Abstract
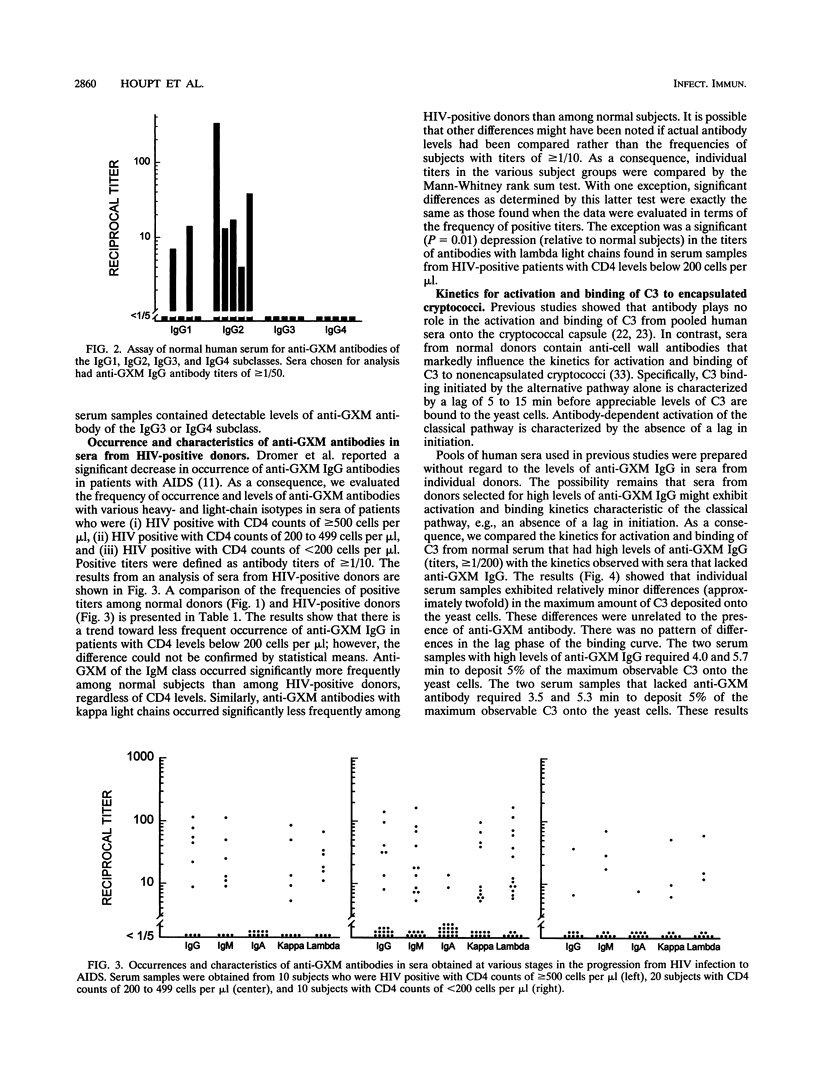
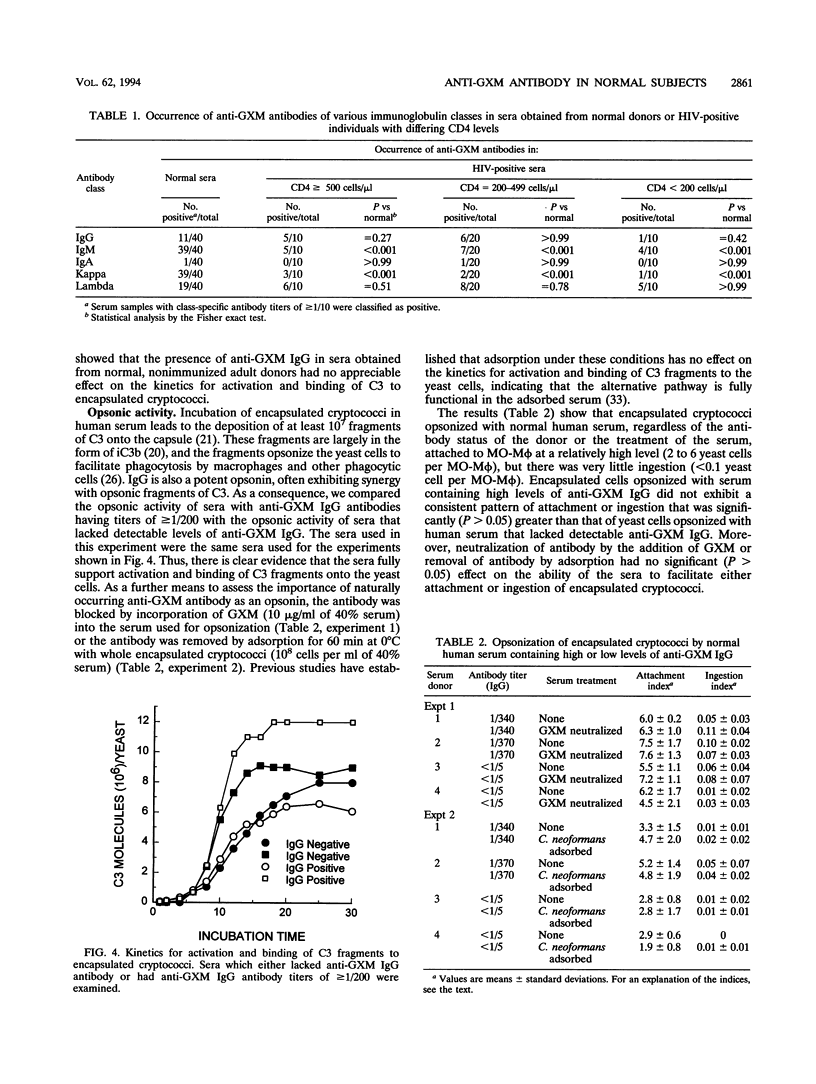
Serum obtained from normal human subjects contains antibodies reactive in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with the glucuronoxylomannan (GXM) of Cryptococcus neoformans. The frequency of occurrence of class-specific antibodies among normal subjects was 28% for immunoglobulin G (IgG), 98% for IgM, and 3% for IgA. Anti-GXM antibodies with kappa light chains occurred in 98% of normal subjects, while the occurrence of lambda light chains was 28%. Each of five subjects with high levels of anti-GXM IgG antibodies had readily detectable antibodies of the IgG2 isotype; two of the five subjects had readily detectable IgG1 antibody. An examination of sera from human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients showed that human immunodeficiency virus infection was accompanied by a significant decrease in the occurrence of IgM antibodies and anti-GXM antibodies with kappa light chains; these decreases occurred early in infection when CD4 counts were still > or = 500 cells per microliter. A slight but not statistically significant decrease in the occurrence of anti-GXM IgG antibodies was seen only in patients with CD4 levels of < 200 cells per microliter. Sera from normal subjects with high levels of anti-GXM IgG antibodies were examined to identify any contribution of the antibodies to complement activation or to opsonization of the yeast cells. An analysis of the kinetics for activation and binding of C3 to the yeast cell showed no pattern of quantitative or qualitative differences between sera with high or low levels of anti-GXM IgG antibodies. Phagocytosis studies showed that the naturally occurring IgG antibodies did not contribute to opsonization of the yeast cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENNETT J. E., HASENCLEVER H. F., TYNES B. S. DETECTION OF CRYPTOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE IN SERUM AND SPINAL FLUID: VALUE IN DIAGNOSIS AND PROGNOSIS. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1964;77:145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballet J. J., Sulcebe G., Couderc L. J., Danon F., Rabian C., Lathrop M., Clauvel J. P., Seligmann M. Impaired anti-pneumococcal antibody response in patients with AIDS-related persistent generalized lymphadenopathy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jun;68(3):479–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Antibody to group B Streptococcus type III in human sera measured by a mouse protection test. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):56–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.56-61.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumer S. O., Kaufman L. Characterization of immunoglobulin classes of human antibodies to cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1977 Jul 29;61(1):55–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00440759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Andersson L. O., Porath J. Covalent attachment of proteins to polysaccharide carriers by means of benzoquinone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 28;386(1):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadevall A., Mukherjee J., Devi S. J., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Scharff M. D. Antibodies elicited by a Cryptococcus neoformans-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine have the same specificity as those elicited in infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165(6):1086–1093. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.6.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherniak R., Morris L. C., Anderson B. C., Meyer S. A. Facilitated isolation, purification, and analysis of glucuronoxylomannan of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):59–64. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.59-64.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Bennett J. E. Prognostic factors in cryptococcal meningitis. A study in 111 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):176–181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., May J. E., Kane M. A., Frank M. M., Bennett J. E. The role of the classical and alternate complement pathways in host defenses against Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2260–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Aucouturier P., Clauvel J. P., Saimot G., Yeni P. Cryptococcus neoformans antibody levels in patients with AIDS. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20(3):283–285. doi: 10.3109/00365548809032452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Perronne C., Barge J., Vilde J. L., Yeni P. Role of IgG and complement component C5 in the initial course of experimental cryptococcosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Dec;78(3):412–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr Roles of macrophage Fc and C3b receptors in phagocytosis of immunologically coated Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3853–3857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. K., Bennett J. E., Huber M. A. Long-lasting, specific immunologic unresponsiveness associated with cryptococcal meningitis. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1185–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI110555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. G., Pfrommer G. S., Kozel T. R. Occurrences, specificities, and functions of ubiquitous antibodies in human serum that are reactive with the Cryptococcus neoformans cell wall. Infect Immun. 1994 Jan;62(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.1.215-220.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. S., Selwyn P. A., Maude D., Pollard C., Freeman K., Schiffman G. Response to pneumococcal vaccine among asymptomatic heterosexual partners of persons with AIDS and intravenous drug users infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):826–831. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Follette J. L. Opsonization of encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans by specific anticapsular antibody. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):978–984. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.978-984.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Hermerath C. A. Benzoquinone activation of Cryptococcus neoformans capsular polysaccharide for construction of an immunoaffinity column. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 24;107(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S. Activation of the complement system by Cryptococcus neoformans leads to binding of iC3b to the yeast. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.1-5.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Pfrommer G. S., Guerlain A. S., Highison B. A., Highison G. J. Strain variation in phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans: dissociation of susceptibility to phagocytosis from activation and binding of opsonic fragments of C3. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2794–2800. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2794-2800.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Wilson M. A., Murphy J. W. Early events in initiation of alternative complement pathway activation by the capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3101–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3101-3110.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Wilson M. A., Pfrommer G. S., Schlageter A. M. Activation and binding of opsonic fragments of C3 on encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans by using an alternative complement pathway reconstituted from six isolated proteins. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1922–1927. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1922-1927.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Wilson M. A., Welch W. H. Kinetic analysis of the amplification phase for activation and binding of C3 to encapsulated and nonencapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1992 Aug;60(8):3122–3127. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.8.3122-3127.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., DiBenedetto D. J. Differential stimulation of murine resident peritoneal cells by selectively opsonized encapsulated and acapsular Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2544–2551. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2544-2551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Tabuni A. Binding of Cryptococcus neoformans by human cultured macrophages. Requirements for multiple complement receptors and actin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):528–535. doi: 10.1172/JCI115027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Mitchell T. G., Storkus W. J., Dawson J. R. Human natural killer cells do not inhibit growth of Cryptococcus neoformans in the absence of antibody. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):639–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.639-645.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. L., Johnston R. B., Jr Role of binding through C3b and IgG in polymorphonuclear neutrophil function: studies with trypsin-generated C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1839–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Schneerson R., Glode M. P., Vann W., Schiffer M. S., Liu T. Y., Parke J. C., Jr, Huntley C. Cross-reactive antigens and immunity to diseases caused by encapsulated bacteria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Aug;56(2):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlageter A. M., Kozel T. R. Opsonization of Cryptococcus neoformans by a family of isotype-switch variant antibodies specific for the capsular polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1914–1918. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1914-1918.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel R. A. The indirect fluorescent antibody test for the detection of antibody in human cryptococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):573–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. A., Kozel T. R. Contribution of antibody in normal human serum to early deposition of C3 onto encapsulated and nonencapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):754–761. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.754-761.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


