II. The effects of dantrolene on Ca2+ release induced by caffeine, Ca2+ and depolarization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 11;816(1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. A comparison of HEp-2 cell invasion by enteropathogenic and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90417-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Epithelial cell invasion: an overlooked property of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) associated with the EPEC adherence factor. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):452–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis C. L., Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B., Falkow S. Characterization of interactions of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O127:H6 with mammalian cells in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):693–703. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Chambers K. A., Stossel T. P. Association of gelsolin with actin filaments and cell membranes of macrophages and platelets. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):467–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashihara M., Takahata K., Kurokawa K. Effect of phosphorylation of myosin light chain by myosin light chain kinase and protein kinase C on conformational change and ATPase activities of human platelet myosin. Blood. 1991 Dec 15;78(12):3224–3231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller T. C., 3rd, Mooseker M. S. Ca++-calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of myosin, and its role in brush border contraction in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):943–959. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. Virulence factors of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemasters J. J., DiGuiseppi J., Nieminen A. L., Herman B. Blebbing, free Ca2+ and mitochondrial membrane potential preceding cell death in hepatocytes. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):78–81. doi: 10.1038/325078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjarrez-Hernandez H. A., Amess B., Sellers L., Baldwin T. J., Knutton S., Williams P. H., Aitken A. Purification of a 20 kDa phosphoprotein from epithelial cells and identification as a myosin light chain. Phosphorylation induced by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80848-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manjarrez-Hernandez H. A., Baldwin T. J., Aitken A., Knutton S., Williams P. H. Intestinal epithelial cell protein phosphorylation in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea. Lancet. 1992 Feb 29;339(8792):521–523. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P., Janmey P. Pieces in the actin-severing protein puzzle. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):139–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90542-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka M., Nishikawa M., Adelstein R. S., Hidaka H. Phorbol ester-induced activation of human platelets is associated with protein kinase C phosphorylation of myosin light chains. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):490–492. doi: 10.1038/306490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. R., Bryan V. M., Oi V. T., Herzenberg L. A. Antigen-specific identification and cloning of hybridomas with a fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1962–1966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M. Traditional enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of infantile diarrhea. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):28–53. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R. J., Partin J. C., Saalfield K., McAdams A. J. An ultrastructural study of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection in human infants. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1983 Jun;4(4):291–304. doi: 10.3109/01913128309140582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torre V., Matthews H. R., Lamb T. D. Role of calcium in regulating the cyclic GMP cascade of phototransduction in retinal rods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7109–7113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., McCartney E. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enteritis: evaluation of the gnotobiotic piglet as a model of human infection. Gut. 1985 Jun;26(6):570–578. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



