Abstract
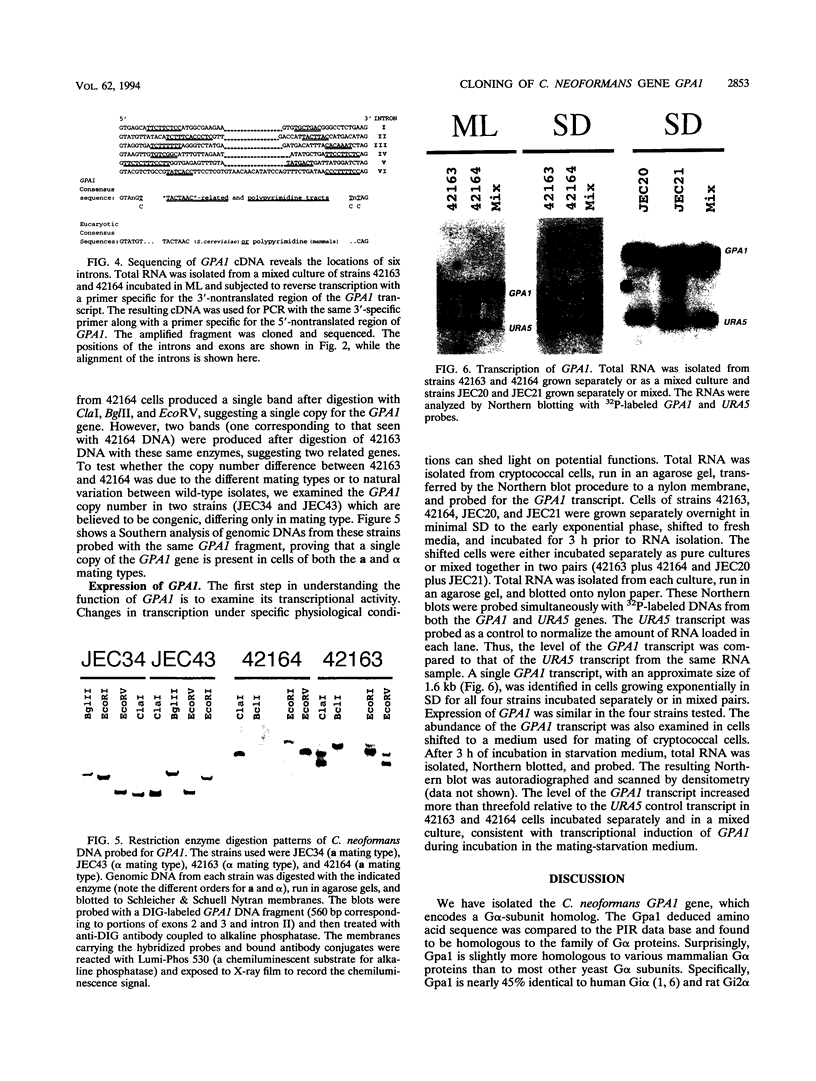
We have isolated a gene, GPA1, from Cryptococcus neoformans by the PCR technique. DNA sequencing of the GPA1 clone suggested that it encodes a protein homologous to the G-protein alpha-subunit family. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of the GPA1-encoded protein revealed that it is about 45% identical to several mammalian Gi alpha subunits and 48% identical to the G alpha protein Gpa2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. G alpha proteins are known to be involved in mating of other yeasts, such as S. cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Southern analysis demonstrated that GPA1 is present in a single copy within the Cryptococcus genome. Isolation of the cDNA for GPA1 confirmed that the gene contains six introns within the coding region. The GPA1 transcript was identified by Northern (RNA) analysis as a 1.6-kb RNA present in exponentially growing cells of both the alpha and a mating types. Moreover, the abundance of this transcript increased in cells shifted to starvation medium. Coincubation of alpha and a cells on starvation medium is required for mating of cryptococcal cells. Thus, our results are consistent with the involvement of C. neoformans GPA1 in mating.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beals C. R., Wilson C. B., Perlmutter R. M. A small multigene family encodes Gi signal-transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7886–7890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F., Hartwell L. H., Jackson C., Konopka J. B. Conjugation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:429–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J. Mating pheromones of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: purification and structural characterization of M-factor and isolation and analysis of two genes encoding the pheromone. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):951–960. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J. R., Ho Y. S., Snyderman R. Human Gi protein alpha-subunit: deduction of amino acid structure from a cloned cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81428-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Kwon-Chung K. J. Isolation of the URA5 gene from Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformans and its use as a selective marker for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4538–4544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis D. H., Pfeiffer T. J. Natural habitat of Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1642–1644. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1642-1644.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kaziro Y., Yamamoto M. Mating pheromone-like diffusible factor released by Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1991–1993. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. A regulatory hierarchy for cell specialization in yeast. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):749–757. doi: 10.1038/342749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nagata S., Nakamura S., Katada T., Ui M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of cDNAs for alpha subunits of the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins Gs, Gi, and Go from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahng K. Y., Ferguson J., Reed S. I. Mutations in a gene encoding the alpha subunit of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae G protein indicate a role in mating pheromone signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2484–2493. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Shimoda C. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe mam2 gene encodes a putative pheromone receptor which has a significant homology with the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ste2 protein. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3743–3751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Edman J. C., Wickes B. L. Genetic association of mating types and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):602–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.602-605.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. Morphogenesis of Filobasidiella neoformans, the sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1976 Jul-Aug;68(4):821–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M. The ecology of Cryptococcus neoformans and the epidemiology of cryptococcosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Nov-Dec;13(6):1163–1169. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.6.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh L., Neiman A. M., Herskowitz I. Signal transduction during pheromone response in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:699–728. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. D., Edman J. C. The alpha-mating type locus of Cryptococcus neoformans contains a peptide pheromone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1962–1970. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Kakegawa T., Kaspar R. L., White M. W. Polypyrimidine tracts and their binding proteins: regulatory sites for posttranscriptional modulation of gene expression. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 30;32(12):2931–2937. doi: 10.1021/bi00063a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Itoh H., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y. Occurrence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of a gene homologous to the cDNA coding for the alpha subunit of mammalian G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Obara T., Kaibuchi K., Miyajima I., Miyajima A., Itoh H., Nakamura S., Arai K., Matsumoto K., Kaziro Y. Isolation of a second yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene (GPA2) coding for guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein: studies on its structure and possible functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara T., Nakafuku M., Yamamoto M., Kaziro Y. Isolation and characterization of a gene encoding a G-protein alpha subunit from Schizosaccharomyces pombe: involvement in mating and sporulation pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5877–5881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfect J. R., Magee B. B., Magee P. T. Separation of chromosomes of Cryptococcus neoformans by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2624–2627. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2624-2627.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer T., Ellis D. Environmental isolation of Cryptococcus neoformans gattii from California. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):929–930. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.4.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. Pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90276-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu C., Hoekstra D., McEachern M. J., Reed S. I., Hicks J. B. A G-protein alpha subunit from asexual Candida albicans functions in the mating signal transduction pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is regulated by the a1-alpha 2 repressor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):1977–1985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugar A. M. Overview: cryptococcosis in the patient with AIDS. Mycopathologia. 1991 Jun;114(3):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00437205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]