Abstract
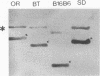
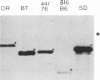
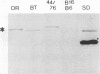
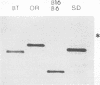
The results reported here show that the two meningococcal transferrin-binding proteins (TBP1 and TBP2) generate different immune responses in different host species and that there is variation in response dependent on the method of antigen preparation and possibly the route of administration. Mice immunized with either whole cells of Neisseria meningitidis SD (B:15:P1.16) or the isolated TBP1-TBP2 complex from the same strain produced antisera which, when tested against a representative panel of meningococcal isolates by Western blotting (immunoblotting), recognized some but not all heterologous TBP2 molecules. In contrast, rabbit antisera raised to the same preparations were cross-reactive with almost all the TBP2 molecules. The immune response to TBP1 was also host species dependent. Western blot analysis with denatured TBP1 failed to detect antibodies in antisera raised in mice to whole cells or in a rabbit to the TBP1-TBP2 complex but detected broadly cross-reactive antibodies in mouse anti-TBP1-TBP2 complex sera and strain-specific antibodies in rabbit anti-whole-cell serum. Human convalescent-phase sera obtained from five patients infected with meningococci of different serogroups and serotypes contained fully cross-reactive antibodies to TBP2 but no anti-TBP1 antibodies, when examined on Western blots. However, on dot immunoblots, the same patients' sera, as well as the mouse anti-whole cell and the rabbit anti-TBP1-TBP2 complex sera, reacted with purified biologically active TBP1 of strain SD. This indicates that native TBP1, a protein which loses its biological and some of its immunological activities when denatured, is immunogenic and that humans generate cross-reactive antibodies to native epitopes. These observations have important implications for assessing the vaccine potential of TBPs and other meningococcal antigens. Conclusions regarding the usefulness of TBPs as candidate components of meningococcal serogroup B vaccines based on results from certain animal species such as mice, or on methods such as Western blotting, may have little bearing on the situation in humans and may lead to some potentially useful antigens being disregarded.
Full text
PDF
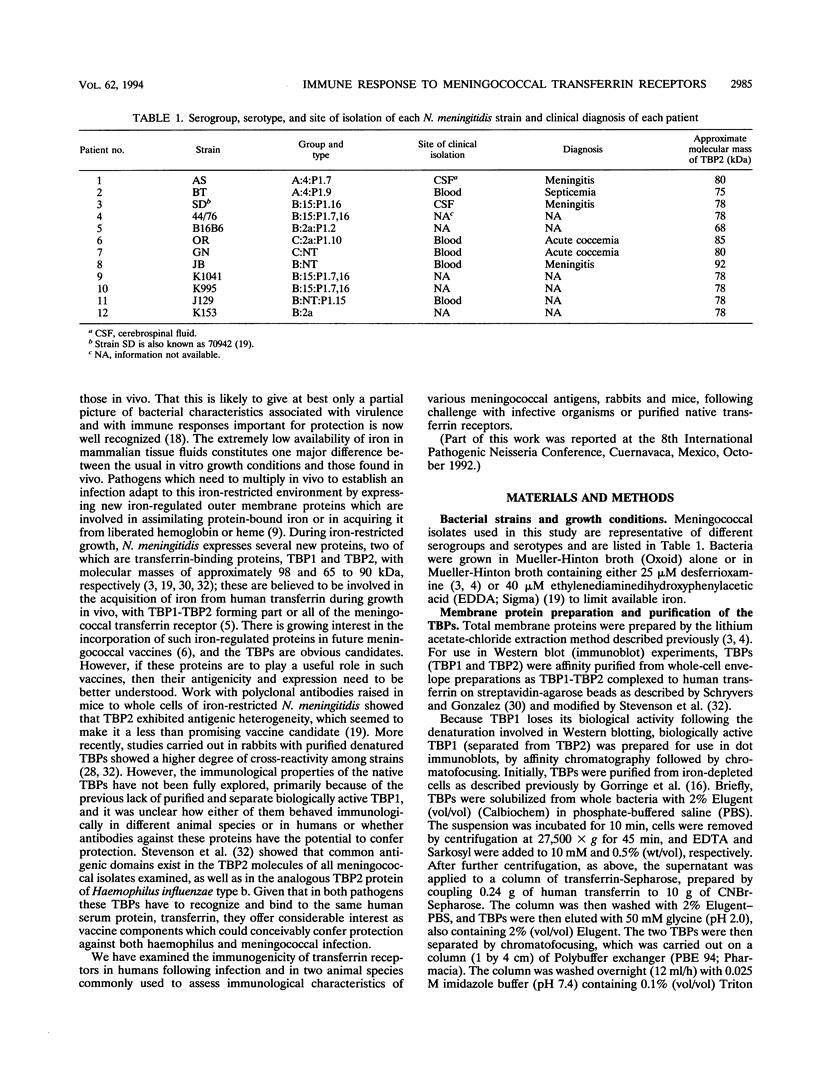

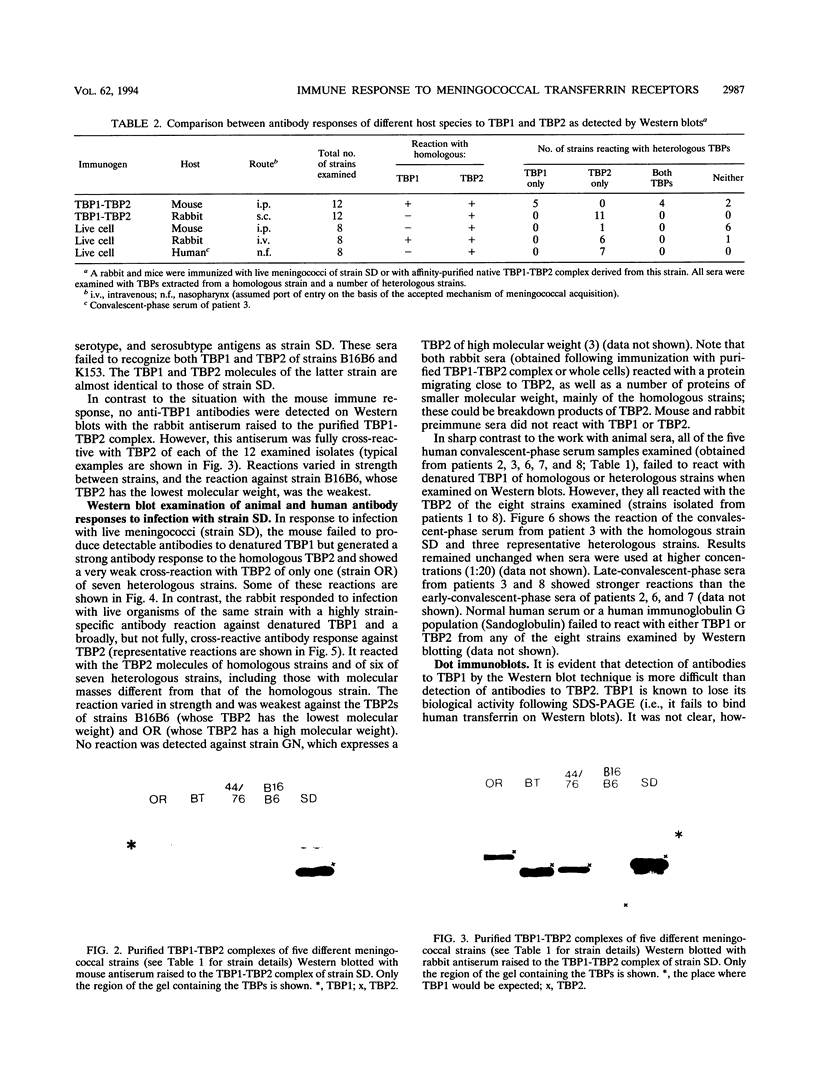
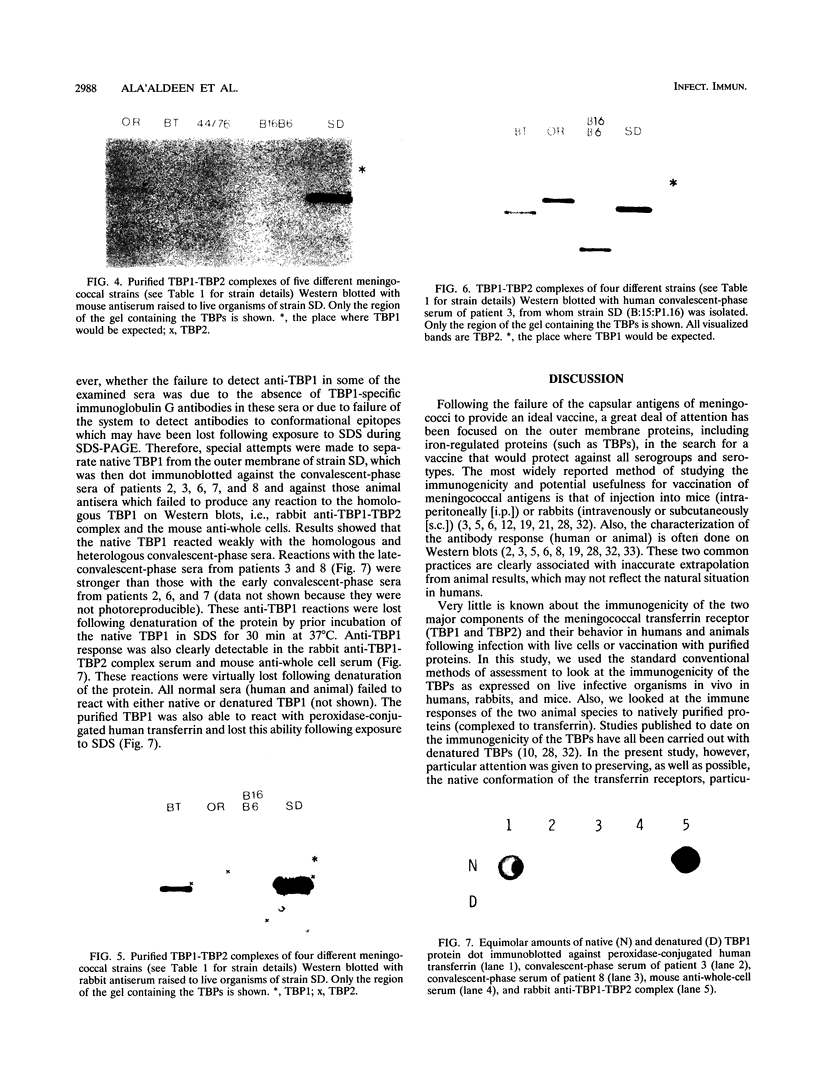


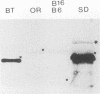
