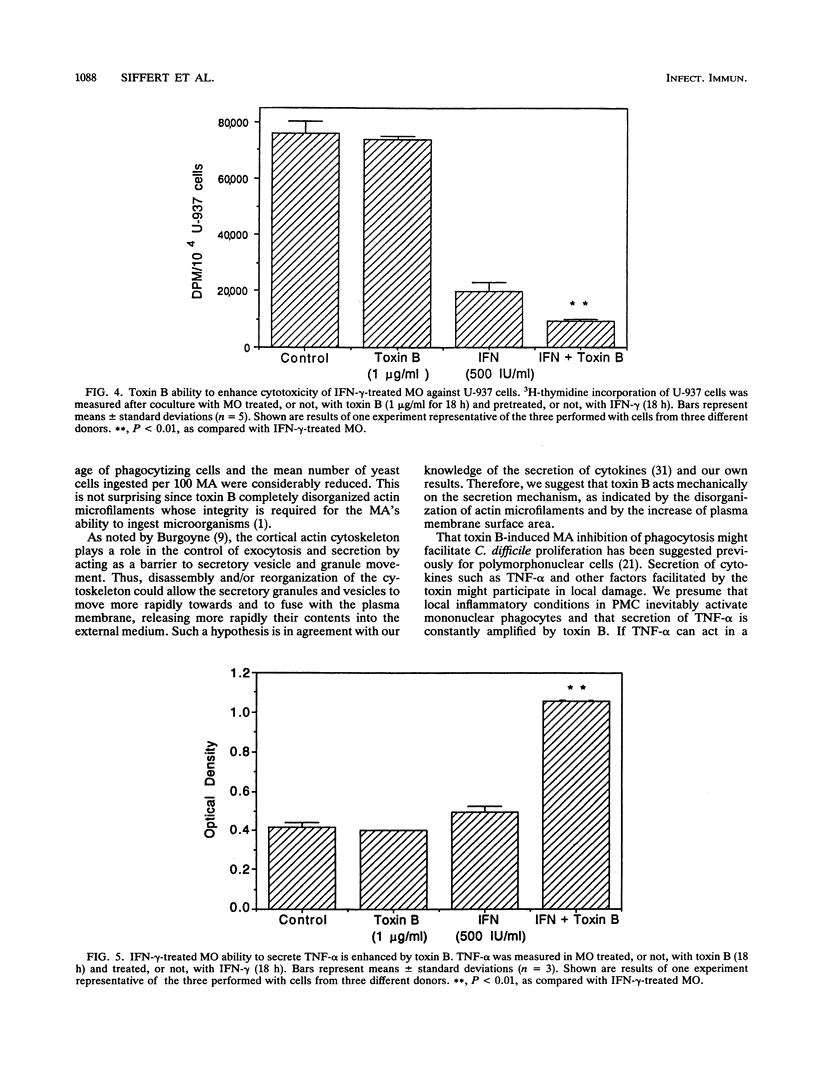
Abstract
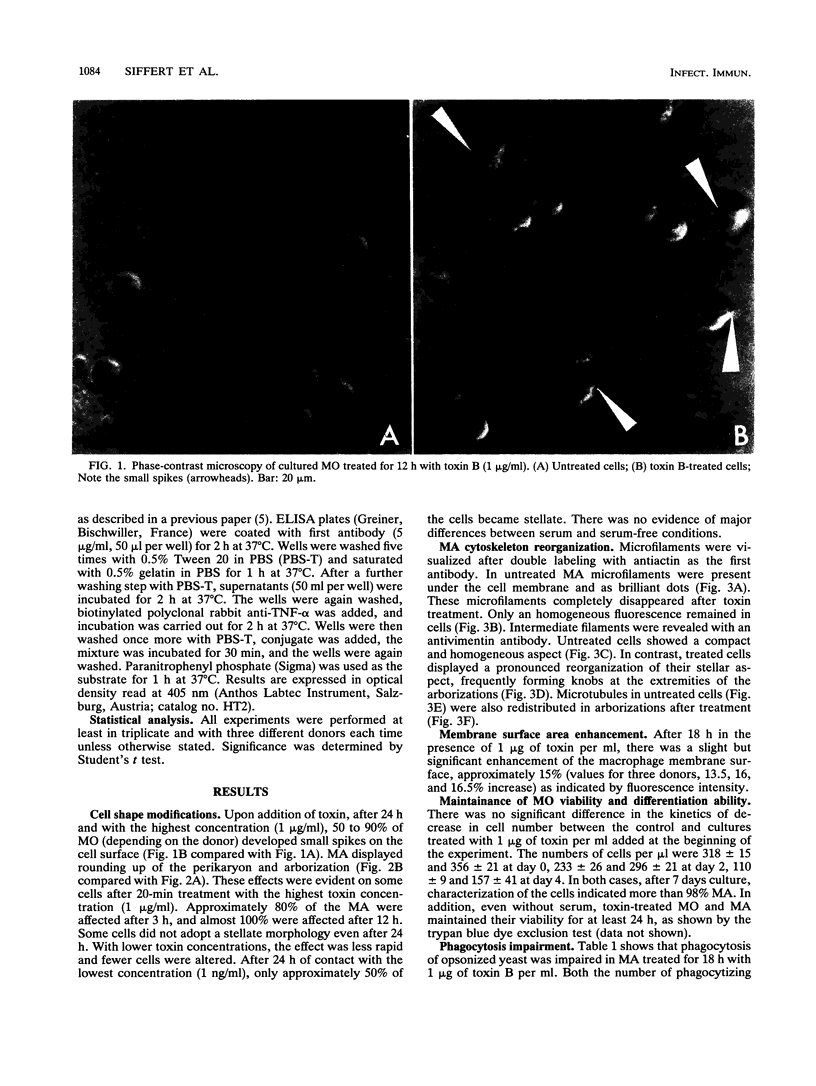
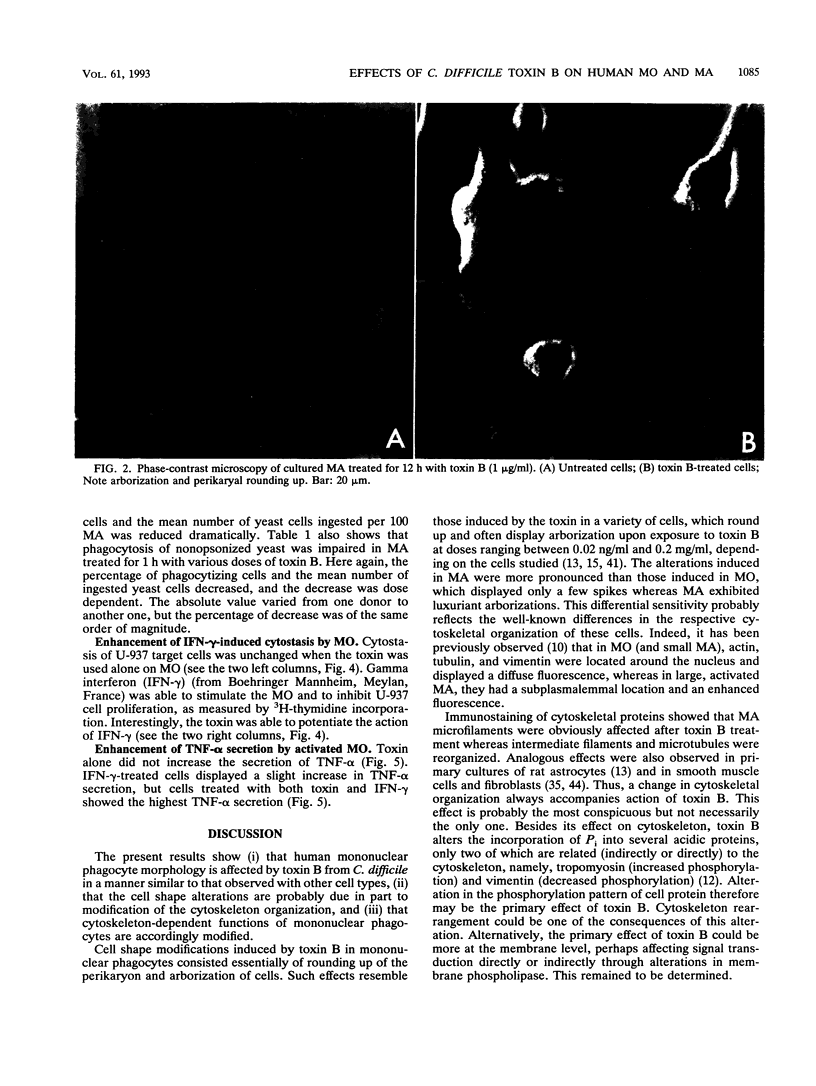
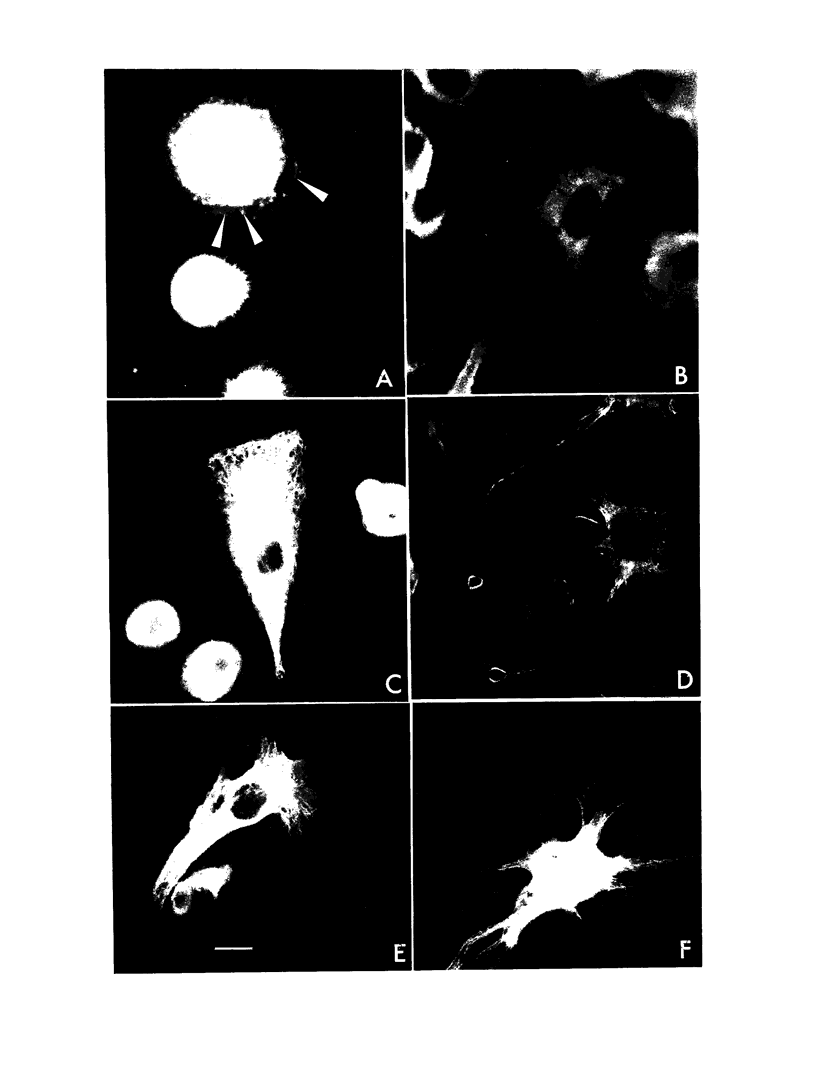
Toxin B from Clostridium difficile is cytopathic in vitro for various types of cells, including polymorphonuclear cells, lymphocytes, and monocytes. Since intestine lamina propria is rich in macrophages, we studied the effect of toxin B on human monocytes and on human macrophages generated in vitro by long-term culture of purified circulating blood monocytes. Upon addition of toxin B, human monocytes exhibited few modifications whereas macrophages adopted a stellate morphology, with rounding up of the perikaryon. Toxin B made microfilaments of actin disappear and induced an important reorganization of vimentin and a redistribution of tubulin. Membrane area increased by approximately 16%. Toxin B did not affect the viability of human mononuclear phagocytes and did not exert any significant lytic effect. It profoundly altered the phagocytic function of macrophages. When activated by gamma interferon in the presence of toxin B, monocytes were more cytotoxic for U-937 target cells than control monocytes activated in absence of toxin. Finally, the combined treatment of monocytes with gamma interferon and toxin B increased significantly the secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha, whereas toxin B alone was unable to induce tumor necrosis factor production. These results suggest that morphological and functional alterations induced in human mononuclear phagocytes by toxin B from C. difficile are due to the disorganization of the cytoskeleton and the resulting impairment of the membrane traffic equilibrium.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axline S. G., Reaven E. P. Inhibition of phagocytosis and plasma membrane mobility of the cultivated macrophage by cytochalasin B. Role of subplasmalemmal microfilaments. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):647–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldacini O., Girardot R., Green G. A., Rihn B., Monteil H. Comparative study of immunological properties and cytotoxic effects of Clostridium difficile toxin B and Clostridium sordellii toxin L. Toxicon. 