Abstract
To investigate the role of heat shock proteins (HSP) of Yersinia enterocolitica for the host immune response against this pathogen, we cloned and expressed a 60-kDa HSP of Y. enterocolitica serotype O8. A fragment of Y. enterocolitica O8 HSP60 encoded by amino acids 90 to 286 was sequenced and showed more than 90% homology with HSP60 of Y. enterocolitica O3 and GroEL of Escherichia coli and 59% homology with HSP65 of Mycobacterium bovis. The arthritogenic T-cell epitope of mycobacterial HSP65 (amino acid residues 180 to 188) was not found on Yersinia HSP60. To determine whether Yersinia HSP60 is an immunodominant antigen, the immune responses of Yersinia-infected C57BL/6 mice were analyzed. Yersinia-infected mice evolved a significant serum antibody and splenic T-cell response against Yersinia HSP60. CD4+ alpha beta T-cell clones which were generated from splenic T cells isolated from either Yersinia-infected or Yersinia HSP60-immunized mice, recognized both heat-killed Yersinia serotypes O3 and O8 as well as recombinant Yersinia HSP60 but not heat-killed Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, Salmonella typhimurium, or recombinant HSP65 of Mycobacterium bovis. The adoptive transfer of HSP60-reactive T-cell clones mediated significant protection against a lethal infection with Y. enterocolitica O8. These results indicate that HSP60 of Y. enterocolitica is an immunodominant antigen which is recognized by both antibodies and CD4+ alpha beta T cells. Moreover, this is the first report providing direct evidence that microbial HSP may elicit a protective immune response which is not associated with autoimmunity.
Full text
PDF


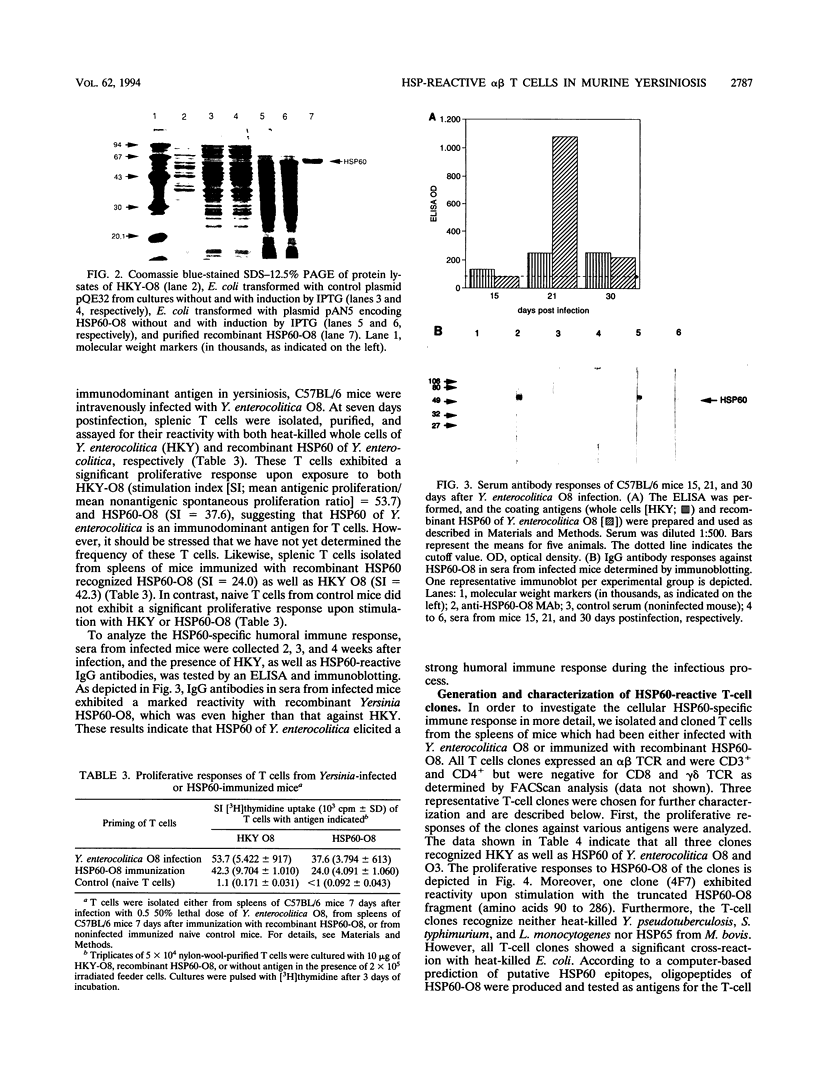
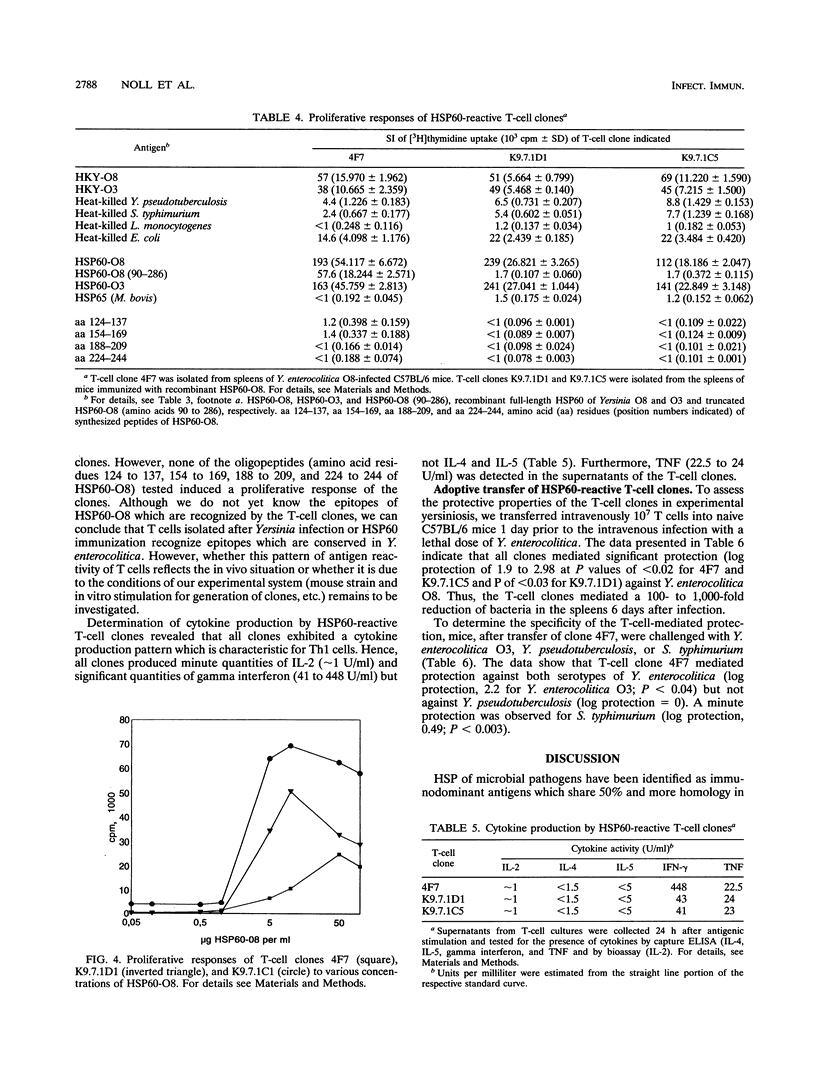



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Autenrieth I. B., Beer M., Bohn E., Kaufmann S. H., Heesemann J. Immune responses to Yersinia enterocolitica in susceptible BALB/c and resistant C57BL/6 mice: an essential role for gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1994 Jun;62(6):2590–2599. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.6.2590-2599.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autenrieth I. B., Beer M., Hantschmann P., Preger S., Vogel U., Heymer B., Heesemann J. The cellular immune response against Yersinia enterocolitica in different inbred strains of mice: evidence for an important role of T lymphocytes. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1993 Apr;278(2-3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8840(11)80855-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autenrieth I. B., Hantschmann P., Heymer B., Heesemann J. Immunohistological characterization of the cellular immune response against Yersinia enterocolitica in mice: evidence for the involvement of T lymphocytes. Immunobiology. 1993 Jan;187(1-2):1–16. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80241-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autenrieth I. B., Heesemann J. In vivo neutralization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma abrogates resistance to Yersinia enterocolitica infection in mice. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181(6):333–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00191545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autenrieth I. B., Tingle A., Reske-Kunz A., Heesemann J. T lymphocytes mediate protection against Yersinia enterocolitica in mice: characterization of murine T-cell clones specific for Y. enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1140–1149. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1140-1149.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autenrieth I. B., Vogel U., Preger S., Heymer B., Heesemann J. Experimental Yersinia enterocolitica infection in euthymic and T-cell-deficient athymic nude C57BL/6 mice: comparison of time course, histomorphology, and immune response. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2585–2595. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2585-2595.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. L., Gould-Kostka J. L., Kessel M., Arciniega J. L. Purification and immunological characterization of a GroEL-like protein from Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1417–1422. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1417-1422.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover T. L., Aber R. C. Yersinia enterocolitica. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):16–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emoto M., Danbara H., Yoshikai Y. Induction of gamma/delta T cells in murine salmonellosis by an avirulent but not by a virulent strain of Salmonella choleraesuis. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):363–372. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emoto M., Naito T., Nakamura R., Yoshikai Y. Different appearance of gamma delta T cells during salmonellosis between Ityr and Itys mice. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3411–3420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Life P. F., Bailey L. C., Bacon P. A. In vitro responses to a 65-kilodalton mycobacterial protein by synovial T cells from inflammatory arthritis patients. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2494–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C., McFarland H. Heat shock proteins in multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases. Immunol Today. 1993 Aug;14(8):373–375. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Gaede K., Autenrieth I. B. Experimental Yersinia enterocolitica infection in rodents: a model for human yersiniosis. APMIS. 1993 Jun;101(6):417–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Laufs R. Construction of a mobilizable Yersinia enterocolitica virulence plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):761–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.761-767.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann E., Lohse A. W., Van der Zee R., Van Eden W., Mayet W. J., Probst P., Poralla T., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Fleischer B. Synovial fluid-derived Yersinia-reactive T cells responding to human 65-kDa heat-shock protein and heat-stressed antigen-presenting cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2139–2143. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromatsu K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Ohga S., Muramori K., Matsumoto K., Bluestone J. A., Nomoto K. A protective role of gamma/delta T cells in primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):49–56. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogervorst E. J., Boog C. J., Wagenaar J. P., Wauben M. H., Van der Zee R., Van Eden W. T cell reactivity to an epitope of the mycobacterial 65-kDa heat-shock protein (hsp 65) corresponds with arthritis susceptibility in rats and is regulated by hsp 65-specific cellular responses. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1289–1296. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. B., Coulson A. F., Duff G. W. Sequence homologies between hsp60 and autoantigens. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90210-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Heat shock proteins and the immune response. Immunol Today. 1990 Apr;11(4):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90050-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Heat-shock proteins: a missing link in the host-parasite relationship? Med Microbiol Immunol. 1990;179(2):61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00198526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Immunity against intracellular bacteria: biological effector functions and antigen specificity of T lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:141–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Schoel B., Wand-Württenberger A., Steinhoff U., Munk M. E., Koga T. T-cells, stress proteins, and pathogenesis of mycobacterial infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;155:125–141. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74983-4_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Wand-Württenberger A., DeBruyn J., Munk M. E., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. T cells against a bacterial heat shock protein recognize stressed macrophages. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1112–1115. doi: 10.1126/science.2788923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Geoffroy M. C., Renauld G. Common accessory genes for the Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin and fimbriae share sequence similarities with the papC and papD gene families. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3175–3183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki G., Hiromatsu K., Yoshikai Y., Muramori K., Nomoto K. Characterization of T-cell receptor gamma delta T cells appearing at the early phase of murine Listeria monocytogenes infection. Immunology. 