Abstract
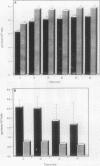
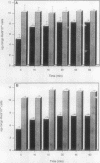
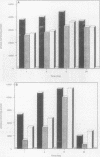
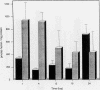
Although hemin is an essential nutrient for the black-pigmented oral bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis, the mechanisms involved in hemin binding and uptake are poorly defined. In this study, we have examined the binding of hemin and Congo red (CR) to P. gingivalis whole cells and have defined the conditions for maximal binding. Additionally, the accumulation of hemin by P. gingivalis under growing conditions has been characterized. P. gingivalis A7436 was grown under hemin- or iron-deplete conditions (basal medium [BM] or Schaedler broth with dipyridyl [SBD]) or under hemin- or iron-replete conditions (BM with hemin [BMH] or Schaedler broth [SB]), and hemin and CR binding were assessed spectrophotometrically. Binding of hemin by P. gingivalis whole cells was rapid and was observed in samples obtained from cells grown under hemin- and iron-replete and hemin-deplete conditions but was not observed in cells grown under iron limitation. We also found that P. gingivalis whole cells bound more hemin when grown in BMH or SB than cells grown in BM or SBD. Binding of CR by P. gingivalis A7436 was also enhanced when cells were grown in the presence of hemin or when cells were incubated with hemin prior to CR binding. Hemin binding and accumulation were also assessed using [14C]hemin and [59Fe]hemin under growing conditions. Both [14C]hemin and [59Fe]hemin were accumulated by P. gingivalis, indicating that iron and the porphyrin ring were taken into the cell. Binding and accumulation of hemin under growing conditions were also induced by growth of P. gingivalis in hemin-replete media. Hemin accumulation was inhibited by the addition of KCN to P. gingivalis cultures, indicating that active transport was required for hemin uptake. [14C]hemin binding and accumulation were also inhibited by the addition of either cold hemin or protoporphyrin IX. Taken together, these results indicate that P. gingivalis transports the entire hemin moiety into the cell and that the binding and accumulation of hemin are induced by growth of cultures in the presence of hemin.
Full text
PDF

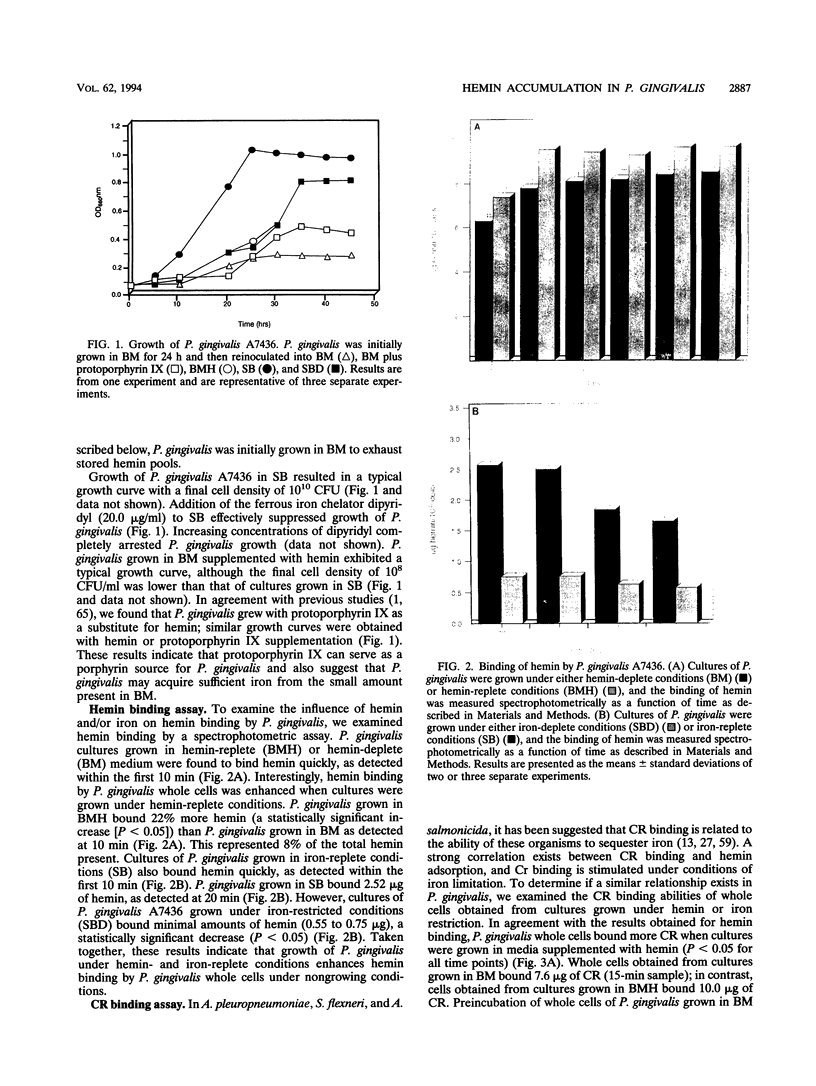



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURROWS T. W., JACKSON S. The virulence-enhancing effect of iron on nonpigmented mutants of virulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Dec;37(6):577–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
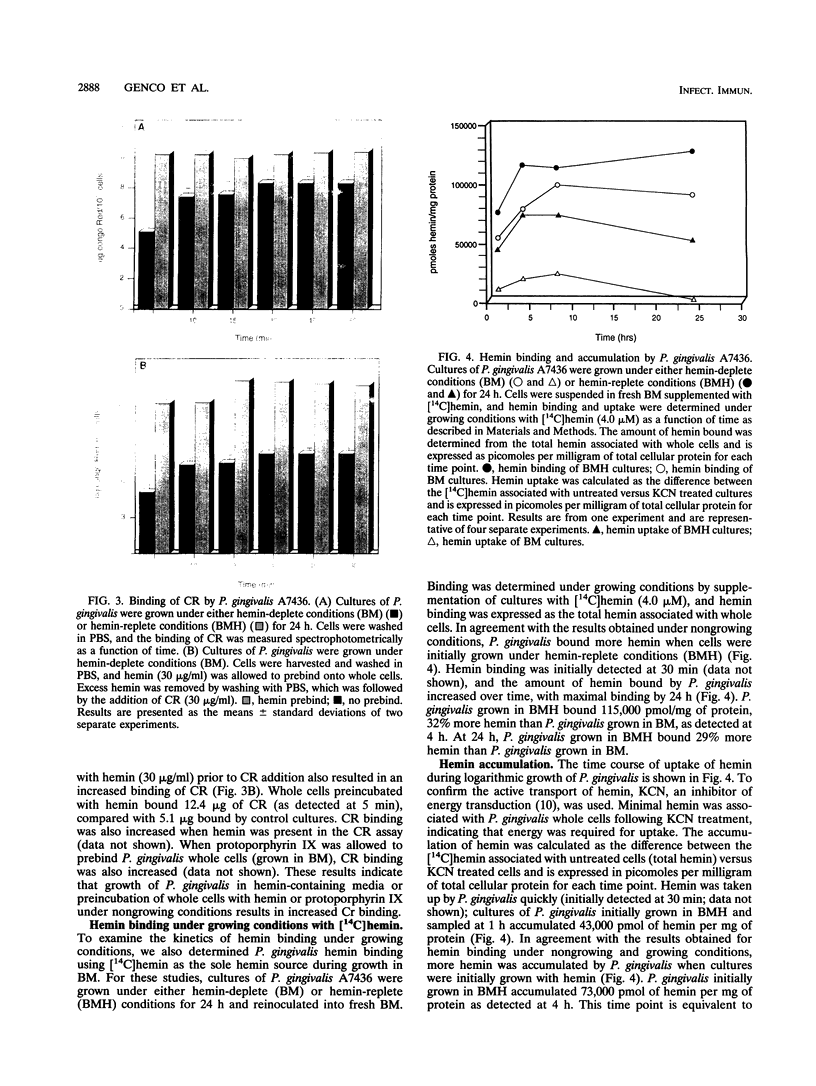
- Barua P. K., Dyer D. W., Neiders M. E. Effect of iron limitation on Bacteroides gingivalis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Oct;5(5):263–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramanti T. E., Holt S. C. Effect of porphyrins and host iron transport proteins on outer membrane protein expression in Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis: identification of a novel 26 kDa hemin-repressible surface protein. Microb Pathog. 1992 Jul;13(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90032-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramanti T. E., Holt S. C. Hemin uptake in Porphyromonas gingivalis: Omp26 is a hemin-binding surface protein. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7413–7420. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7413-7420.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramanti T. E., Holt S. C. Localization of a Porphyromonas gingivalis 26-kilodalton heat-modifiable, hemin-regulated surface protein which translocates across the outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5827–5839. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5827-5839.