Abstract
We have investigated the memory T-cell immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. C57BL/6J mice infected with M. tuberculosis were found to generate long-lived memory immunity which provided a heightened state of acquired resistance to a secondary infection. The T-cell response of memory immune mice was directed to all parts of the bacilli, i.e., both secreted and somatic proteins. Major parts of the memory T-cell repertoire were maintained in a highly responsive state by cross-reactive restimulation with antigens present in the normal microbiological environment of the animals. A resting non-cross-reactive part of the memory repertoire was restimulated early during a secondary infection to expand and produce large amounts of gamma interferon. The molecular target of these T cells was identified as a secreted mycobacterial protein with a molecular mass of 3 to 9 kDa.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abou-Zeid C., Smith I., Grange J. M., Ratliff T. L., Steele J., Rook G. A. The secreted antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and their relationship to those recognized by the available antibodies. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):531–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Askgaard D., Gottschau A., Bennedsen J., Nagai S., Heron I. Identification of immunodominant antigens during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Dec;36(6):823–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Askgaard D., Ljungqvist L., Bennedsen J., Heron I. Proteins released from Mycobacterium tuberculosis during growth. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1905–1910. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1905-1910.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Askgaard D., Ljungqvist L., Bentzon M. W., Heron I. T-cell proliferative response to antigens secreted by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1558–1563. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1558-1563.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Ljungqvist L., Hasløv K., Bentzon M. W., Heron I. Proliferative response to seven affinity purified mycobacterial antigens in eight strains of inbred mice. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1991 Mar;59(1):58–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird P. N., Hall L. M., Coates A. R. Cloning and sequence analysis of the 10 kDa antigen gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Apr;135(4):931–939. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-4-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. F., Mehra V., Hirschfield G. R., Fong S. J., Abou-Zeid C., Rook G. A., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J., Modlin R. L. Characterization of T cell antigens associated with the cell wall protein-peptidoglycan complex of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2656–2662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beschin A., Brijs L., De Baetselier P., Cocito C. Mycobacterial proliferation in macrophages is prevented by incubation with lymphocytes activated in vitro with a mycobacterial antigen complex. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):793–797. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley P. C. Is T-cell memory maintained by crossreactive stimulation? Immunol Today. 1990 Jun;11(6):203–205. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90083-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Lamb J. R., Young D. B. Biological activity of protein antigens isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis culture filtrate. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1260–1266. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1260-1266.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterial growth inhibition by interferon-gamma-activated bone marrow macrophages and differential susceptibility among strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4408–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R. D., Flory C. M., Collins F. M. Memory T cell-mediated resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in innately susceptible and resistant mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2012–2016. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2012-2016.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., McNeil M., Modlin R. L., Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Brennan P. J. Isolation and characterization of the highly immunogenic cell wall-associated protein of Mycobacterium leprae. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2864–2872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. R., Hickling J. K., Targett G. A., Playfair J. H. Polyclonal in vitro proliferative responses from nonimmune donors to Plasmodium falciparum malaria antigens require UCHL1+ (memory) T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):307–315. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungi T. W. Nonrecirculating memory T lymphocytes in cellular resistance to infection. Cell Immunol. 1980 Oct;55(2):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Väth U., Thole J. E., Van Embden J. D., Emmrich F. Enumeration of T cells reactive with Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms and specific for the recombinant mycobacterial 64-kDa protein. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):351–357. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Mitsuyama M., Handa T., Yayama T., Muramori K., Nomoto K. Induction by killed Listeria monocytogenes of effector T cells mediating delayed-type hypersensitivity but not protection in mice. Immunology. 