1993 Jan;78(1):22–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Belland R. J., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. The 57-kD chlamydial hypersensitivity antigen is a stress response protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Schoel B., Modrow S., Karr R. W., Young R. A., Kaufmann S. H. T lymphocytes from healthy individuals with specificity to self-epitopes shared by the mycobacterial and human 65-kilodalton heat shock protein. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2844–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Fu Y. X., Cranfill R., Dallas A., Ellis C., Reardon C., Lang J., Carding S. R., Kubo R., Born W. Heat shock protein Hsp60-reactive gamma delta cells: a large, diversified T-lymphocyte subset with highly focused specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4348–4352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. Immunology. Antigens for gamma/delta T cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):342–343. doi: 10.1038/339342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D., Harn D. A. Candidate vaccine antigens identified by antibodies from mice vaccinated with 15- or 50-kilorad-irradiated cercariae of Schistosoma mansoni. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):146–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.146-154.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt M. C., Hindersson P., Soderberg C., Mensi N., Turck C. W., Webb D., Yssel H., Peltz G. T cell and antibody reactivity with the Borrelia burgdorferi 60-kDa heat shock protein in Lyme arthritis. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3985–3992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Hiromatsu K., Matsuzaki G., Muramori K., Nomoto K. Peritoneal gamma delta T cells induced by Escherichia coli infection in mice. Correlation between Thy-1 phenotype and host minor lymphocyte-stimulating phenotype. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):2062–2069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. R., Maclean I. W., Brunham R. C., Pal S., Whittum-Hudson J. Chlamydial heat shock proteins and trachoma. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3061–3063. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3061-3063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U., Autenrieth I. B., Berner R., Heesemann J. Role of plasmid-encoded antigens of Yersinia enterocolitica in humoral immunity against secondary Y. enterocolitica infection in mice. Microb Pathog. 1993 Jul;15(1):23–36. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1993.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin S. S., Jeremias J., Toth M., Ledger W. J. Cell-mediated immune response to the recombinant 57-kDa heat-shock protein of Chlamydia trachomatis in women with salpingitis. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1379–1383. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Russ F., Teixeira H. C., Conradt P., Kaufmann S. H. Listeria monocytogenes-induced gamma interferon secretion by intestinal intraepithelial gamma/delta T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2154–2161. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2154-2161.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B. Chaperonins and the immune response. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):27–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B. Heat-shock proteins: immunity and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Aug;4(4):396–400. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(06)80029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Hogervorst E. J., Hensen E. J., van der Zee R., van Embden J. D., Cohen I. R. A cartilage-mimicking T-cell epitope on a 65K mycobacterial heat-shock protein: adjuvant arthritis as a model for human rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;145:27–43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74594-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Holoshitz J., Nevo Z., Frenkel A., Klajman A., Cohen I. R. Arthritis induced by a T-lymphocyte clone that responds to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and to cartilage proteoglycans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5117–5120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Thole J. E., van der Zee R., Noordzij A., van Embden J. D., Hensen E. J., Cohen I. R. Cloning of the mycobacterial epitope recognized by T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):171–173. doi: 10.1038/331171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]