Abstract
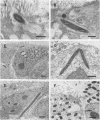
An in vitro model of Bacillus piliformis infection was developed to investigate the mechanisms of adhesion and internalization of this obligate intracellular bacterium. Adhesion and internalization events were examined by electron microscopic evaluation of infected Caco-2 cell monolayers. A few bacteria were identified in apical surface invaginations and in vacuoles subjacent to the apical surface, whereas the majority of bacteria were observed free within the cytoplasm, suggesting that B. piliformis entered epithelial cells via a phagocytic process and rapidly escaped the phagosome. To confirm that host cell phagocytosis was involved in entry of B. piliformis into mammalian cells, Intestine 407 cells were treated with the phagocytic inhibitor cytochalasin D, infected with B. piliformis, and evaluated for bacterial internalization by double-fluorescence labeling. The results showed decreased intracellular bacteria, suggesting that internalization was dependent on host cell microfilament function. To examine the role of B. piliformis in internalization, growth of live and Formalin-killed bacteria was compared. Dead bacteria were not internalized, suggesting that B. piliformis actively participates in internalization. B. piliformis appears to enter host cells by a bacterially directed phagocytic process. The in vitro system described should prove invaluable in further investigations of B. piliformis pathogenic mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubel D., Darfeuille-Michaud A., Joly B. New adhesive factor (antigen 8786) on a human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O117:H4 strain isolated in Africa. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1290–1299. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1290-1299.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardini M. L., Mounier J., d'Hauteville H., Coquis-Rondon M., Sansonetti P. J. Identification of icsA, a plasmid locus of Shigella flexneri that governs bacterial intra- and intercellular spread through interaction with F-actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovallius A., Nilsson G. Ingestion and survival of Y. pseudotuberculosis in HeLa cells. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;21(12):1997–2007. doi: 10.1139/m75-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Moulder J. W. Parasite-specified phagocytosis of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis by L and HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):598–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.598-606.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1473–1478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie J. 'Bacillus piliformis' (Tyzzer) and Tyzzer's disease of the laboratory mouse. I. Propagation of the organism in embryonated eggs. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Jul 19;165(998):35–60. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Allison A. C. Effects of cytochalasin B on endocytosis and exocytosis. Front Biol. 1978;46:143–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detilleux P. G., Deyoe B. L., Cheville N. F. Penetration and intracellular growth of Brucella abortus in nonphagocytic cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2320–2328. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2320-2328.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella as an intracellular parasite. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1833–1841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Salmonella interactions with polarized human intestinal Caco-2 epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1096–1106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Heffron F., Falkow S. Epithelial cell surfaces induce Salmonella proteins required for bacterial adherence and invasion. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):940–943. doi: 10.1126/science.2919285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Curtiss R., 3rd Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6383–6387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grund S., Thunert A. Electron microscopic studies of three forms of Bacillus piliformis. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1983 Mar;30(2):117–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1983.tb01820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of Henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the bacterium. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):879–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.879-886.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Morris R. E., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the host cell. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.887-894.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer G. V., Taylor C. E. Improved mountant for immunofluorescence preparations. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Mar;27(3):254–256. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kagiyama N., Fujiwara K. Production of Tyzzer's disease in rats by ingestion of bacterial spores. Jpn J Exp Med. 1989 Feb;59(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Gorby G. L., Wyrick P. B., Hodinka R., Hoffman L. H. Parasite-directed endocytosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S311–S316. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motzel S. L., Riley L. K. Bacillus piliformis flagellar antigens for serodiagnosis of Tyzzer's disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2566–2570. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2566-2570.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Comparative biology of intracellular parasitism. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):298–337. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.298-337.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Interaction of chlamydiae and host cells in vitro. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):143–190. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.143-190.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Toriumi W., Sakamoto K., Fujiwara K. Pathologic observations of mouse liver infected with Tyzzer's organisms using immunoperoxidase method. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1986 Feb;48(1):89–98. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.48.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi P., Tall B. D., Russell R. G., Detolla L. J., Morris J. G., Jr Development of an in vitro model for study of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae virulence using Caco-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3415–3424. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3415-3424.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters J. E., Charlier G., Halen P., Geeroms R., Raeymaekers R. Naturally-occurring Tyzzer's disease (Bacillus piliformis infection) in commercial rabbits: a clinical and pathological study. Ann Rech Vet. 1985;16(1):69–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Port C. D., Richter W. R., Moize S. M. An ultrastructural study of Tyzzer's disease in the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Lab Invest. 1971 Jul;25(1):81–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. K., Besch-Williford C., Waggie K. S. Protein and antigenic heterogeneity among isolates of Bacillus piliformis. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1010-1016.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. K., Caffrey C. J., Musille V. S., Meyer J. K. Cytotoxicity of Bacillus piliformis. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Jul;37(1):77–80. doi: 10.1099/00222615-37-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M. The human colon carcinoma cell lines HT-29 and Caco-2: two in vitro models for the study of intestinal differentiation. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1035–1040. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer T. H., Ganaway J. R., Waggie K. S. Cultivation of Bacillus piliformis (Tyzzer) in mouse fibroblasts (3T3 cells). Vet Microbiol. 1990 Apr;22(2-3):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90116-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Hoffman L. H., McGee Z. A. Interaction of Neisseria meningitidis with human nasopharyngeal mucosa: attachment and entry into columnar epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):369–376. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunert A. Is it possible to cultivate the agent of Tyzzer's disease (Bacillus piliformis) in cellfree media? Z Versuchstierkd. 1984;26(4):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Turco J. Rickettsia prowazekii and the host cell: entry, growth and control of the parasite. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:81–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Choong J., Davis C. H., Knight S. T., Royal M. O., Maslow A. S., Bagnell C. R. Entry of genital Chlamydia trachomatis into polarized human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2378–2389. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2378-2389.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]