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ala'Aldeen D. A., Davies H. A., Borriello S. P. Vaccine potential of meningococcal FrpB: studies on surface exposure and functional attributes of common epitopes. Vaccine. 1994 May;12(6):535–541. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(94)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala'Aldeen D. A., Davies H. A., Wall R. A., Borriello S. P. The 70 kilodalton iron regulated protein of Neisseria meningitidis is not the human transferrin receptor. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90409-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala'Aldeen D. A., Powell N. B., Wall R. A., Borriello S. P. Localization of the meningococcal receptors for human transferrin. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):751–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.751-759.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala'Aldeen D. A., Wall R. A., Borriello S. P. Immunogenicity and cross-reactivity of the 70-Kda iron-regulated protein of Neisseria meningitidis in man and animals. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Aug;32(4):275–281. doi: 10.1099/00222615-32-4-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee-Bhatnagar N., Frasch C. E. Expression of Neisseria meningitidis iron-regulated outer membrane proteins, including a 70-kilodalton transferrin receptor, and their potential for use as vaccines. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2875–2881. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2875-2881.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjune G., Høiby E. A., Grønnesby J. K., Arnesen O., Fredriksen J. H., Halstensen A., Holten E., Lindbak A. K., Nøkleby H., Rosenqvist E. Effect of outer membrane vesicle vaccine against group B meningococcal disease in Norway. Lancet. 1991 Nov 2;338(8775):1093–1096. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91961-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. R., Dyer D. W., Thompson M. K., Sparling P. F. Human immune response to iron-repressible outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):710–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.710-713.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen C. N., Biswas G. D., Tsai J., Paruchuri D. K., Thompson S. A., Sparling P. F. Gonococcal transferrin-binding protein 1 is required for transferrin utilization and is homologous to TonB-dependent outer membrane receptors. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5788–5797. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5788-5797.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVoe I. W. The meningococcus and mechanisms of pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):162–190. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.162-190.