1992 Feb;30(2):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90466-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barroso L. A., Wang S. Z., Phelps C. J., Johnson J. L., Wilkins T. D. Nucleotide sequence of Clostridium difficile toxin B gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4004–4004. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T. W., Gurwith M., Gorbach S. L., Onderdonk A. B. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxin-producing clostridia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):531–534. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benabdelmoumene S., Dumont S., Petit C., Poindron P., Wachsmann D., Klein J. P. Activation of human monocytes by Streptococcus mutans serotype f polysaccharide: immunoglobulin G Fc receptor expression and tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 production. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3261–3266. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3261-3266.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner C., Landry Y., Fonteneau P., Kuhry J. G. A fluorescent hydrophobic probe used for monitoring the kinetics of exocytosis phenomena. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2149–2154. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Control of exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 22;1071(2):174–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90024-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain H., Kraus B. Cytoskeleton in cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Immunofluorescence microscopic and electron microscopic studies. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;36(2-3):159–176. doi: 10.1007/BF02912064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Lauermann M., Bartlett J. G. Cytotoxicity assay in antibiotic-associated colitis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):765–770. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciesielski-Treska J., Ulrich G., Baldacini O., Monteil H., Aunis D. Phosphorylation of cellular proteins in response to treatment with Clostridium difficile toxin B and Clostridium sordellii toxin L. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;56(1):68–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciesielski-Treska J., Ulrich G., Rihn B., Aunis D. Mechanism of action of Clostridium difficile toxin B: role of external medium and cytoskeletal organization in intoxicated cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;48(2):191–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey D. C., Kaiser A., Schloemer R. H. Factors influencing the phagocytosis of Clostridium difficile by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1541–1546. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1541-1546.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Sullivan N., Wilkins T. D. Differential effects of Clostridium difficile toxins on tissue-cultured cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1157–1158. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1157-1158.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont S., Hartmann D., Poindron P., Oberling F., Faradji A., Bartholeyns J. Control of the antitumoral activity of human macrophages produced in large amounts in view of adoptive transfer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Nov;24(11):1691–1698. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(88)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faradji A., Bohbot A., Frost H., Schmitt-Goguel M., Siffert J. C., Dufour P., Eber M., Lallot C., Wiesel M. L., Bergerat J. P. Phase I study of liposomal MTP-PE-activated autologous monocytes administered intraperitoneally to patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis. J Clin Oncol. 1991 Jul;9(7):1251–1260. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.7.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentini C., Thelestam M. Clostridium difficile toxin A and its effects on cells. Toxicon. 1991;29(6):543–567. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegel W. A., Müller F., Däubener W., Fischer H. G., Hadding U., Northoff H. Cytokine response by human monocytes to Clostridium difficile toxin A and toxin B. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3659–3666. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3659-3666.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin I., Thelestam M. Intoxication of cultured human lung fibroblasts with Clostridium difficile toxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):67–74. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.67-74.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. L. Antimicrobial agent-associated colitis and diarrhea: historical background and clinical aspects. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S208–S213. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaimis J., Lombard Y., Makaya-Kumba M., Fonteneau P., Poindron P. A new and simple method for studying the binding and ingestion steps in the phagocytosis of yeasts. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Oct 2;154(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90191-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyerly D. M., Krivan H. C., Wilkins T. D. Clostridium difficile: its disease and toxins. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):1–18. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malorni W., Fiorentini C., Paradisi S., Giuliano M., Mastrantonio P., Donelli G. Surface blebbing and cytoskeletal changes induced in vitro by toxin B from Clostridium difficile: an immunochemical and ultrastructural study. Exp Mol Pathol. 1990 Jun;52(3):340–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(90)90074-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malorni W., Paradisi S., Dupuis M. L., Fiorentini C., Ramoni C. Enhancement of cell-mediated cytotoxicity by Clostridium difficile toxin A: an in vitro study. Toxicon. 1991;29(4-5):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90016-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniar A. C., Chubb H., Louie T. J., Williams T. W., Forsyth W., Wilt J. C. Detection of Clostridium difficile toxin with McCoy cell monolayers and cell suspensions and comparison with HeLa cell assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):294–295. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.294-295.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland L. V., Elmer G. W., Stamm W. E., Mulligan M. E. Correlation of immunoblot type, enterotoxin production, and cytotoxin production with clinical manifestations of Clostridium difficile infection in a cohort of hospitalized patients. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2456–2462. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2456-2462.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador J., 3rd, Tweten R. K. Purification and characterization of toxin B from Clostridium difficile. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1708–1714. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1708-1714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. D., Pothoulakis C., Baeker T. R., LaMont J. T., Rothstein T. L. Macrophage-dependent stimulation of T cell-depleted spleen cells by Clostridium difficile toxin A and calcium ionophore. Cell Immunol. 1990 Mar;126(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90308-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. J., Laughon B. E., Lin S. Biochemical studies on the effect of Clostridium difficile toxin B on actin in vivo and in vitro. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1610–1615. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1610-1615.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottlinger M. E., Lin S. Clostridium difficile toxin B induces reorganization of actin, vinculin, and talin in cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):215–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rihn B., Bisseret F., Girardot R., Scheftel J. M., Nguyen V. K., Monteil H. Fast protein purification of Clostridium difficile cytotoxin. J Chromatogr. 1988 Jul 15;428(2):408–414. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83936-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J., Jr, Iezzi C. Clostridium difficile as a nosocomial pathogen. J Hosp Infect. 1988 Feb;11 (Suppl A):378–385. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(88)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson H. C. Isolation of human mononuclear leukocyte subsets by countercurrent centrifugal elutriation. Methods Enzymol. 1984;108:242–249. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)08087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedel N., Toselli P., Pothoulakis C., Faris B., Oliver P., Franzblau C., LaMont T. Ultrastructural effects of Clostridium difficile toxin B on smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Oct 15;148(2):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. The biology of the monocyte system. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;49(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Cohn Z. A., Hirsch J. G., Humphrey J. H., Spector W. G., Langevoort H. L. The mononuclear phagocyte system: a new classification of macrophages, monocytes, and their precursor cells. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(6):845–852. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]