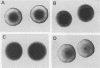
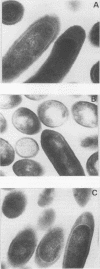
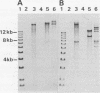
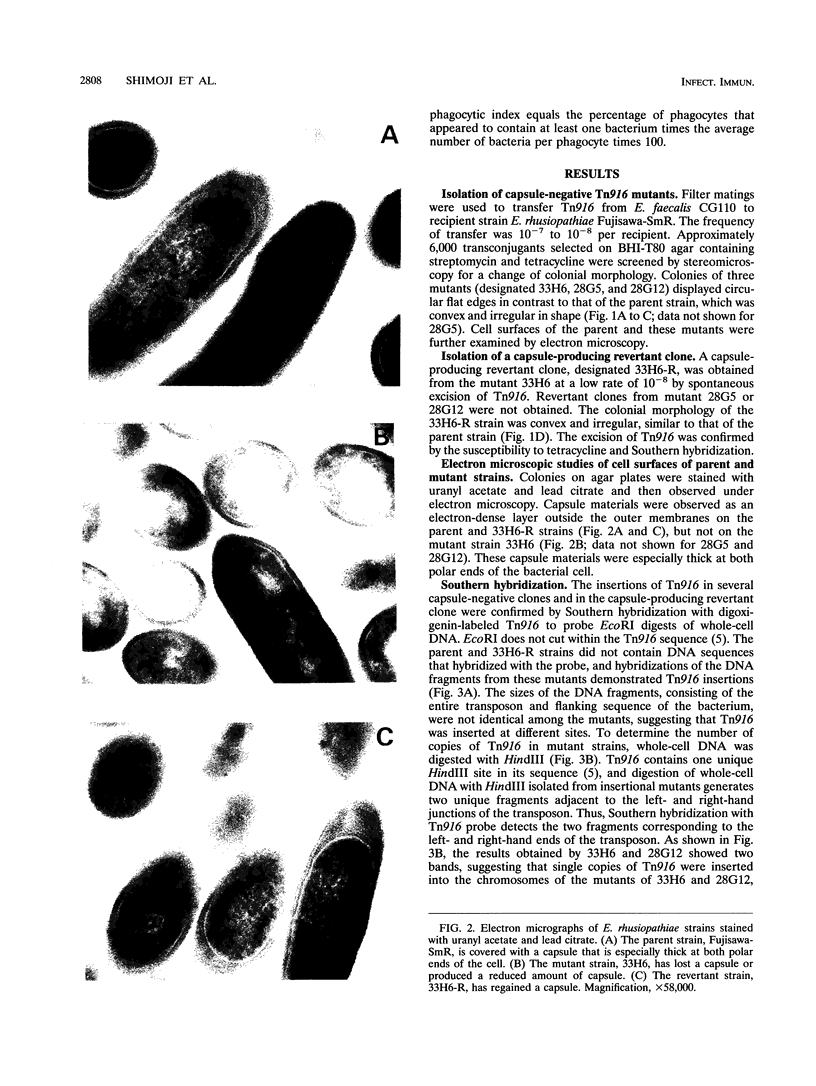
Abstract
Three avirulent insertional mutants of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae were obtained by the technique of transposon mutagenesis with the self-conjugative transposon Tn916. The interactions between murine polymorphonuclear leukocytes and parent and mutant strains were studied in vitro. In the presence of normal serum, the virulent parent strain was resistant to phagocytosis, whereas the avirulent mutant strains were efficiently phagocytosed. In the presence of immune serum, the parent and the mutant strains were both efficiently phagocytosed. Electron microscopic examination of the parent strain demonstrated the presence of a structure resembling a capsule which was absent on the mutant strains, suggesting that a capsule may be involved in virulence. This was confirmed in studies in which an avirulent mutant strain reverted to virulence following acquisition of a capsule when the transposon was lost by spontaneous excision. These results strongly suggest that virulence of E. rhusiopathiae is associated, at least in part, with resistance to phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes and that this antiphagocytic ability of the bacterium results from its possession of a capsule.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAER H., EHRENWORTH L. The pathogenicity of Klebsiella pneumoniae for mice: the relationship to the quantity and rate of production of type-specific capsular polysaccharide. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):713–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.713-717.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes from immune and nonimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Feb;35(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galán J. E., Timoney J. F. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a protective antigen of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3116–3121. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3116-3121.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawron-Burke C., Clewell D. B. Regeneration of insertionally inactivated streptococcal DNA fragments after excision of transposon Tn916 in Escherichia coli: strategy for targeting and cloning of genes from gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):214–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.214-221.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L. Bacterial capsule--old dogmas and new tricks. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):407–415. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasemann C., Müller H. E. Die Virulenz von Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae-Stämmen und ihre Neuraminidase-Produktion. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975;231(1-3):206–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. G., Deicher H. Solubilization and characterization of surface antigenic components of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae T28. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):818–822. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.818-822.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Betley M. J., Hopkins C. A., Perez N. E., Pier G. B. Virulence studies, in mice, of transposon-induced mutants of Staphylococcus aureus differing in capsule size. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):741–750. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLEOD C. M., KRAUS M. R. Relation of virulence of pneumococcal strains for mice to the quantity of capsular polysaccharide formed in vitro. J Exp Med. 1950 Jul 1;92(1):1–9. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., Duke L. J., Liau D. F., Hash J. H. Biological properties of the encapsulated Staphylococcus aureus M. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.389-397.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of transposon-induced mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa deficient in production of exoenzyme S. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):470–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.470-474.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podschun R., Penner I., Ullmann U. Interaction of Klebsiella capsule type 7 with human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Microb Pathog. 1992 Nov;13(5):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Wessels M. R., Heggen L. M., Kasper D. L. Transposon mutagenesis of type III group B Streptococcus: correlation of capsule expression with virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7208–7212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto K., Nishimura Y., Fujiki M., Azechi H., Suzuki K. [Attenuated acriflavin-fast Erysipelothrix insidiosa. Relationship between its capability to cause arthritis in mice and immunogenicity in swine]. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1971 Aug;33(4):161–171. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.33.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoons-Smit A. M., Verweij-van Vught A. M., MacLaren D. M. The role of K antigens as virulence factors in Klebsiella. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Mar;21(2):133–137. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-2-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Hirayama N., Sawada T., Tamura Y., Muramatsu M. Correlation between adherence of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae strains of serovar 1a to tissue culture cells originated from porcine kidney and their pathogenicity in mice and swine. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Jan;13(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. The effect of decomplementation on Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae infection in the mouse. Immunology. 1970 Oct;19(4):561–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. R., Verwey W. F. Isolation and Characterization of a Protective Antigen-Containing Particle from Culture Supernatant Fluids of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):380–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.380-386.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. R., Verwey W. F. Solubilization and Characterization of a Protective Antigen of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):387–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.387-393.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. L. Swine erysipelas--a review of prevalence and research. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Apr 15;184(8):944–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomizo Y., Isayama Y. Antibody activities of IgM and IgG fractions from rabbit anti-Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae sera. Res Vet Sci. 1972 May;13(3):294–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]