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi S. J., Robbins J. B., Schneerson R. Antibodies to poly[(2----8)-alpha-N-acetylneuraminic acid] and poly[(2----9)-alpha-N-acetylneuraminic acid] are elicited by immunization of mice with Escherichia coli K92 conjugates: potential vaccines for groups B and C meningococci and E. coli K1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7175–7179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feavers I. M., Heath A. B., Bygraves J. A., Maiden M. C. Role of horizontal genetic exchange in the antigenic variation of the class 1 outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):489–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E. Vaccines for prevention of meningococcal disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2 (Suppl):S134–S138. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.suppl.s134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E. Environmental regulation of bacterial virulence--implications for vaccine design and production. Trends Biotechnol. 1991 Sep;9(9):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(91)90101-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Stevenson P., Ray A. Antigenic and molecular heterogeneity of the transferrin-binding protein of Neisseria meningitidis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 May;57(1-2):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90408-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E., Stevenson P., Thorpe R., Chart H. Naturally occurring antibodies in human sera that react with the iron-regulated outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):808–813. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.808-813.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. J., Gamian A., Michon F., Ashton F. E. Unique intermolecular bactericidal epitope involving the homosialopolysaccharide capsule on the cell surface of group B Neisseria meningitidis and Escherichia coli K1. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3585–3591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiden M. C., Suker J., McKenna A. J., Bygraves J. A., Feavers I. M. Comparison of the class 1 outer membrane proteins of eight serological reference strains of Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):727–736. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness B., Barlow A. K., Clarke I. N., Farley J. E., Anilionis A., Poolman J. T., Heckels J. E. Deduced amino acid sequences of class 1 protein (PorA) from three strains of Neisseria meningitidis. Synthetic peptides define the epitopes responsible for serosubtype specificity. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1871–1882. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer H. M., Powell N. B., Ala'Aldeen D. A., Wilton J., Borriello S. P. Neisseria meningitidis transferrin-binding protein 1 expressed in Escherichia coli is surface exposed and binds human transferrin. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Jun 15;110(2):139–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson A., Kuipers B., Pelzer M., Verhagen E., Tiesjema R. H., Tommassen J., Poolman J. T. Monoclonal antibodies against the 70-kilodalton iron-regulated protein of Neisseria meningitidis are bactericidal and strain specific. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3036–3041. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3036-3041.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., van der Ley P. A., Wiertz E. J., Hoogerhout P. Second generation meningococcal OMP-LPS vaccines. NIPH Ann. 1991 Dec;14(2):233–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reingold A. L., Broome C. V., Hightower A. W., Ajello G. W., Bolan G. A., Adamsbaum C., Jones E. E., Phillips C., Tiendrebeogo H., Yada A. Age-specific differences in duration of clinical protection after vaccination with meningococcal polysaccharide A vaccine. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):114–118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist E., Harthug S., Frøholm L. O., Høiby E. A., Bøvre K., Zollinger W. D. Antibody responses to serogroup B meningococcal outer membrane antigens after vaccination and infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1543–1548. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1543-1548.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schryvers A. B., Gonzalez G. C. Comparison of the abilities of different protein sources of iron to enhance Neisseria meningitidis infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2425–2429. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2425-2429.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra G. V., Campa H. C., Varcacel N. M., Garcia I. L., Izquierdo P. L., Sotolongo P. F., Casanueva G. V., Rico C. O., Rodriguez C. R., Terry M. H. Vaccine against group B Neisseria meningitidis: protection trial and mass vaccination results in Cuba. NIPH Ann. 1991 Dec;14(2):195–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson P., Williams P., Griffiths E. Common antigenic domains in transferrin-binding protein 2 of Neisseria meningitidis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2391–2396. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2391-2396.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedege E., Bjune G., Frøholm L. O., Høiby E. A., Rosenqvist E. Immunoblotting studies of vaccinee and patient sera from a Norwegian serogroup B meningococcal vaccination trial. NIPH Ann. 1991 Dec;14(2):183–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Moraes J. C., Perkins B. A., Camargo M. C., Hidalgo N. T., Barbosa H. A., Sacchi C. T., Landgraf I. M., Gattas V. L., Vasconcelos H. de G., Gral I. M. Protective efficacy of a serogroup B meningococcal vaccine in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Lancet. 1992 Oct 31;340(8827):1074–1078. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]