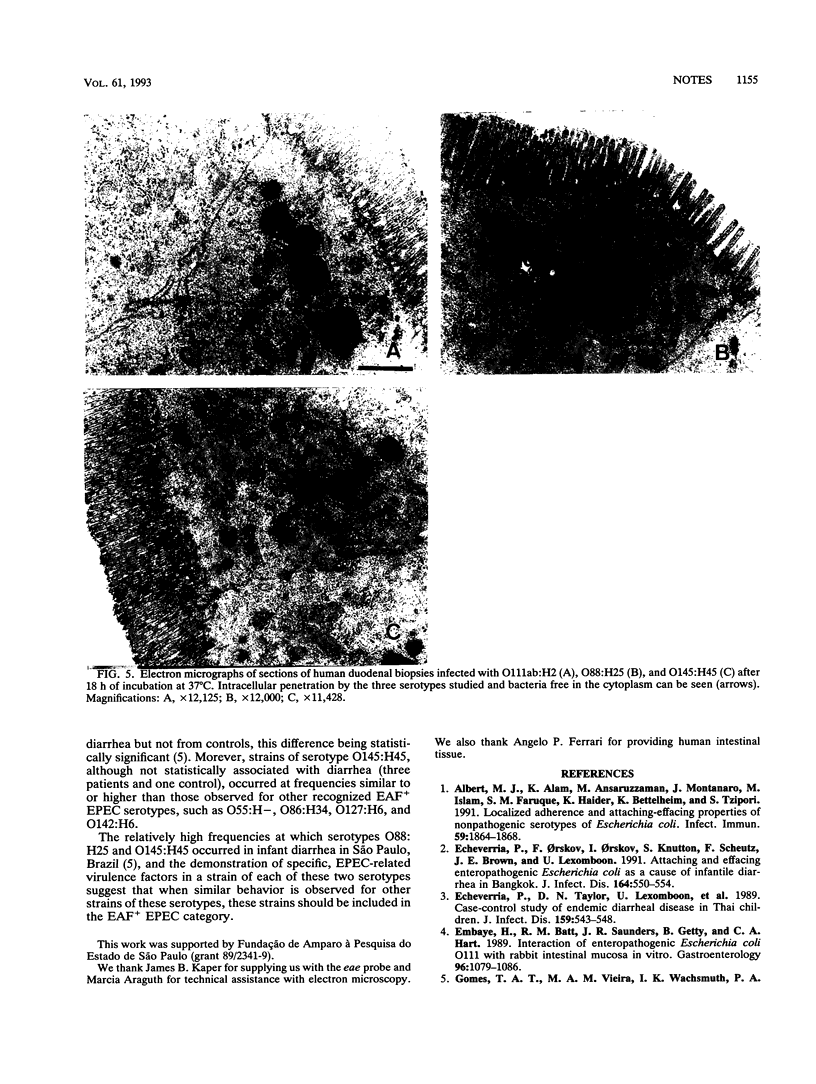
Abstract
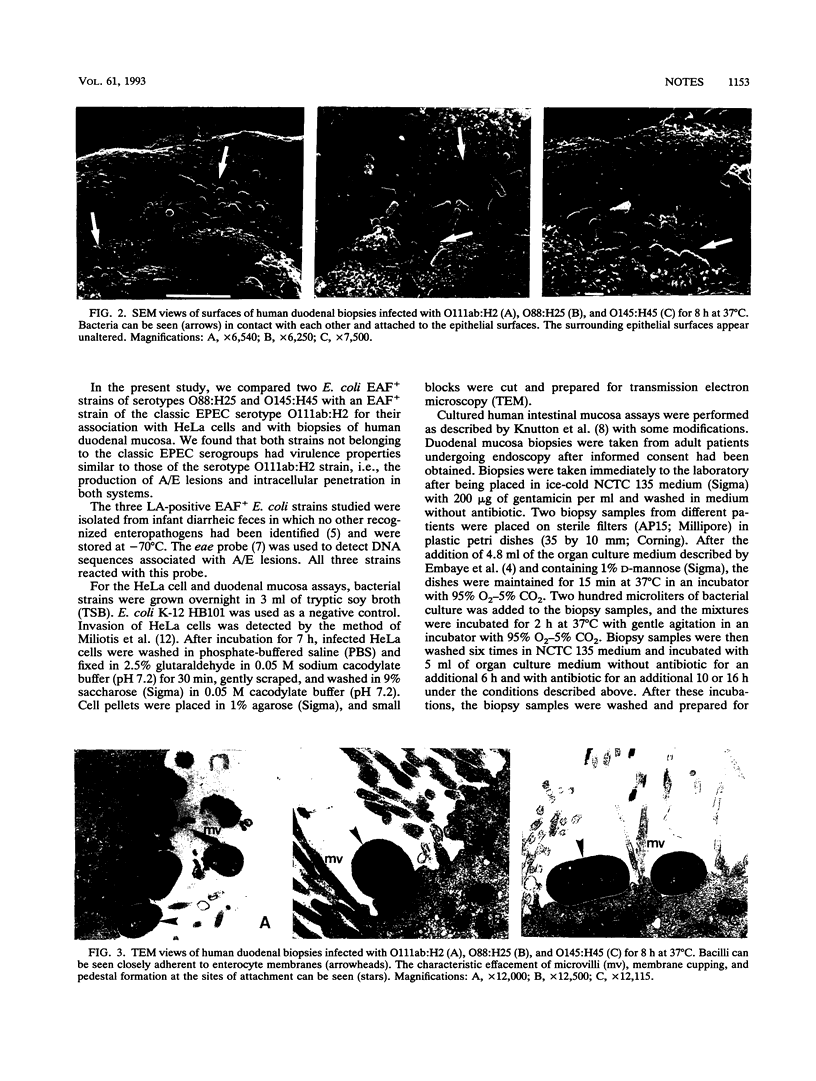
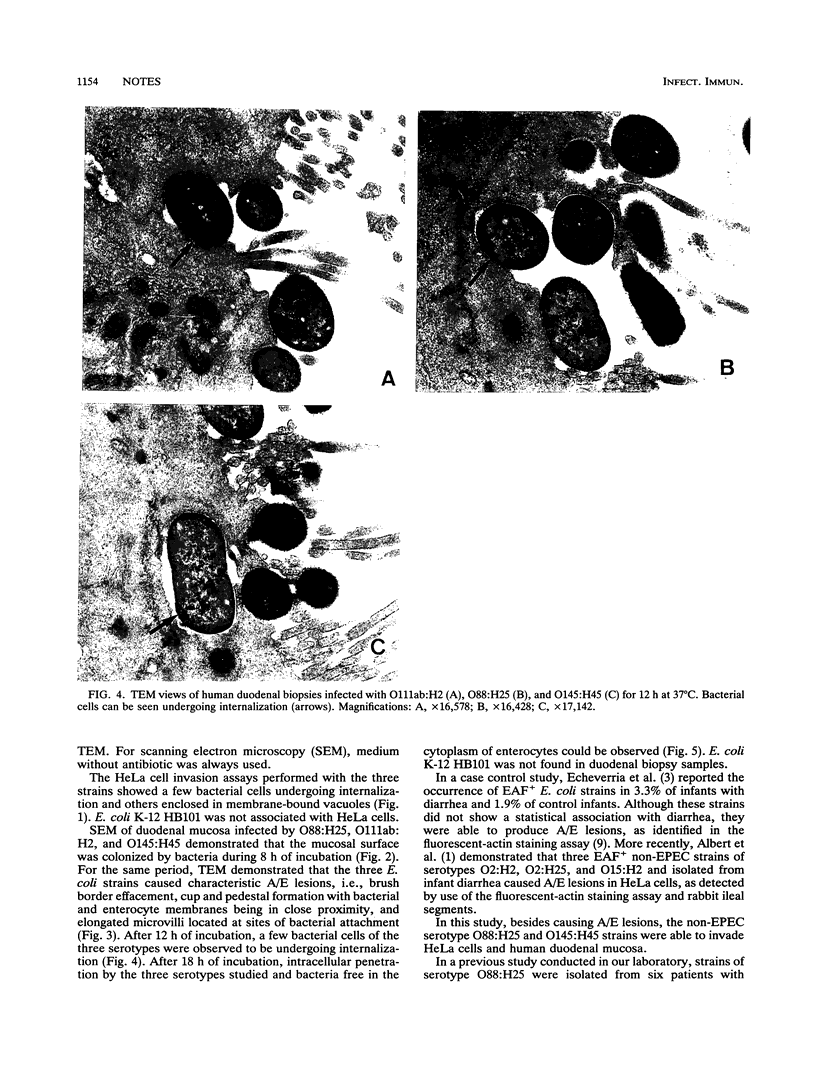
In the present study, we compared two strains of serotypes O88:H25 and O145:H45 with an enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) adherence factor-positive (EAF+) strain of the classic enteropathogenic E. coli serotype O111ab:H2 for their association with HeLa cells and with biopsies of human duodenal mucosa. Both strains not belonging to the classic EPEC serotype showed virulence properties similar to those of the serotype O111ab:H2 strain, i.e., the production of attaching-effacing lesions and intracellular penetration in both systems. These virulence properties associated with the relatively high frequency at which the two serotypes had been detected in infant diarrhea in São Paulo, Brazil (T. A. T. Gomes, M. A. M. Vieira, I. K. Wachsmuth, P. A. Blake, and L. R. Trabulsi, J. Infect. Dis. 160:131-135, 1989) allowed us to suggest that strains of serotypes O88:H25 and O145:H45 should be included in the EAF+ EPEC category.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. J., Alam K., Ansaruzzaman M., Montanaro J., Islam M., Faruque S. M., Haider K., Bettelheim K., Tzipori S. Localized adherence and attaching-effacing properties of nonenteropathogenic serotypes of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1864–1868. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1864-1868.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Orskov F., Orskov I., Knutton S., Scheutz F., Brown J. E., Lexomboon U. Attaching and effacing enteropathogenic Escherichia coli as a cause of infantile diarrhea in Bangkok. J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):550–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Lexsomboon U., Bhaibulaya M., Blacklow N. R., Tamura K., Sakazaki R. Case-control study of endemic diarrheal disease in Thai children. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):543–548. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embaye H., Batt R. M., Saunders J. R., Getty B., Hart C. A. Interaction of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli 0111 with rabbit intestinal mucosa in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1989 Apr;96(4):1079–1086. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes T. A., Vieira M. A., Wachsmuth I. K., Blake P. A., Trabulsi L. R. Serotype-specific prevalence of Escherichia coli strains with EPEC adherence factor genes in infants with and without diarrhea in São Paulo, Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;160(1):131–135. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huilan S., Zhen L. G., Mathan M. M., Mathew M. M., Olarte J., Espejo R., Khin Maung U., Ghafoor M. A., Khan M. A., Sami Z. Etiology of acute diarrhoea among children in developing countries: a multicentre study in five countries. Bull World Health Organ. 1991;69(5):549–555. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Phillips A. D., Smith H. R., Gross R. J., Shaw R., Watson P., Price E. Screening for enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in infants with diarrhea by the fluorescent-actin staining test. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):365–371. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.365-371.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Epidemiol Rev. 1984;6:31–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miliotis M. D., Koornhof H. J., Phillips J. I. Invasive potential of noncytotoxic enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in an in vitro Henle 407 cell model. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1928–1935. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1928-1935.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo M. R., Alvariza M. do C., Murahovschi J., Ramos S. R., Trabulsi L. R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serotypes and endemic diarrhea in infants. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):586–589. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.586-589.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]