Abstract
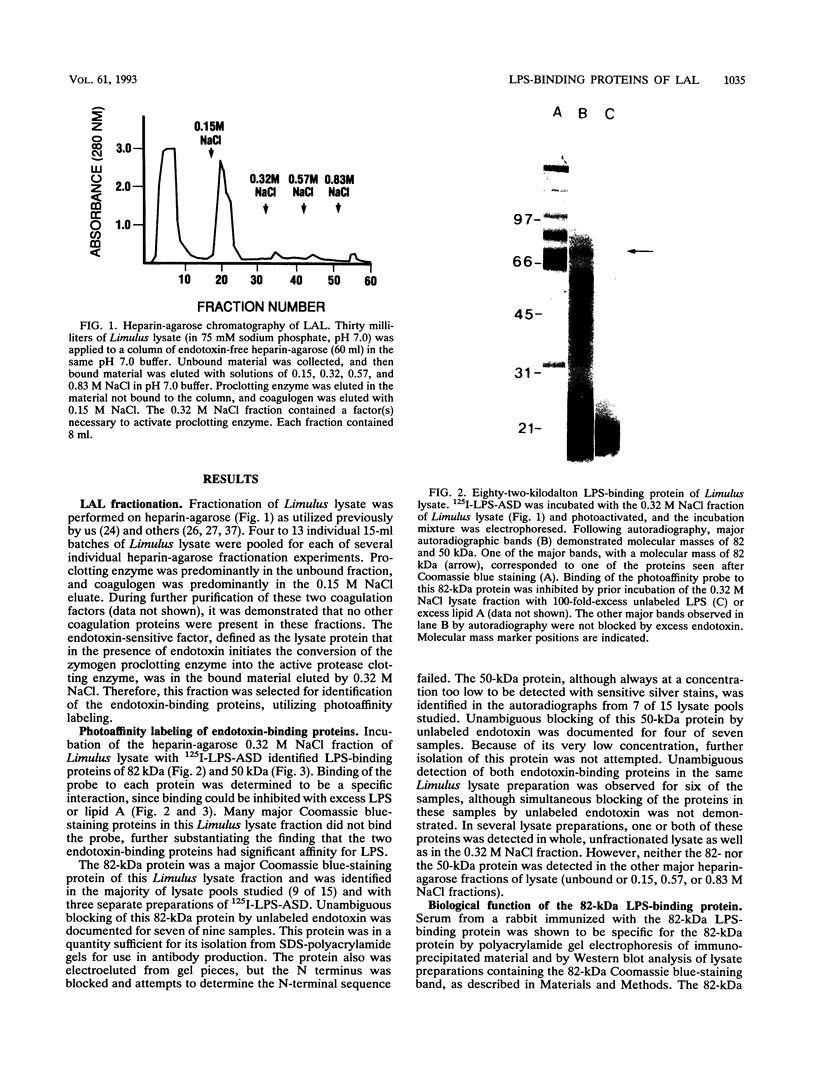
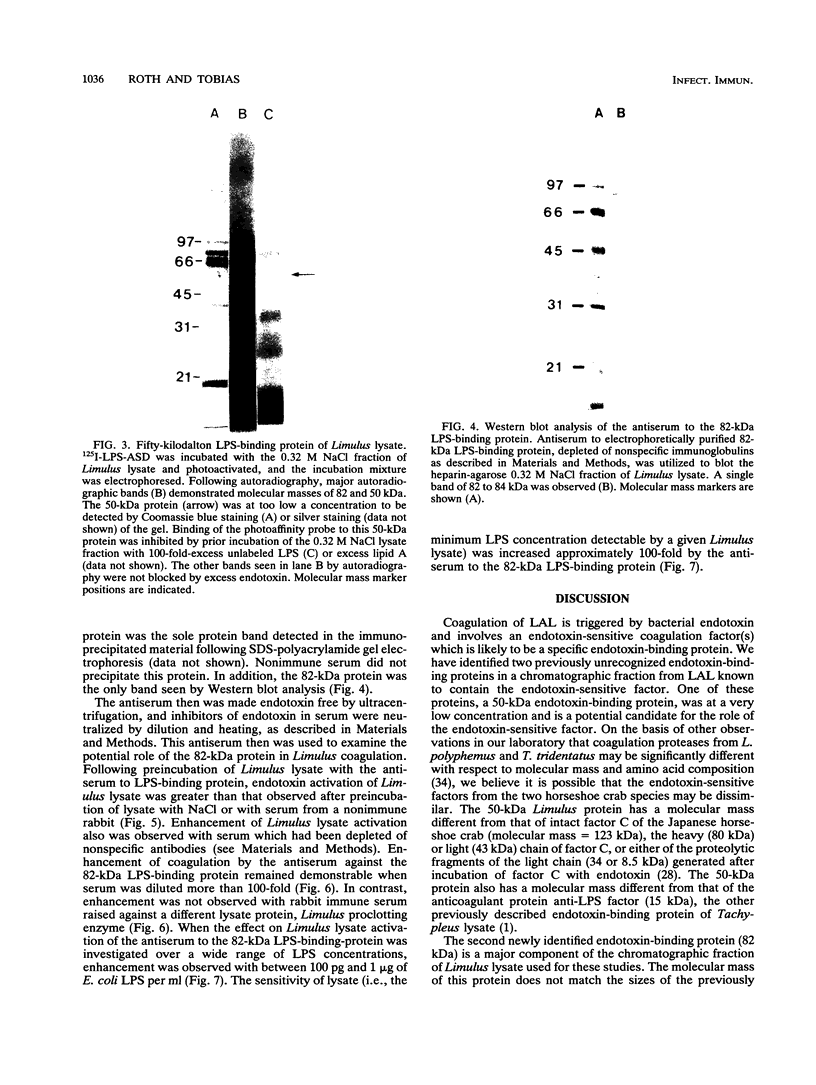
Limulus amebocyte lysate, obtained from horseshoe crab (Limulus polyphemus) blood cells, contains a coagulation system which is activated by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). A chromatographic fraction of Limulus lysate, containing the endotoxin-sensitive factor(s) which initiates the coagulation cascade, was studied. We utilized a photoreactive, cleavable, radiolabeled derivative of Salmonella minnesota LPS, LPS-(p-azidosalicylamido)-1,3'-dithiopropionamide (LPS-ASD), to identify LPS-binding proteins. The lysate fraction was incubated with LPS-ASD, and LPS-binding proteins were identified by autoradiography of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. An 82-kDa protein, a major protein component of this fraction from Limulus lysate, was identified as a LPS-binding protein in a majority of lysates. Incubation of whole Limulus lysate with antiserum to this protein resulted in enhanced sensitivity of the lysate to LPS, suggesting that this 82-kDa protein is a negative regulator of coagulation. A minor 50-kDa protein component of lysate also was identified as a LPS-binding protein and is a candidate for the LPS-sensitive coagulation protein in L. polyphemus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aketagawa J., Miyata T., Ohtsubo S., Nakamura T., Morita T., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Iwanaga S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Primary structure of limulus anticoagulant anti-lipopolysaccharide factor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7357–7365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert G., Baldwin G., Thompson C., Wainwright N., Novitsky T. J., Gillis Z., Parsonnet J., Fleisher G. R., Siber G. R. Limulus antilipopolysaccharide factor protects rabbits from meningococcal endotoxin shock. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):494–500. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANG F. B. A bacterial disease of Limulus polyphemus. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1956 May;98(5):325–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson H. S. Activation of Hageman factor by lipopolysaccharides of Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides vulgatus, and Fusobacterium mortiferum. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S30–S33. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Biology of endotoxin. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:127–141. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite-Quagliata S., Schneider A., Harris L. Separation and purification of a potent bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and a closely associated phospholipase A2 from rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Observations on their relationship. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11000–11009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jomori T., Kubo T., Natori S. Purification and characterization of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein from hemolymph of American cockroach Periplaneta americana. Eur J Biochem. 1990 May 31;190(1):201–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J., BANG F. B. THE ROLE OF ENDOTOXIN IN THE EXTRACELLULAR COAGULATION OF LIMULUS BLOOD. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Sep;115:265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. I. Detection of lipopolysaccharide-binding sites on splenocytes and splenocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):996–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. II. Membrane localization and binding characteristics. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):1006–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Bang F. B. Clottable protein in Limulus; its localization and kinetics of its coagulation by endotoxin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. The horseshoe crab: a model for gram-negative sepsis in marine organisms and humans. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;272:3–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang S. M., Sakmar T. P., Liu T. Y. Studies on Limulus amoebocyte lysate. III. Purification of an endotoxin-binding protein from Limulus amoebocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5586–5590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra M. N., Wilde C. G., Collins M. S., Snable J. L., Thornton M. B., Scott R. W. The role of bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein as a natural inhibitor of bacterial endotoxin. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 15;148(2):532–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minetti C. A., Lin Y. A., Cislo T., Liu T. Y. Purification and characterization of an endotoxin-binding protein with protease inhibitory activity from Limulus amebocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20773–20780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L. Detoxification of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins) by a human neutrophil enzyme. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):203–205. doi: 10.1126/science.3529396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S., Hall C. L. Purification of acyloxyacyl hydrolase, a leukocyte enzyme that removes secondary acyl chains from bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15613–15619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mürer E. H., Levin J., Holme R. Isolation and studies of the granules of the amebocytes of Limulus polyphemus, the horseshoe crab. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Dec;86(3 Pt 1):533–542. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040860310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Levin J. Endotoxin-mediated Limulus proclotting enzyme activator and detection of a previously undescribed protease(Protease N). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1619–1623. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Levin J. Fractionation of Limulus amebocyte lysate. Characterization of activation of the proclotting enzyme by an endotoxin-mediated activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 5;707(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Horiuchi T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Purification and properties of intracellular clotting factor, factor B, from horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus) hemocytes. J Biochem. 1986 Mar;99(3):847–857. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Intracellular proclotting enzyme in limulus (Tachypleus tridentatus) hemocytes: its purification and properties. J Biochem. 1985 Jun;97(6):1561–1574. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Lipopolysaccharide-sensitive serine-protease zymogen (factor C) found in Limulus hemocytes. Isolation and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):511–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno N., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide interaction with lysozyme. Binding of lipopolysaccharide to lysozyme and inhibition of lysozyme enzymatic activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4434–4441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Munford R. S. Dephosphorylation of the lipid A moiety of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide by mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):974–978. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.974-978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder D. J., Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Endotoxic-lipopolysaccharide-specific binding proteins on lymphoid cells of various animal species: association with endotoxin susceptibility. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1054–1058. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1054-1058.