Abstract
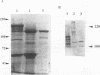
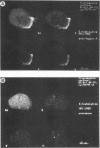
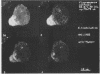
To recognize myosin II in trophozoites of the human pathogen Entamoeba histolytica, a specific antimyosin polyclonal serum was raised against a fusion protein consisting of a 146-amino-acid fragment of the myosin II heavy chain A of E. histolytica (MhcA) fused with beta-galactosidase. The hybrid protein was encoded by a chimera gene formed by a DNA fragment, from the mhcA gene, amplified by polymerase chain reaction and fused with the lacZ gene of Escherichia coli. Polymerase chain reaction-amplified DNA is located within the region encoding the tail domain of myosin. This antibody recognized a 250-kDa protein in extracts of E. histolytica trophozoites. Confocal microscope analysis of antibody-labelled trophozoites indicated that MhcA localizes at the posterior pole of locomoting cells and concentrates within the uroid. These results might indicate that MhcA is involved in movement and in the uroid formation which help amoebas to escape the host immune response. These data are the first evidence indicating that myosin exists in E. histolytica. In addition, two other peptides were found in myosin-enriched extracts of amoebas, indicating that other myosins may be present in this parasite.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aust Kettis A., Utter G. The influence of specific antibodies and complement on the motility and the viability of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jul;33(4):569–577. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aust-Kettis A., Sundqvist K. G. Dynamics of the interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and components of the immune response. I. Capping and endocytosis; influence of inhibiting and accelerating factors; variation of the expression of surface antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aust-Kettis A., Sundqvist K. G. Dynamics of the interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and components of the immune response. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(5):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey G. B., Day D. B., McCoomer N. E. Entamoeba motility: dynamics of cytoplasmic streaming, locomotion and translocation of surface-bound particles, and organization of the actin cytoskeleton in Entamoeba invadens. J Protozool. 1992 Mar-Apr;39(2):267–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb01313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Bourguignon G. J. Capping and the cytoskeleton. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;87:195–224. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Singer S. J. Transmembrane interactions and the mechanism of capping of surface receptors by their specific ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5031–5035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Endocytosis: relation to capping and cell locomotion. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):681–686. doi: 10.1126/science.6719108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler-Browne G. S., Whalen R. G. Myosin isozyme transitions occurring during the postnatal development of the rat soleus muscle. Dev Biol. 1984 Apr;102(2):324–334. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderón J., Avila E. E. Antibody-induced caps in Entamoeba histolytica: isolation and electrophoretic analysis. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):927–932. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderón J., de Lourdes Muñoz M., Acosta H. M. Surface redistribution and release of antibody-induced caps in entamoebae. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):184–193. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L. S. Axenic cultivation of Entamoeba hitolytica. Science. 1961 Aug 4;134(3475):336–337. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3475.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Spudich J. A. Molecular genetics of cell migration: Dictyostelium as a model system. Trends Genet. 1991 May;7(5):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Structure and function of the cytoskeleton of a Dictyostelium myosin-defective mutant. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):367–378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer J. A., 3rd, Bowers B., Paterson B. M., Korn E. D. Complete nucleotide sequence and deduced polypeptide sequence of a nonmuscle myosin heavy chain gene from Acanthamoeba: evidence of a hinge in the rodlike tail. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):913–925. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer J. A. Novel myosins. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;1(2-3):50–56. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90089-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M., Garfinkel L., Gitler C., Mirelman D., Revel M., Rozenblatt S. Entamoeba histolytica: cloning and characterization of actin cDNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jul;24(3):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay P. Y., Elson E. L. Surface particle transport mechanism independent of myosin II in Dictyostelium. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):438–440. doi: 10.1038/356438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bonet A., Audemard E., Bonicel J. Functional sequences of the myosin head. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Feb;10(1):10–24. doi: 10.1007/BF01739853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell P. C., Liu G. Streamer F mutants and chemotaxis of Dictyostelium. Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):473–479. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak C., Spudich J. A., Elson E. L. Capping of surface receptors and concomitant cortical tension are generated by conventional myosin. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):549–551. doi: 10.1038/341549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I. Pathogenesis of disease caused by Entamoeba histolytica: studies of adherence, secreted toxins, and contact-dependent cytolysis. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):247–260. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shohet R. V., Conti M. A., Kawamoto S., Preston Y. A., Brill D. A., Adelstein R. S. Cloning of the cDNA encoding the myosin heavy chain of a vertebrate cellular myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7726–7730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus M. A., Warrick H. M., Spudich J. A. Multiple actin-based motor genes in Dictyostelium. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):55–63. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A. One-step purification of hybrid proteins which have beta-galactosidase activity. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., De Lozanne A., Leinwand L. A., Spudich J. A. Conserved protein domains in a myosin heavy chain gene from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9433–9437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Hamada Y., Katsuragawa Y., Imamura M., Mikawa T., Masaki T. Complete primary structure of vertebrate smooth muscle myosin heavy chain deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Implications on topography and function of myosin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):143–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yumura S., Mori H., Fukui Y. Localization of actin and myosin for the study of ameboid movement in Dictyostelium using improved immunofluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):894–899. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Garza M., Gallegos B., Meza I. Characterization of a cytochalasin D-resistant mutant of Entamoeba histolytica. J Protozool. 1989 Nov-Dec;36(6):556–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb01095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]