1987 Oct;62(2):241–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara S. Amino acid sequence of tuberculin-active protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2563–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The relationship of delayed hypersensitivity to acquired cellular resistance. Br Med Bull. 1967 Jan;23(1):52–54. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Torigian V. K., Mandich D., Reichel M., Young S. M., Salgame P., Convit J., Hunter S. W., McNeil M. Characterization of Mycobacterium leprae cell wall-associated proteins with the use of T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2873–2878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. S., Orme I. M. Patterns of IL-2 production and utilization in mice heavily infected with Mycobacterium bovis BCG reflect the phase of protective immunity being expressed. Immunology. 1989 Jun;67(2):221–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutis T., van Schooten W. C., de Vries R. R. A peptidoglycan protein complex purified from M. leprae cell walls contains most or all immunodominant M. leprae T-cell antigens. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1989 Dec;57(4):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. Characteristics and specificity of acquired immunologic memory to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3589–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. Induction of nonspecific acquired resistance and delayed-type hypersensitivity, but not specific acquired resistance in mice inoculated with killed mycobacterial vaccines. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3310–3312. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3310-3312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Miller E. S., Roberts A. D., Furney S. K., Griffin J. P., Dobos K. M., Chi D., Rivoire B., Brennan P. J. T lymphocytes mediating protection and cellular cytolysis during the course of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Evidence for different kinetics and recognition of a wide spectrum of protein antigens. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. The kinetics of emergence and loss of mediator T lymphocytes acquired in response to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Ab B. K., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kiessling R. The recombinant 65-kD heat shock protein of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin/M. tuberculosis is a target molecule for CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1947–1952. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A. The role of activated macrophages in protection and immunopathology in tuberculosis. Res Microbiol. 1990 Feb;141(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90040-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton antigen is a heat shock protein which corresponds to common antigen and to the Escherichia coli GroEL protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.446-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratsuchi H., Johnson J. L., Ellner J. J. Bidirectional effects of cytokines on the growth of Mycobacterium avium within human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3165–3170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes R. W., Collins F. M. Passive transfer of immunity of Mycobacterium avium in susceptible and resistant strains of mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jul;81(1):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Nilsson B. S. PPD tuberculin--a B-cell mitogen. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):198–200. doi: 10.1038/newbio240198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thole J. E., van Schooten W. C., Keulen W. J., Hermans P. W., Janson A. A., de Vries R. R., Kolk A. H., van Embden J. D. Use of recombinant antigens expressed in Escherichia coli K-12 to map B-cell and T-cell epitopes on the immunodominant 65-kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1633–1640. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1633-1640.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada H., Kawamura I., Arakawa M., Nomoto K., Mitsuyama M. Dissociated development of T cells mediating delayed-type hypersensitivity and protective T cells against Listeria monocytogenes and their functional difference in lymphokine production. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3589–3595. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3589-3595.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schooten W. C., Ottenhoff T. H., Klatser P. R., Thole J., De Vries R. R., Kolk A. H. T cell epitopes on the 36K and 65K Mycobacterium leprae antigens defined by human T cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):849–854. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
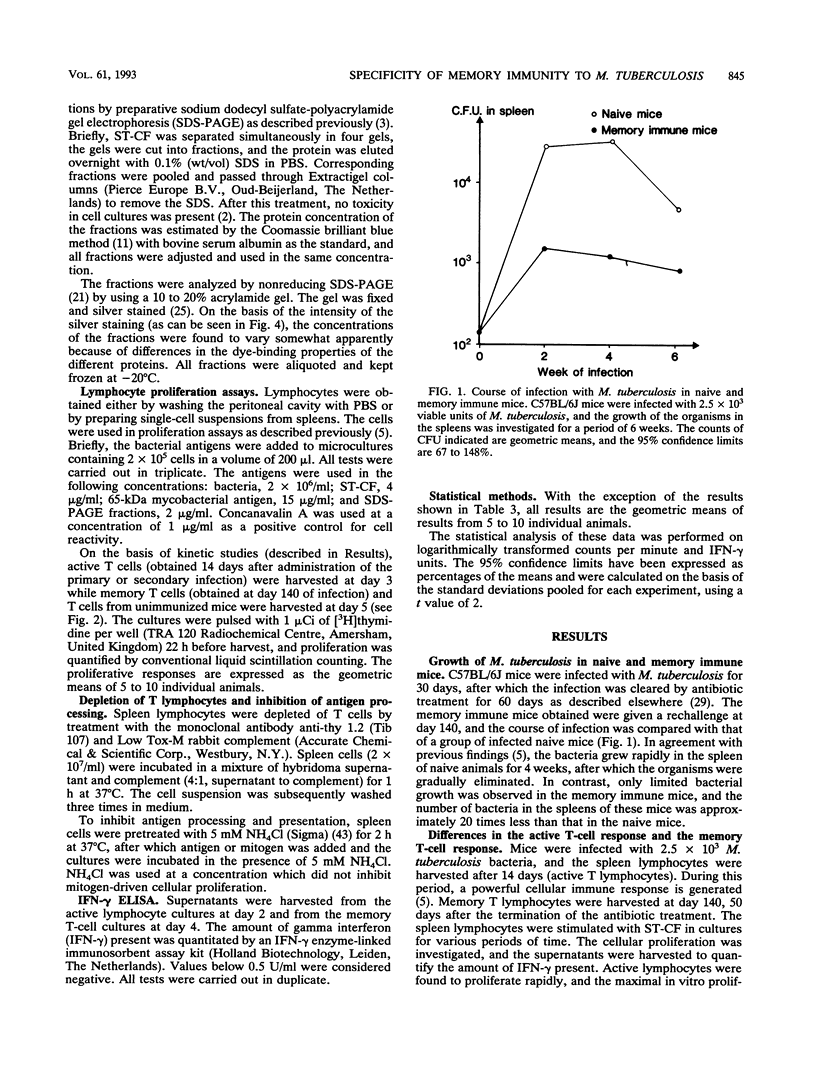
- Wiker H. G., Harboe M., Nagai S. A localization index for distinction between extracellular and intracellular antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Apr;137(4):875–884. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-4-875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Kaufmann S. H., Hermans P. W., Thole J. E. Mycobacterial protein antigens: a compilation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(2):133–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler H. K., Unanue E. R. Decrease in macrophage antigen catabolism caused by ammonia and chloroquine is associated with inhibition of antigen presentation to T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):175–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Koenig C. H., Finger H., Hof H. Failure of killed Listeria monocytogenes vaccine to produce protective immunity. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):233–234. doi: 10.1038/297233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]