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. I., Levin F. C., Levin J. Optimization of detection of bacterial endotoxin in plasma with the Limulus test. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Aug;116(2):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. I., Levin J. Purification of Limulus polyphemus proclotting enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):24097–24102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadduck R. K., Waheed A., Porcellini A., Rizzoli V., Levin J. A method for the removal of endotoxin from purified colony-stimulating factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 May;164(1):40–44. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srimal S., Miyata T., Kawabata S., Miyata T., Iwanaga S. The complete amino acid sequence of coagulogen isolated from Southeast Asian horseshoe crab, Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda. J Biochem. 1985 Aug;98(2):305–318. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Nakamura T., Morita T., Iwanaga S. Limulus anti-LPS factor: an anticoagulant which inhibits the endotoxin mediated activation of Limulus coagulation system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 30;105(2):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91493-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh V. L., Vukajlovich S. W., Morrison D. C. Endotoxin interactions with serum proteins relationship to biological activity. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;272:47–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. A family of lipopolysaccharide binding proteins involved in responses to gram-negative sepsis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13479–13481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Soldau K., Ulevitch R. J. Identification of a lipid A binding site in the acute phase reactant lipopolysaccharide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10867–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Soldau K., Ulevitch R. J. Isolation of a lipopolysaccharide-binding acute phase reactant from rabbit serum. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):777–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten B. J., Fogelman A. M., Haberland M. E., Edwards P. A. The role of lipoproteins and receptor-mediated endocytosis in the transport of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2704–2708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Muello K., Victor M., Elsbach P. The role of lipopolysaccharides in the action of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing neutrophil protein on the bacterial envelope. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3109–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenweber H. W., Morrison D. C. Synthesis and biochemical characterization of a photoactivatable, iodinatable, cleavable bacterial lipopolysaccharide derivative. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15068–15074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Levin S. M., Jong M. T., Chad Z., Kabbash L. G. CR3 (CD11b/CD18) expresses one binding site for Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides and a second site for bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):175–183. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D. Multiple receptors for endotoxin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90082-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Hermanowski-Vosatka A., Rockwell P., Detmers P. A. Activation of the adhesive capacity of CR3 on neutrophils by endotoxin: dependence on lipopolysaccharide binding protein and CD14. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N. S., Levin J., Prendergast R. A. An invertebrate coagulation system activated by endotoxin: evidence for enzymatic mediation. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1790–1797. doi: 10.1172/JCI106980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