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramanti T. E., Holt S. C. Roles of porphyrins and host iron transport proteins in regulation of growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis W50. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7330–7339. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7330-7339.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briat J. F. Iron assimilation and storage in prokaryotes. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Dec;138(12):2475–2483. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-12-2475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman R. J., Ramakrishnan M. D., Harper F. H. Hemin levels in culture medium of Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis regulate both hemin binding and trypsinlike protease production. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4016–4019. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4016-4019.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. K., DeNardin A., Dyer D. W., Genco R. J., Neiders M. E. Human immunoglobulin G antibody response to iron-repressible and other membrane proteins of Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2427–2433. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2427-2433.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu L., Bramanti T. E., Ebersole J. L., Holt S. C. Hemolytic activity in the periodontopathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis: kinetics of enzyme release and localization. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1932–1940. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1932-1940.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
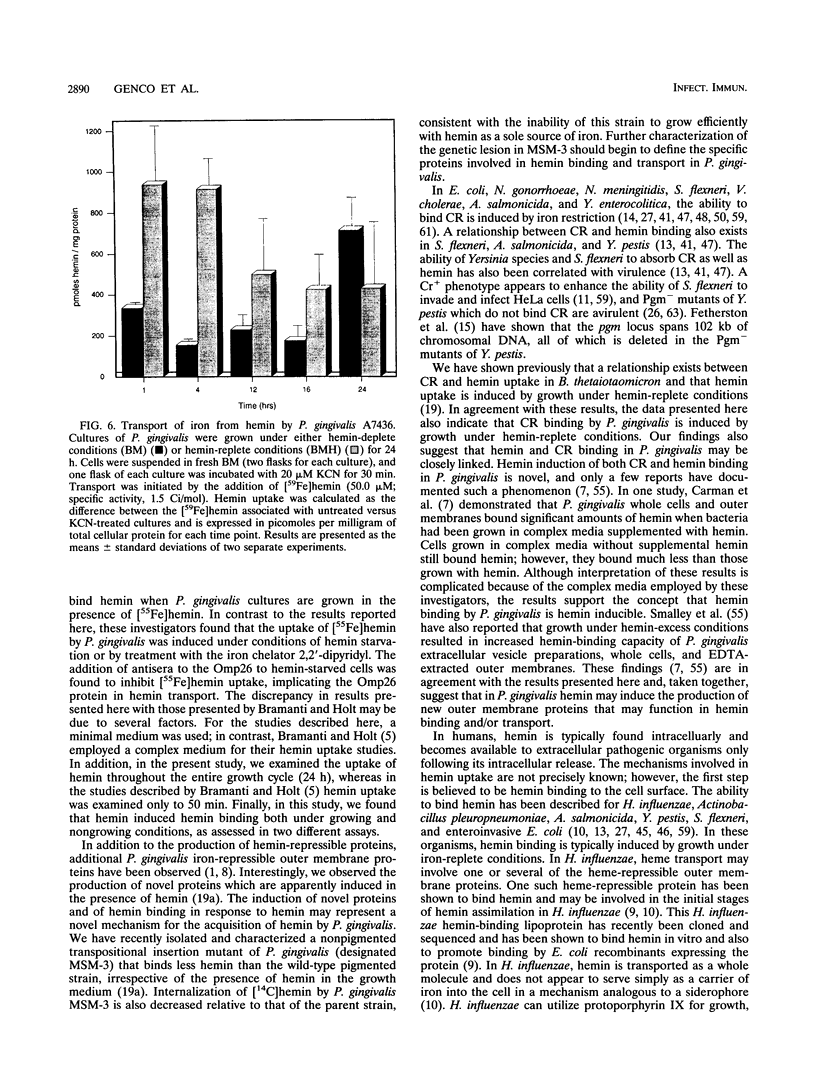
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Characterization of Shigella flexneri sequences encoding congo red binding (crb): conservation of multiple crb sequences and role of IS1 in loss of the Crb+ phenotype. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.435-443.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. Congo red binding phenotype is associated with hemin binding and increased infectivity of Shigella flexneri in the HeLa cell model. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1393–1398. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1393-1398.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneer H. G., Potter A. A. Effect of iron restriction on the outer membrane proteins of Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):798–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.798-804.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., West E. P., Sparling P. F. Effects of serum carrier proteins on the growth of pathogenic neisseriae with heme-bound iron. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2171–2175. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2171-2175.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetherston J. D., Schuetze P., Perry R. D. Loss of the pigmentation phenotype in Yersinia pestis is due to the spontaneous deletion of 102 kb of chromosomal DNA which is flanked by a repetitive element. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2693–2704. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., MACDONALD J. B. Hemin and vitamin K compounds as required factors for the cultivation of certain strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:164–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.164-170.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco C. A., Chen C. Y., Arko R. J., Kapczynski D. R., Morse S. A. Isolation and characterization of a mutant of Neisseria gonorrhoeae that is defective in the uptake of iron from transferrin and haemoglobin and is avirulent in mouse subcutaneous chambers. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jun;137(6):1313–1321. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-6-1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco C. A., Cutler C. W., Kapczynski D., Maloney K., Arnold R. R. A novel mouse model to study the virulence of and host response to Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1255–1263. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1255-1263.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco C. A., Kapczynski D. R., Cutler C. W., Arko R. J., Arnold R. R. Influence of immunization on Porphyromonas gingivalis colonization and invasion in the mouse chamber model. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1447–1454. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1447-1454.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. S., Hansen E. J. Molecular cloning, partial purification, and characterization of a haemin-binding lipoprotein from Haemophilus influenzae type b. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):267–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. S., Slaughter C., Hansen E. J. The hbpA gene of Haemophilus influenzae type b encodes a heme-binding lipoprotein conserved among heme-dependent Haemophilus species. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2257–2266. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2257-2266.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms S. D., Oliver J. D., Travis J. C. Role of heme compounds and haptoglobin in Vibrio vulnificus pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):345–349. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.345-349.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoshita E., Iwakura K., Amano A., Tamagawa H., Shizukuishi S. Effect of transferrin on the growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Dent Res. 1991 Sep;70(9):1258–1261. doi: 10.1177/00220345910700090501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Phipps B. M., Ishiguro E. E., Trust T. J. Porphyrin binding by the surface array virulence protein of Aeromonas salmonicida. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1332–1336. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1332-1336.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor K. M., Daskaleros P. A., Robinson R. E., Payne S. M. Virulence of iron transport mutants of Shigella flexneri and utilization of host iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):594–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.594-599.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. C. Iron sources for Haemophilus ducreyi. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Jun;34(6):317–322. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-6-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev M., Keudell K. C., Milford A. F. Succinate as a growth factor for Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):175–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.175-178.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Importance of nutrition in gingival crevice microbial ecology. Periodontics. 1968 Dec;6(6):245–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., Bourgeau G., Grenier D., Lacroix J. M. Properties of oral asaccharolytic black-pigmented Bacteroides. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Sep;30(9):1133–1136. doi: 10.1139/m84-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., Holt S. C. Biology of asaccharolytic black-pigmented Bacteroides species. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):134–152. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.134-152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. L., Charles H. P. Mutants of Escherichia coli K12 permeable to haemin. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jul;113(1):165–168. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee A. S., McDermid A. S., Baskerville A., Dowsett A. B., Ellwood D. C., Marsh P. D. Effect of hemin on the physiology and virulence of Bacteroides gingivalis W50. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):349–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.349-355.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S. The role of crevicular fluid iron in periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1985 Nov;56(11 Suppl):22–27. doi: 10.1902/jop.1985.56.11s.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parton R. Differentiation of phase I and variant strains of Bordetella pertussis on Congo red media. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(4):301–306. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-4-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M., Finkelstein R. A. Detection and differentiation of iron-responsive avirulent mutants on Congo red agar. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):94–98. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.94-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendrak M. L., Perry R. D. Characterization of a hemin-storage locus of Yersinia pestis. Biol Met. 1991;4(1):41–47. doi: 10.1007/BF01135556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendrak M. L., Perry R. D. Proteins essential for expression of the Hms+ phenotype of Yersinia pestis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):857–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Accumulation of iron by yersiniae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1290-1298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Pendrak M. L., Schuetze P. Identification and cloning of a hemin storage locus involved in the pigmentation phenotype of Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5929–5937. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5929-5937.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidcock K. A., Wooten J. A., Daley B. A., Stull T. L. Iron acquisition by Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):721–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.721-725.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic J. K., Robins-Browne R. M., Davey R. B. Differentiation between virulent and avirulent Yersinia enterocolitica isolates by using Congo red agar. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):486–490. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.486-490.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri F., Hossain S. A., Ciznár I., Haider K., Ljungh A., Wadstrom T., Sack D. A. Congo red binding and salt aggregation as indicators of virulence in Shigella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1343–1348. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1343-1348.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza V., Sinclair P. R., White D. C., Cuorant P. R. Electron transport system of the protoheme-requiring anaerobe Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.665-671.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins-Browne R. M., Prpic J. K., Davey R. B. Influence of the virulence plasmid and the Congo red reaction on the antimicrobial susceptibility of Yersinia species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 May;17(5):553–557. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah H. N., Bonnett R., Mateen B., Williams R. A. The porphyrin pigmentation of subspecies of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):45–50. doi: 10.1042/bj1800045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides species, Capnocytophaga species, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):412–421. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Reynolds H. S. Long-wave UV light fluorescence for identification of black-pigmented Bacteroides spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1148–1151. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1148-1151.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalley J. W., Birss A. J., McKee A. S., Marsh P. D. Haemin-restriction influences haemin-binding, haemagglutination and protease activity of cells and extracellular membrane vesicles of Porphyromonas gingivalis W50. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Dec 15;69(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90647-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoebner J. A., Payne S. M. Iron-regulated hemolysin production and utilization of heme and hemoglobin by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2891–2895. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2891-2895.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stojiljkovic I., Hantke K. Hemin uptake system of Yersinia enterocolitica: similarities with other TonB-dependent systems in gram-negative bacteria. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4359–4367. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stugard C. E., Daskaleros P. A., Payne S. M. A 101-kilodalton heme-binding protein associated with congo red binding and virulence of Shigella flexneri and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli strains. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3534–3539. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3534-3539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L. Protein sources of heme for Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):148–153. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.148-153.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surgalla M. J., Beesley E. D. Congo red-agar plating medium for detecting pigmentation in Pasteurella pestis. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):834–837. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.834-837.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Săsărman A., Surdeanu M., Szégli G., Horodniceanu T., Greceanu V., Dumitrescu A. Hemin-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):570–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.570-572.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai S. S., Lee C. J., Winter R. E. Hemin utilization is related to virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1993 Dec;61(12):5401–5405. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.12.5401-5405.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Brubaker R. R. In vivo comparison of avirulent Vwa- and Pgm- or Pstr phenotypes of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):895–900. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.895-900.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., GRANICK S. HEMIN BIOSYNTHESIS IN HAEMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:842–850. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.842-850.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. G., Hammond J. S., Bullen J. J. Effect of iron compounds on antibacterial function of human polymorphs and plasma. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):723–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.723-730.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyss C. Growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, T. pectinovorum, T. socranskii, and T. vincentii in a chemically defined medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Sep;30(9):2225–2229. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.9.2225-2229.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]